Abstract
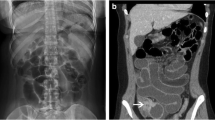
We report a case of perforation, fistula formation, and small bowel obstruction in a 2-year-old child who had ingested 32 small magnets. Multiple magnets will attract one another through the bowel wall and lead to pressure necrosis with complications. We recommend early surgical intervention before the onset of gastrointestinal complications if ingested multiple magnets have not moved on the follow-up radiograph. Both clinicians and the lay population need to be aware that multiple magnets can be hazardous foreign bodies for children.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartz GF, Polsky HS (1976) Ingested foreign bodies of the gastrointestinal tract. Am Surg 42:236–238
Takao S, Matsuo Y, Shinchi H, et al (2001) Magnetic compression anastomosis for benign obstruction of the common bile duct. Endoscopy 33:988–990
Okajima H, Kotera A, Takeichi T, et al (2005) Magnet compression anastomosis for bile duct stenosis after duct-to-duct biliary reconstruction in living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 11:473–475
Cauchi JA, Shawis RN (2002) Multiple magnet ingestion and gastrointestinal morbidity. Arch Dis Child 87:539–540
Oestreich AE (2004) Multiple magnet ingestion alert. Radiology 233:615
Lee SK, Beck NS, Kim HH (1996) Mischievous magnets: unexpected health hazard in children. J Pediatr Surg 31:1694–1695
Honzumi M, Shigemori C, Ito H, et al (1995) An intestinal fistula in a 3-year-old child caused by the ingestion of magnets: report of a case. Surg Today 25:552–553
Kubota Y, Tokiwa K, Tanaka S, et al (1995) Intestinal obstruction in an infant due to magnet ingestion. Eur J Pediatr Surg 5:11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchida, K., Otake, K., Iwata, T. et al. Ingestion of multiple magnets: hazardous foreign bodies for children. Pediatr Radiol 36, 263–264 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-0056-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-0056-3