Abstract
Background
In mental retardation (MR) an aetiological diagnosis is not always obtained despite a detailed history, physical examination and metabolic or genetic investigations. In some of these patients, MRI is recommended and may identify subtle abnormal brain findings.
Objective
We reviewed the cerebral MRI of children with non-specific mental retardation in an attempt to establish a neuroanatomical picture of this disorder.
Materials and methods
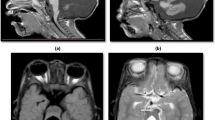
Thirty children with non-specific MR were selected to undergo cerebral MRI. The examination included supratentorial axial slices, mid-sagittal images and posterior fossa coronal images. Brain malformations, midline and cerebellar abnormalities were studied.
Results
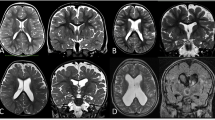
In 27 of 30 patients, the neuroimaging evaluation revealed a relatively high incidence of cerebral and posterior fossa abnormalities. The most frequent were: dysplasia of the corpus callosum (46%; hypoplasia, short corpus callosum and vertical splenium), partially opened septum pellucidum and/or cavum vergae (33%), ventriculomegaly (33%), cerebral cortical dysplasia (23%), subarachnoid space enlargement (16.6%), vermian hypoplasia (33%), cerebellar and/or vermian disorganised folia (20%), and subarachnoid spaces enlargement in the posterior fossa (20%). Other anomalies were: enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces (10%), white matter anomalies (10%) and cerebellar or vermian atrophy.
Conclusions
MRI has shown a high incidence of subtle cerebral abnormalities and unexpected minor forms of cerebellar cortical dysplasia. Even if most of these abnormalities are considered as subtle markers of brain dysgenesis, their role in the pathogenesis of mental retardation needs further investigation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daily DK, Ardinger HH, Holmes GE (2000) Identification and evaluation of mental retardation. Am Fam Physician 61:1059–1067
Curry CJ, Stevenson RE, Aughton D, et al (1997) Evaluation of mental retardation: recommendations of a consensus conference: American College of Medical Genetics. Am J Med Genet 72:468–477
Schaefer GB, Bodensteiner JB, Thompson JN, et al (1991) Clinical and morphometric analysis of the hypoplastic corpus callosum. Arch Neurol 48:933–936
Schaefer GB, Bodensteiner JB (1992) Evaluation of the child with idiopathic mental retardation. Pediatr Clin North Am 39:929–943
Majnemer A, Shevell MI (1995) Diagnostic yield of the neurologic assessment of the developmentally delayed child. J Pediatr 127:193–199
Cunningham RD Jr (1996) Neuroimaging studies in children with developmental delay. J Pediatr 128:302
Orazio G, Pierluigi G, Ugo S (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging in children with mental retardation. J Pediatr 130:334
Barkovich AJ (2000) Pediatric neuroimaging, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 13–45
Gabrielli O, Salvolini U, Bonifaci V, et al (1993) Morphological studies of the corpus callosum by MRI in children with malformative syndromes. Neuroradiology 35:109–112
O'Hayon BB, Drake JM, Ossip MG, et al (1998) Frontal and occipital horn ratio: a linear estimate of ventricular size for multiple imaging modalities in pediatric hydrocephalus. Pediatr Neurosurg 29:245–249
Schaefer GB, Sheth RD, Bodensteiner JB (1994) Cerebral dysgenesis: an overview. Neurol Clin 12:773–788
Bodensteiner JB (1995) The saga of the septum pellucidum: a tale of unfunded clinical investigations. J Child Neurol 10:227–231
Bodensteiner JB, Gay CT, Marks WA, et al (1988) The macro cisterna magna: a marker for maldevelopment of the brain? Pediatr Neurol 4:284–286
Polednak AP (1977) Post-mortem neuropathology in a mentally retarded population. Lancet 1:492–493
Crome L (1960) The brain and mental retardation. BMJ 1:897–904
Sugimoto T, Yasuhara A, Nishida N, et al (1993) MRI of the head in the evaluation of microcephaly. Neuropediatrics 24:4-7
Kjos BO, Umansky R, Barkovich AJ (1990) Brain MR imaging in children with developmental retardation of unknown cause: results in 76 cases. AJNR 11:1035–1040
Shevell MI, Majnemer A, Rosenbaum P, et al (2000) Etiologic yield of subspecialists' evaluation of young children with global developmental delay. J Pediatr 136:593–598
Pulsifier MB (1996) The neuropsychology of mental retardation. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2:159–176
De Brasi D, Della Casa R, Titomanlio L, et al (2000) Mental retardation, tall stature and minor phenotypic abnormalities associated with a de novo complex chromosome rearrangement. Neuropediatrics 31:164–166
