Abstract
Background
Children with hydronephrosis are typically investigated by a combination of diuretic renal scintigraphy, ultrasound, and voiding cystourethrography. Unfortunately, there is no gold standard to assess obstruction.
Purpose
The purpose of our study was to evaluate the utility of dynamic contrast enhanced MR urography in the investigation of children with hydronephrosis to define urinary tract anatomy, to calculate differential renal function and to assess urinary tract obstruction.
Materials and methods
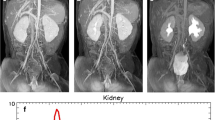
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging was performed in 40 children with unilateral hydronephrosis. There were 14 girls and 26 boys with an age range of 1 month to 14 years (mean 1.4 years). The information from traditional imaging modalities was compared to the information obtained from the single MR study.
Results
The anatomic imaging with MR urography was superior to other modalities. The split renal function was estimated with MR urography by calculating the volume of enhancing renal parenchyma and was comparable to renal scintigraphy (r=0.98). By using surgery versus non-surgery as the decision point, with MR urography the sensitivity was 100%, specificity 71%, positive predictive value 86%, negative predictive value 100%, and diagnostic efficiency 90%. For renal scintigraphy the sensitivity was 96%, the specificity 56%, positive predictive value 76%, negative predictive value 90%, and diagnostic efficiency 79%.
Conclusions
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR urography provides superior anatomic and functional information when compared with ultrasound and diuretic renal scintigraphy. The information is gathered in a single study that does not use ionizing radiation. It is likely that MR urography will replace renal scintigraphy in the evaluation of hydronephrosis in children.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borthne A, Nordshus T, Reiseter T, et al (1999) MR urography: the future gold standard in pediatric urogenital imaging? Pediatr Radiol 29:694–701
Rohrschneider WK, Hoffend J, Becker K, et al (2000) Combined static-dynamic MR urography for the simultaneous evaluation of morphology and function in urinary tract obstruction. I. Evaluation of the normal status in an animal model. Pediatr Radiol 30:511–522
Rohrschneider WK, Becker K, Hoffend J, et al (2000) Combined static-dynamic MR urography for the simultaneous evaluation of morphology and function in urinary tract obstruction. II. Findings in experimentally induced ureteric stenosis. Pediatr Radiol 30:523–532
Takeda M, Katayama Y, Tsutsui T, et al (1994) Value of dimercaptosuccinic acid single photon emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in detecting rebal injury in pediatric patients with vesicoureteral reflux. Eur Urol 25:320–325
Lonergan G, Pennington D, Morrison J, et al (1998) Childhood pyelonephritis: comparision of gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging and renal cortical scintigraphy for diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 207:377–384
Poustchi-Amin M, Leonidas J, Palestro C, et al (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging in acute pyelonephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 12:579–380
Rodriguez L, Spielman D, Herfkens R, et al (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of hydronephrosis, reflux and renal scarring in children. J Urol 166:1023–1027
Hinman F, Hinman F Jr (1971) Hydronephrosis. In: Karafin L, Kendrall A (eds) Urology. Harper & Row, New York
Staatz G, Nolte-Ernsting CC, Adam GB, et al (2000) Feasibility and utility of respiratory-gated, gadoliniu-enhanced T1-weighted magnetic resonance urography in children. Invest Radiol 35:504–512
Fukuda Y, Watanabe H, Tomita T, et al (1996) Evaluation of glomerular function in individual kidneys using dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Radiol 26:324–328
Flashner S, King L (1992) Ureteropelvic junction. In: Clinical Pediatric Urology, 3rd edn Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 693–725
Peters C (1995) Urinary tract obstruction in children. J Urol 154:1874–1883
Dacher J, Pfister C, Thoumas D, et al (1999) Shortcomings of diuresis scintigraphy in evaluating urinary obstruction: comparision with pressure flow studies. Pediatr Radiol 29:742–747
O'Reilly P (1992) Diuresis renography: recent advances and recommended protocols. Br J Urol 69:113–120
Koff S, Cambell K (1994) The nonoperative management of unilateral neonatal hydreonephrosis: natural history of poorly functioning kidneys. J Urol 152:593–595
Wen JG, Frokiaer J, Jorgensen TM, et al (1999) Obstructive uropathy: an update of the experimental research. J Urol Res 27:29–39
Houben C, Sischerman A, Borner G, et al (2000) Outcome analysis of pyeloplasty in children. Pediatr Surg Int 16:189–193
McAleer I, Kaplan G (1999) Renal function before and after pyeloplasty: does it improve? J Urol 162:1041–1044
Maizels M, Reisman ME, Flom LS, et al (1992) Grading nephroureteral dilatation detected in the first year of life: correlation with obstruction. J Urol 148:609–614
English PJ, Testa HJ, Lawson RS, et al (1987) Modified method of diuresis renogaphy for the assessment of equivocal pelviureteric junction obstruction. Br J Urol 54:10–14
Moonen M, Granerus G (1992) Subtraction of extra-renal background in 99mTc-DTPA renography: comparison of various regions of interest. Clin Physiol 12:453–461
Fitchner J, Spielman D, Herfkens R, et al (1994) Ultrafast contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of congenital hydronephrosis in a rat model. J Urol 152:682–687
Semelka R, Hricak H, Tomei E, et al (1990) Obstructive uropathy: evaluation with dynamic Gd-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 175:797–803
Nolte-Ernsting CCA, Bucker A, Adam GB, et al (1998) Gadolinium-enhanced excretory MR urography after low dose diuretic injection: comparison with conventional excretory urography. Radiology 209:147–157
Chan A, Pottumarthi P, Saltzman B (2001) Magnetic resonance imaging in endourology. J Endourol 15:17–23
Roy C, Saussine C, Guth S, et al (1998) MR urography in the evaluation of urinary tract obstruction. Abdom Imaging 23:27–34
Wen JG, Chen Y, Ringgaard S, et al (2000) Evaluation of renal function in normal and hydronephrotic kidneys in rats using gadolinium diethylenetriamine-pentacetic acid enhanced dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. J Urol 163:1264–1270
Louca G, Liberopoulos K, Fidas A, et al (1999) MR urography in the diagnosis of urinary tract obstruction. Eur Urol 35:102–108
Thurnher S, Tzika A, Hricak H, et al (1989) Noncontrast and contrast enhanced MR imaging in the evaluation of partial ureteral obstruction: an experimental study in the micropig. Invest Radiol 24:544–554
Weinmann H, Brasch R, Press W, et al (1984) Characteristics of gadolinium-DTPA complex: a potential NMR contrast agent. AJR 142:619–624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grattan-Smith, J.D., Perez-Bayfield, M.R., Jones, R.A. et al. MR imaging of kidneys: functional evaluation using F-15 perfusion imaging. Ped Radiol 33, 293–304 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-0896-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-0896-7