Abstract
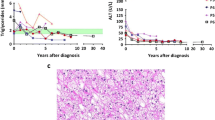
Background: Type I glycogen storage disease (GSD-I) is an inherited disorder affecting glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. The characteristic manifestations are hepatomegaly, hypoglycemia, hyperlacticacidemia, hyperuricemia, and hyperlipidemia. Renal disease is regarded as a long-term complication and is reported mainly in older patients. Objective: We report the renal manifestations and renal ultrasonographic findings of GSD-I in infancy and early childhood in order to assess the role of renal sonography in the diagnosis of GSD-I. Materials and methods: We retrospectively reviewed our hospital’s database for patients with GSD-I from January 1993 to September 2004. The records of five patients were reviewed for this study. These five patients were diagnosed when they were younger than 3 years old. Data extracted from the charts included the initial extrarenal and renal manifestations, laboratory data, and imaging studies. We analyzed the indications for, and results of, renal sonography. Results: In addition to the clinical presentations and laboratory abnormalities, all five children had nephromegaly and increased echogenicity on ultrasonography on their first visit, although only a minor degree of tubular dysfunction was noted clinically. Three of these five patients had nephrocalcinosis or renal stones or both. Conclusion: Hyperechoic large kidneys, nephrocalcinosis, and renal stones are common in GSD-I. They can be present in early infancy. Abnormalities on renal sonography might suggest GSD-I in a patient with suspected inborn errors of metabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen YT (2004) Glycogen storage disease. In: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jeson HB (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 17th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 469–475
Grünfeld JP (1998) Glycogen storage disease (von Gierk’s disease). In: Morgan SH, Grünfeld JP (eds) Inherited disorders of the kidney. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 406–411
Wolfsdorf JI, Holm IA, Weinstein DA (1999) Glycogen storage diseases: phenotypic, genetic, and biochemical characteristics and therapy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 28:801–823
Chen YT, Coleman RA, Scheinman JI, et al (1988) Renal disease in Type I glycogen storage disease. N Engl J Med 318:7–11
Stapleton FB (1994) Hematuria associated with hypercalciuria and hyperuricosuria: a practical approach. Pediatr Nephrol 8:756–761
Stapleton FB, Nash D (1983) A screening test for hyperuricosuria. J Pediatr 102:88–90
Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, et al (1976) A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–163
Schwartz GJ, Brion LP, Spitzer A (1987) The use of plasma creatinine concentration to estimate glomerular filtration rate in infancy, children and adolescence. Pediatr Clin North Am 34:571–590
Chantler C (1979) Clinical pediatric physiology. In: Godfrey S, Baum JD (eds) The kidney. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford, pp 356–398
Han BK, Babcock DS (1985) Sonographic measurements and appearance of normal kidneys in children. AJR 145:611–616
Von Gierke E (1929) Hepato-nephromegalia glykogenica (Glykogenspeicher krankheit der Leber und Nieren). Beitr Pathol Anat 82:497–513
Reitsma-Bierens WCC (1993) Renal complications in glycogen storage disease Type I. Eur J Pediatr 152:S60–S62
Obara K, Saito T, Sato H, et al (1993) Renal histology in two adult patients with Type I glycogen storage disease. Clin Nephrol 39:59–64
Chen YT, Feinstein KA, Coleman RA, et al (1990) Variability of renal length in Type I glycogen storage disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 13:259–262
Bajer L, Dahlem S, Goldfarb S, et al (1989) Hyperfiltration and renal disease in glycogen storage disease, Type I. Kidney Int 35:1345–1350
Lee PI, Dalton RN, Shah V, et al (1995) Glomerular and tubular function in glycogen storage disease. Pediatr Nephrol 9:705–710
Verani R, Bernstein J (1988) Renal glomerular and tubular abnormalities in glycogen storage disease Type I. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112:271–274
Yokoyama K, Hayashi H, Hinoshita F, et al (1995) Renal lesion of Type Ia glycogen storage disease: the glomerular size and renal localization of apolipoprotein. Nephron 70:348–352
Jonas AJ, Verani RR, Howell RR, et al (1988) Hypertension in a child with Type 1A glycogen storage disease. Am J Kidney Dis 11:264–266
Hahn-Ullrich H, Sciuk J, Bartenstein P, et al (1993) Effective renal plasma flow in patients with glycogen storage disease Type I. Eur J Pediatr 152:674–676
Reitsma-Bierens WCC, Smit GPA, Troelstra JA (1992) Renal function and kidney size in glycogen storage disease Type I. Pediatr Nephrol 6:236–238
Talente GM, Coleman RA, Alter C, et al (1994) Glycogen storage disease in adult. Ann Intern Med 120:218–226
Weinstein DA, Somers MJG, Wolfsdorf JI (2001) Decreased urinary citrate excretion in Type 1a glycogen storage disease. J Pediatr 138:378–382
Restaino I, Kaplan BS, Stanley C, et al (1993) Nephrolothiasis, hypocitraturia, and a distal renal tubular acidification defect in Type I glycogen storage disease. J Pediatr 122:392–396
Fick JJA, Beek FJA (1992) Echogenic kidneys and medullary calcium deposition in a young child with glycogen storage disease Type Ia. Pediatr Radiol 22:72–73
Slovis TL, Bernstein J, Gruskin A (1993) Hyperechoic kidneys in the newborn and young infant. Pediatr Nephrol 7:294–302
Kraus RA, Gaisie G, Young LW (1990) Increased renal parenchymal echogenicity: cause in pediatric patients. Radiographics 10:1009–1018
Karlowicz NG, Adelman RD (1998) What are the possible causes of neonatal nephrocalcinosis? Semin Nephrol 18:364–367
Moxey-Mims MM, Stapleton FB (1993) Hypercalciuria and nephrocalcinosis in children. Curr Opin Pediatr 5:186–190
Shultz PK, Strife JL, Strife CF, et al (1991) Hyperechoic renal medullary pyramids in infants and children. Radiology 181:163–167
Toyoda K, Miyamoto Y, Ida M, et al (1989) Hyperechoic medulla of the kidneys. Radiology 173:431–434
Glazer GM, Callen PW, Filly RA (1982) Medullary nephrocalcinosis: sonographic evaluation. AJR 138:55–57
Cremin B, Wiggelinkhuizen J, Bonnici F (1982) Nephrocalcinosis in children. Br J Radiol 55:413–418
Chakrapani A, Cleary MA, Wraith JE (2001) Detection of inborn errors of metabolism in the newborn. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 84:205–210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CC., Tsai, JD., Lin, SP. et al. Renal sonographic findings of type I glycogen storage disease in infancy and early childhood. Pediatr Radiol 35, 786–791 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1478-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1478-7