Rorke LB, Fogelson MH, Riggs HE (1968) Cerebellar heterotopia in infancy. Dev Med Child Neurol 10:644–650
Friede RL (1989) Developmental neuropathology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 361–371
Aida N, Tamagawa K, Takada K, et al (1996) Brain MR in Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy. AJNR 17:605–613
Sugita K, Ando M, Makino M, et al (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in congenital rubella virus and cytomegalovirus infections. Neuroradiology 33:239–242
Marques Dias MJ, Harmant-van Rijckeevorsel G, Landrieu P, et al (1984) Prenatal cytomegalovirus disease and cerebral microgyria: evidence for perfusion failure, not disturbance of histogenesis, as the major cause of fetal cytomegalovirus encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics 15:18-24
Inouye M, Hayasaka S, Funahshi A, et al (1992) Gamma-radiation produces abnormal Bergman fibers and ectopic granule cells in mouse cerebellar cortex. J Radiat Res 33:275–281
Sakata-Haga H, Sawada K, Hisano S, et al (2001) Abnormalities of cerebellar foliation in rats prenatally exposed to ethanol. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 102:36–40
Soto-Ares G, Delmaire C, Deries B, et al (2000) Cerebellar cortical dysplasia: MR findings in a complex entity. AJNR 21:1511–1519
Demarel P, Lievel-Lagae PC, Baert AL (1998) MR of cerebellar cortical dysplasia. AJNR 19:984–986
Sasaki M, Oikawa H, Ehara S, et al (2001) Disorganised unilateral cerebellar folia: a mild form of cerebellar cortical dysplasia? Neuroradiology 43:151–155
Kuwamura M, Morikawa T, Yamate J, et al (2000) Glial pathology in development of cerebellar dysplasia in the hereditary cerebellar vermis defect (CVD) rat. Acta Neuropathol 99:305–309
Ciesielski KT, Harris RJ, Hart BL, et al (1997) Cerebellar hypoplasia and frontal lobe cognitive deficits in disorders of early childhood. Neuropsychologia 35:643–655
Ivry RB, Baldo JV (1992) Is the cerebellum involved in learning and cognition? Curr Opin Neurobiol 2:212–216
Loeber RT, Cintron CM, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2001) Morphometry of individual cerebellar lobules in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 158:952–954
Leiner CH, Alan L Dow RS (1993) Cognitive and language functions of the human cerebellum. Trends Neurosci 16:444–447
Leiner HC, Leiner AL, Dow RS (1995) The underestimated cerebellum. Hum Brain Mapp 2:244–254
Andreasen NC, Paradiso S, O'Leary DS (1998) "Cognitive dysmetria" as an integrative theory of schizophrenia: a dysfunction in cortical-subcortical-cerebellar circuitry? Schizophr Bull 24:203–218
Daum I, Ackerman H (1995) Cerebellar contributions to cognition. Behav Brain Res 67:201–210
Rapoport M, van Reekum R, Mayberg H (2000) The role of the cerebellum in cognition and behaviour: a selective review. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 12:193–198
Paradisio S, Andreasen NC, O'Leary DS, et al (1997) Cerebellar size and cognition: correlations with IQ, verbal memory and motor dexterity. Neuropsychiatry Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 10:1-8
Middleton FA, Strick PL (1994) Anatomical evidence for cerebellar and basal ganglia involvement in higher cognitive function. Science 266:458–461
Schmahman JD, Sherman JC (1998) The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121:561–579
Becker LE (1991) Synaptic dysgenesis. Can J Neurol Sci 18:170–180
Gressens P (1998) Mechanisms of cerebral dysgenesis. Cur Opin Pediatr 10:556–560
Crino PB, Eberwine J (1997) Cellular and molecular basis of cerebral dysgenesis. J Neurosci Res 50:907–916
Harum KH, Johnston MV (1998) Developmental neurobiology: new concepts in learning, memory, and neuronal development. MRDD Res Rev 4:20–25
Pomeroy SL, Kim JY (2000) Biology and pathobiology of neuronal development. MRDD Res Rev 6:41–46
Mehler MF (2000) Brain dystrophin, neurogenetics and mental retardation. Brain Res Rev 32:277–307
Johnston MV, Harum KH (1999) Recent progress in the neurology of learning: memory molecules in the developing brain. J Dev Behav Pediatr 20:50–56
Kriegstein AR (1996) Cortical neurogenesis and its disorders. Curr Opin Pediatr 9:113–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soto-Ares, G., Joyes, B., Lemaître, MP. et al. MRI in children with mental retardation. Ped Radiol 33, 334–345 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-0891-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-003-0891-z