Abstract
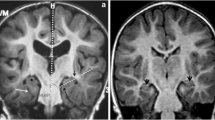
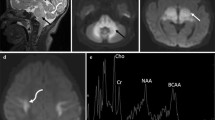
Neonatal maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) is associated with diffuse oedema and characteristic MSUD oedema. We present a newborn infant with two coexisting different types of oedema. The myelinated white matter showed a marked decrease in the water apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) compatible with cytotoxic oedema. The unmyelinated white matter showed an increase in ADC, consistent with vasogenic-interstitial oedema. On follow-up studies, the cytotoxic oedema showed improvement, but the vasogenic-interstitial oedema progressed into brain atrophy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chuang DT, Shih VE (2001) Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketoaciduria). In: Scriver CR, Sly WS, Childs B (eds) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1971–2005
Brismar J, Aqeel A, Brismar G, et al (1990) Maple syrup urine disease: findings on CT and MR scans of the brain in 10 infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 11:1219–1228
Cavalleri F, Beradi A, Burlina AB, et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI of maple syrup urine disease encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 44:499–502
Righini A, Ramenghi LA, Parini R, et al (2003) Water apparent diffusion coefficient and T2 changes in the acute stage of maple syrup urine disease: evidence of intramyelinic and vasogenic-interstitial edema. J Neuroimaging 13:162–165
Jan W, Zimmerman RA, Wang ZJ, et al (2003) MR diffusion imaging and MR spectroscopy of maple syrup urine disease during acute metabolic decompensation. Neuroradiology 45:393–399
Neil J, Shiran SI, McKinstry RC, et al (1998) Normal brain in human newborns: apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion anisotropy measured by using diffusion tensor MR imaging. Radiology 200:57–66
Tanner SF, Ramenghi LA, Ridgway JP (2000) Quantitative comparison of intrabrain diffusion in adults and preterm and term neonates and infants. AJR Am J Radiol 174:1643–1649
Jouvet P, Rustin P, Taylor DL, et al (2000) Branched chain amino acids induce apoptosis in neural cells without mitochondrial membrane depolarization or cytochrome release: implications for neurological impairment associated with maple syrup urine disease. Mol Biol Cell 11:1919–1932
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, J.S., Kim, TK., Eun, BL. et al. Maple syrup urine disease encephalopathy: a follow-up study in the acute stage using diffusion-weighted MRI. Pediatr Radiol 34, 163–166 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-1058-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-1058-7