Abstract
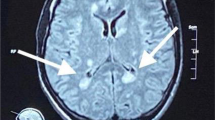
Susac syndrome is a microangiopathy of unknown origin affecting the brain, retina and inner ear. This rare entity is often misdiagnosed as a demyelinating condition such as multiple sclerosis or acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. A high index of suspicion must be present as the majority of patients do not have the complete clinical triad at the time of onset of symptoms. The radiologist plays an important role when the disease is suspected and helps orient the investigations. The syndrome has characteristic imaging features on MRI that include multifocal white matter and occasional grey matter lesions, the corpus callosum being always involved. The predominant central callosal lesions, especially with rapid cystic transformation (central callosal holes) can be considered pathognomonic of this condition in the appropriate clinical setting. This disease is extremely rare in children. We report a case of Susac syndrome in a 9-year-old girl to increase the awareness among paediatric radiologists of this entity, which is usually not considered as a differential diagnosis of multifocal white matter involvement in this age group.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Susac JO, Hardman JM, Selhorst JB (1979) Microangiopathy of the brain and retina. Neurology 29:313–316
Mass M, Bourdette D, Bernstein W et al (1988) Retinopathy, encephalopathy, deafness associated microangiopathy (the RED M syndrome): three new cases. Neurology 38 (Suppl):215
Schwitter J, Agosti R, Ott P et al (1992) Small infarctions of cochlear, retinal, and encephalitic tissue in young women. Stroke 23:903–907
Petty GW, Engel AG, Younge BR et al (1998) Retinocochleocerebral vasculopathy. Medicine (Baltimore) 77:12–40
Susac JO (1994) Susac’s syndrome: the triad of microangiopathy of the brain and retina with hearing loss in young women. Neurology 44:591–593
Do TH, Fisch C, Evoy F (2004) Susac syndrome: report of four cases and review of the literature. AJNR 25:382–388
Hahn JS, Lannin WC, Sarwal MM (2004) Microangiopathy of brain, retina, and inner ear (Susac’s syndrome) in an adolescent female presenting as acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Pediatrics 114:276–281
Delaney WV Jr, Torrisi PF (1976) Occlusive retinal vascular disease and deafness. Am J Ophthalmol 82:232–236
Susac JO (2004) Susac’s syndrome. AJNR 25:351–352
Chang KH, Cha SH, Han MH et al (1992) Marchiafava-Bignami disease: serial changes in corpus callosum in MRI. Neuroradiology 34:480–482
Lim CC, Lee WL, Leo YS et al (2003) Late clinical and magnetic resonance imaging follow-up of Nipah virus infection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:131–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eluvathingal Muttikkal, T.J., Vattoth, S. & Keluth Chavan, V.N. Susac syndrome in a young child. Pediatr Radiol 37, 710–713 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0492-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0492-3