Abstract
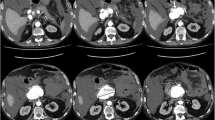
Pseudoaneurysms (PAn) are uncommon in adults and even less common in children. They are most often encountered after iatrogenic arterial injury. Presentation may be substantially delayed after the iatrogenic event, and diagnosis can be difficult, especially when the PAn occurs in an unexpected location. Treatment of PAn has evolved during the last two decades from a reliance on surgical resection to US-guided compression, coil embolization, covered stents, and stent-graft exclusion. More recently, direct percutaneous US-guided thrombin injection has been used in the treatment of PAn. We present three cases of successful PAn thrombosis by US-guided percutaneous thrombin injection in children, one of the epigastric artery and two of the femoral artery.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosai J (1996) Cardiovascular system. Ackerman’s surgical pathology. Mosby, Philadelphia, pp 2204–2205
Titus JL, Kim H-S (1990) Blood vessels and lymphatics. Anderson’s pathology. Mosby, St. Louis, p 778
Zarins CK, Hill BB, Wolf YG (2001) Aneurysmal vascular disease. Textbook of surgery. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 1371
Morgan R, Belli AM (2003) Current treatment methods for postcatheterization pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:697–710
Abu-Yousef MM, Wiese JA, Shamma AR (1988) The “to-and-fro” sign: duplex Doppler evidence of femoral artery pseudoaneurysm. AJR 150:632–634
Frush DP, Paulson EK, O‘Laughlin MP (2000) Successful sonographically guided thrombin injection in an infant with a femoral artery pseudoaneurysm. AJR 175:485–487
Norwood MG, Lloyd GM, Moore S, et al (2004) The changing face of femoral artery false aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 27:385–388
Ello FV, Nunn DB (1973) False aneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery as a complication of abdominal retention sutures. Surgery 74:460–461
Ferrer JV, Soriano P, Zazpe C, et al (1996) Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Arch Surg 131:102–103
Gage TS, Sussman SK, Conard FU III, et al (1990) Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery: diagnosis and percutaneous treatment. AJR 155:529–530
Segev Y, Orron D, Alon R, et al (1994) Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery mimicking abdominal wall hematoma. J Ultrasound Med 13:483–484
Verbist J, Stillaert F, Dujardin P, et al (1997) Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery. Acta Chir Belg 97:196–198
Lam EY, McLafferty RB, Taylor LM Jr, et al (1998) Inferior epigastric artery pseudoaneurysm: a complication of paracentesis. J Vasc Surg 28:566–569
Todd AW (2001) Inadvertent puncture of the inferior epigastric artery during needle biopsy with fatal outcome. Clin Radiol 56:989–990
Werner M, Bernheim J, Witz M, et al (1999) Pseudoaneurysm of the inferior epigastric artery—a rare complication of Tenckhoff catheter removal. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:1297–1299
Shabani AG, Baxter GM (2002) Inferior epigastric artery pseudoaneurysm: ultrasound diagnosis and treatment with percutaneous thrombin. Br J Radiol 75:689–691
Saito S, Arai H, Kim K, et al (1992) Percutaneous transfemoral spring coil embolization of a pseudoaneurysm of the femoral artery. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 26:229–231
Waigand J, Uhlich F, Gross CM, et al (1999) Percutaneous treatment of pseudoaneurysms and arteriovenous fistulas after invasive vascular procedures. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 47:157–164
Engelke C, Quarmby J, Ubhayakar G, et al (2002) Autologous thrombin: a new embolization treatment for traumatic intrasplenic pseudoaneurysm. J Endovasc Ther 9:29–35
Fellmeth BD, Roberts AC, Bookstein JJ, et al (1991) Postangiographic femoral artery injuries: nonsurgical repair with US-guided compression. Radiology 178:671–675
Elford J, Burrell C, Freeman S, et al (2002) Human thrombin injection for the percutaneous treatment of iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:115–118
Cope C, Zeit R (1986) Coagulation of aneurysms by direct percutaneous thrombin injection. AJR 147:383–387
Liau CS, Ho FM, Chen MF, et al (1997) Treatment of iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysm with percutaneous thrombin injection. J Vasc Surg 26:18–23
Kang SS, Labropoulos N, Mansour MA, et al (1998) Percutaneous ultrasound guided thrombin injection: a new method for treating postcatheterization femoral pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg 27:1032–1038
Monroe DM, Hoffman M, Roberts HR (2002) Platelets and thrombin generation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1381–1389
Lennox AF, Delis KT, Szendro G, et al (2000) Duplex-guided thrombin injection for iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysm is effective even in anticoagulated patients. Br J Surg 87:796–801
Lennox A, Griffin M, Nicolaides A, et al (1998) Regarding “Percutaneous ultrasound guided thrombin injection: a new method for treating postcatheterization femoral pseudoaneurysms”. J Vasc Surg 28:1120–1121
Pope M, Johnston KW (2000) Anaphylaxis after thrombin injection of a femoral pseudoaneurysm: recommendations for prevention. J Vasc Surg 32:190–191
Pezzullo JA, Wallach MT (2002) Successful percutaneous thrombin injection of a brachial artery pseudoaneurysm in a neonate. AJR 178:244–245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelchovitz, D.J., Cahill, A.M., Baskin, K.M. et al. Pseudoaneurysm in children: diagnosis and interventional management. Pediatr Radiol 35, 434–439 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1320-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1320-7