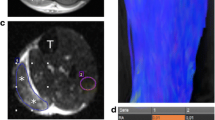
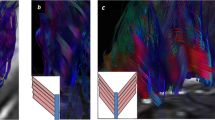
Abstract
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a powerful tool that has recently been applied to evaluate several pediatric musculoskeletal disorders. DWI probes abnormalities of tissue structure by detecting microscopic changes in water mobility that develop when disease alters the organization of normal tissue. DWI provides tissue characterization at a cellular level beyond what is available with other imaging techniques, and can sometimes identify pathology before gross anatomic alterations manifest. These features of early detection and tissue characterization make DWI particularly appealing for probing diseases that affect the musculoskeletal system. This article focuses on the current and future applications of DWI in the musculoskeletal system, with particular attention paid to pediatric disorders. Although most of the applications are experimental, we have emphasized the current state of knowledge and the main research questions that need to be investigated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D et al (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161:401–407
Burdette JH, Elster AD, Ricci PE (1999) Acute cerebral infarction: quantification of spin-density and T2 shine-through phenomena on diffusion-weighted MR images. Radiology 212:333–339
Chun T, Ulug AM, van Zijl PC (1998) Single-shot diffusion-weighted trace imaging on a clinical scanner. Magn Reson Med 40:622–628
Raya JG, Dietrich O, Reiser MF et al (2005) Techniques for diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow. Eur J Radiol 55:64–73
Baur A, Stabler A, Bruning R et al (1998) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of bone marrow: differentiation of benign versus pathologic compression fractures. Radiology 207:349–356
Gudbjartsson H, Maier SE, Mulkern RV et al (1996) Line scan diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 36:509–519
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:534–546
Vogler JB 3rd, Murphy WA (1988) Bone marrow imaging. Radiology 168:679–693
Jaramillo D, Menezes NM, Olear EA et al (2004) Line scan diffusion shows epiphyseal and metaphyseal abnormalities in Legg-Calve-Perthes disease. Pediatr Radiol 34:S48
Nonomura Y, Yasumoto M, Yoshimura R et al (2001) Relationship between bone marrow cellularity and apparent diffusion coefficient. J Magn Reson Imaging 13:757–760
Mulkern RV, Schwartz RB (2003) In re: characterization of benign and metastatic vertebral compression fractures with quantitative diffusion MR imaging. AJNR 24:1489–1490; author reply 1490–1491
Lehnert A, Machann J, Helms G et al (2004) Diffusion characteristics of large molecules assessed by proton MRS on a whole-body MR system. Magn Reson Imaging 22:39–46
Jaramillo D, Connolly SA, Vajapeyam S et al (2003) Normal and ischemic epiphysis of the femur: diffusion MR imaging study in piglets. Radiology 227:825–832
Menezes NM, Connolly SA, Shapiro F et al (2007) Early ischemia in growing piglet skeleton: MR diffusion and perfusion imaging. Radiology 242:129–136
Castillo M, Arbelaez A, Smith JK et al (2000) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging offers no advantage over routine noncontrast MR imaging in the detection of vertebral metastases. AJNR 21:948–953
Herneth AM, Friedrich K, Weidekamm C et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted imaging of bone marrow pathologies. Eur J Radiol 55:74–83
Hayashida Y, Hirai T, Yakushiji T et al (2006) Evaluation of diffusion-weighted imaging for the differential diagnosis of poorly contrast-enhanced and T2-prolonged bone masses: initial experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 23:377–382
Byun WM, Shin SO, Chang Y et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of metastatic disease of the spine: assessment of response to therapy. AJNR 23:906–912
Hayashida Y, Yakushiji T, Awai K et al (2006) Monitoring therapeutic responses of primary bone tumors by diffusion-weighted image: initial results. Eur Radiol 16:2637–2643
Lang P, Wendland MF, Saeed M et al (1998) Osteogenic sarcoma: noninvasive in vivo assessment of tumor necrosis with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Radiology 206:227–235
Uhl M, Saueressig U, Koehler G et al (2006) Evaluation of tumour necrosis during chemotherapy with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: preliminary results in osteosarcomas. Pediatr Radiol 36:1306–1311
Uhl M, Saueressig U, van Buiren M et al (2006) Osteosarcoma: preliminary results of in vivo assessment of tumor necrosis after chemotherapy with diffusion- and perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 41:618–623
Yasumoto M, Nonomura Y, Yoshimura R et al (2002) MR detection of iliac bone marrow involvement by malignant lymphoma with various MR sequences including diffusion-weighted echo-planar imaging. Skeletal Radiol 31:263–269
Stabler A, Baur A, Kruger A et al (1998) Differential diagnosis of erosive osteochondrosis and bacterial spondylitis: magnetic resonance tomography (MRT). Rofo 168:421–428
Chan JH, Peh WC, Tsui EY et al (2002) Acute vertebral body compression fractures: discrimination between benign and malignant causes using apparent diffusion coefficients. Br J Radiol 75:207–214
Pui MH, Mitha A, Rae WI et al (2005) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of spinal infection and malignancy. J Neuroimaging 15:164–170
Filidoro L, Dietrich O, Weber J et al (2005) High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging of human patellar cartilage: feasibility and preliminary findings. Magn Reson Med 53:993–998
Deng X, Farley M, Nieminen MT et al (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of native and degenerated human articular cartilage. Magn Reson Imaging 25:168–171
Turner R, Le Bihan D, Chesnick AS (1991) Echo-planar imaging of diffusion and perfusion. Magn Reson Med 19:247–253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacKenzie, J.D., Gonzalez, L., Hernandez, A. et al. Diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging for pediatric musculoskeletal disorders. Pediatr Radiol 37, 781–788 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0517-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0517-y