Abstract
Background
US detection of a normal appendix can safely rule out appendicitis. However, there is a wide range of accuracy in detection of a normal appendix.
Objective
To optimize US examination to detect the normal and the abnormal appendix according to the potential positions of the appendix.
Materials and methods
This prospective study included 107 children who underwent gray-scale US scanning. Noncompressive and compressive graded sonography was performed to detect normal and abnormal appendices according to their potential positions. The maximum transverse diameter of the appendices was measured.
Results
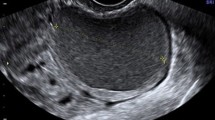
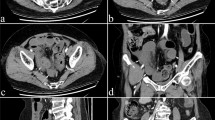
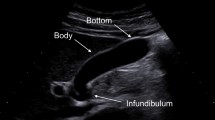
Of the 107 children examined, 56 had a histologic diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Sonography had a sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 98% for the diagnosis of appendicitis. A normal appendix was visualized in 44 (86.2%) of the 51 patients without acute appendicitis, and of these 44, 43 were true-negative and 1 was false-positive. Normal and abnormal appendices, respectively, were positioned as follows: 54.4% and 39.3% were mid-pelvic; 27.2% and 28.6% were retrocecal; 11.4% and 17.8% were deep pelvic; and 6.8% and 14.3% were abdominal.
Conclusion
US scanning according to the potential positions of the appendix was useful in the detection of normal appendices in children suspected of having appendicitis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Puylaert JB (1986) Acute appendicitis: US evaluation using graded compression. Radiology 158:355–360
Jeffrey RB, Laing FC, Townsend RR (1988) Acute appendicitis: sonographic criteria based on 250 cases. Radiology 167:327–329
Rioux M (1992) Sonographic detection of the normal and abnormal appendix. AJR 158:773–778
Patriquin HB, Garcier J-M, Lafortune M, et al (1996) Appendicitis in children and young adults: Doppler sonographic-pathologic correlation. AJR 166:629–633
Lim HK, Lee WJ, Kim TH, et al (1996) Appendicitis: usefulness of color Doppler US. Radiology 201:221–225
Simonovsky V (1999) Sonographic detection of normal and abnormal appendix. Clin Radiol 54:533–539
Kessler N, Cyteval C, Gallix B, et al (2004) Appendicitis: evaluation of sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values of US, Doppler US, and laboratory findings. Radiology 230:472–478
Wiersma F, Srámek A, Holscher HC (2005) US features of the normal appendix and surrounding area in children. Radiology 235:1018–1022
Baldisserotto M, Marchiori E (2000) Accuracy of noncompressive sonography of children with appendicitis according to the potential positions of the appendix. AJR 175:1387–1392
Jaeschke R, Gordon GH, Sackett DL (1994) Users’ guides to the medical literature. How to use an article about a diagnostic test. JAMA 271:703–707
Langlotz CP (2003) Fundamental measures of diagnostic examination performance: usefulness for clinical decision making and research. Radiology 228:3–9
Peitz U, Malfertheiner P (1999) Chronic appendicitis. Recurrent abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant from the viewpoint of the internist (review). Zentralbl Chir 124:1103–1108
Sivit CJ (1993) Diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children: spectrum of sonographic findings. AJR 161:147–152
Quillin SP, Siegel MJ (1994) Appendicitis: efficacy of color Doppler sonography. Radiology 191:557–560
Acknowledgements
We thank Johny Acosta for assistance with computer issues; Marcelo Dourado Dora and Ana Paula Cardoso Pertence, who also performed sonographic examinations for this study; Anelise Burmeister for assistence in writing and proofreading the text; Mario Wagner for help with the statistical calculations; and Ana Lovatto for drawing Fig. 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peletti, A.B., Baldisserotto, M. Optimizing US examination to detect the normal and abnormal appendix in children. Pediatr Radiol 36, 1171–1176 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0305-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-006-0305-0