Abstract
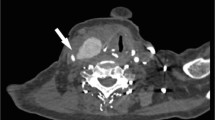
We present a case of a giant mycotic aneurysm of the left internal carotid artery in a child, the result of direct extension of a deep neck space infection. This lesion is life threatening and may put the patient at risk of unwarranted biopsy or drainage if not recognized. Diagnosis and treatment planning rely heavily on cross-sectional imaging, and angiography is frequently necessary. This case is unique for two reasons: (1) we present for the first time the MRI findings and (2) we describe an alternative to surgical ligation -- neurointerventional embolotherapy. Minimally invasive transcatheter embolization was successfully performed on our patient to occlude the abnormal left internal carotid artery segment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michielsen D, Van Hee R, Discart H (1997) Mycotic aneurysm of the carotid artery. A case report and review of the literature. Acta Chir Belg 97:44–46
Krysl J, de Tilly LN, Armstrong D (1993) Pseudoaneurysm of the internal carotid artery: complication of deep neck space infection. AJNR 14:696–698
Kato T, Oto K, Endo T, et al (1999) Microbial extracranial aneurysm of the internal carotid artery: complication of cervical lymphadenitis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:314–317
Wells RG, Sty JR (1991) Cervical lymphadenitis complicated by mycotic carotid artery aneurysm. Pediatr Radiol 21:402–403
Constantinides H, Passant C, Waddell AN (2000) Mycotic pseudoaneurysm of common carotid artery mimicking parapharyngeal abscess. J Laryngol Otol 114:796–797
Lueg EA, Awerbuck D, Forte V (1995) Ligation of the common carotid artery for the management of a mycotic pseudoaneurysm of an extracranial internal carotid artery. A case report and a review of the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 33:67–74
Hubaut JJ, Albat B, Frapier JM, et al (1997) Mycotic aneurysm of the extracranial carotid artery: an uncommon complication of bacterial endocarditis. Ann Vasc Surg 11:634–636
Willemsen P, De Roover D, Kock M, et al (1997) Mycotic common carotid artery aneurysm in an immunosuppressed pediatric patient: case report. J Vasc Surg 25:784–785
Matamoros A, Lydiatt WM, Lydiatt D, et al (2000) Pediatric neck masses: CT and MR imaging. Appl Radiol 29:5–9
Jarvis SJ, Parker AJ (2001) External carotid artery aneurysm in an infant presenting with oropharyngeal haemorrhage. J Laryngol Otol 115:500–501
Zimmerman MC, Mickel RA, Kessler DJ, et al (1987) Treatment of impending carotid rupture with detachable balloon embolization. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113:1169–1175
Raymond J, Theron J (1986) Intracavernous aneurysms: treatment by proximal balloon occlusion of the internal carotid artery. Am J Neuroradiol 7:1087–1092
Eckard DA, Purdy PD, Bonte FJ (2001) Carotid artery balloon test occlusion. Am J Neuroradiol 22:8S-9S
Marshall RS, Lazar RM, Young WL, et al (2002) Clinical utility of quantitative cerebral blood flow measurements during internal carotid artery test occlusions. Neurosurgery 50:996–1004
Gupta DK, Young WL, Hashimoto T, et al (2002) Characterization of the cerebral blood flow in response to balloon deflation after temporary internal carotid artery test occlusion. Neurosurg Anesthesiol 14:123–129
Mathews D, Walker BS, Purdy PD, et al (1993) Brain blood flow SPECT in temporary balloon occlusion of carotid and intracerebral arteries. J Nucl Med 34:1239–1243
Cilley RE, Zwischenberger JB, Andrews AF, et al (1986) Intracranial hemorrhage during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in neonates. Pediatrics 78:699–704
Raju TN, Kim SY, Meller JL, et al (1989) Circle of Willis blood velocity and flow direction after common carotid ligation for neonatal extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Pediatrics 83:343–347
Taylor GA, Short BL, Fitz CR (1989) Imaging of cerebrovascular injury in infants treated with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. J Pediatr 114:635–639
Wiznitzer M, Masaryk T, Lewin J, et al (1990) Parenchymal and vascular magnetic resonance imaging of the brain after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. ADJC 144:1323–1326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glaiberman, C.B., Towbin, R.B. & Boal, D.K.B. Giant mycotic aneurysm of the internal carotid artery in a child: endovascular treatment. Ped Radiol 33, 211–215 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-002-0844-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-002-0844-y