Abstract
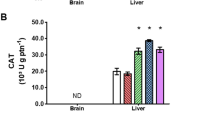
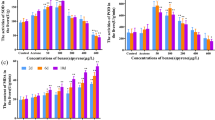
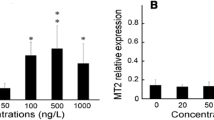
Synthetic polycyclic musks, widely used as additives in personal care products, are present in both biotic and abiotic matrices of the aquatic environment at concentrations of ng/l to µg/l. Although they are determined at comparatively low concentrations, these levels are biologically relevant and pose a significant growing risk as stressors to aquatic organisms. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the effects of 28-day-long exposure to polycyclic musk tonalide in zebrafish juvenile stages (Danio rerio) using selected biomarkers. Environmentally relevant concentrations of tonalide caused significant changes in selected enzyme activities in the experimental groups exposed to the highest concentrations. The activity of glutathione S-transferase and lipid peroxidation increased significantly (p < 0.05) after exposure to the highest concentration (50,000 ng/l) compared with the control. A similar trend was observed in catalase activity; there was a significant increase (p < 0.05) after exposure to two highest concentrations of tonalide (5000 and 50,000 ng/l). In addition, a statistically significant decrease (p < 0.05) in glutathione reductase activity was found in the lowest test concentration of tonalide (50 ng/l). None of the tested concentrations resulted in histopathological changes in liver, kidney, skin, or gill. Furthermore, no effects on body weight, body length, specific growth rate, and behavior were observed. Our results showed that tonalide exposure induced profound changes in the activities of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes, such changes representing an adaptive response of the fish organism to tonalide toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Bartoskova M, Dosbikova R, Stancova V, Zivna D, Blahova J, Marsalek P, Zelnickova L, Bartos M, Di Tocco FC, Faggio C (2013) Evaluation of ibuprofen toxicity for zebrafish (Danio rerio) targeting on selected biomarkers of oxidative stress. Neuroendocrinol Lett 34:102–108
Birben E, Sahiner UM, Sackesen C, Erzurum S, Kalayci O (2012) Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ J 5:9–19
Blahová J, Plhalová L, Hostovský M, Divišová L, Dobšíková R, Mikulíková I, Štěpánová S, Svobodová Z (2013) Oxidative stress responses in zebrafish Danio rerio after subchronic exposure to atrazine. Food Chem Toxicol 61:82–85
Brausch JM, Rand GM (2011) A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 82:1518–1532
Breitholtz M, Wollenberger L, Dinan L (2003) Effects of four synthetic musks on the life cycle of the harpacticoid copepod Nitocra spinipes. Aquat Toxicol 63:103–118
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1975) Purification and characterization of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 250:5475–5480
Carlsson G, Norrgren L (2004) Synthetic musk toxicity to early life stages of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:102–105
Chen C, Cai Z (2015) Physiological and antioxidant responses in wheat (Triticum aestivum) to HHCB in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:272–277
Chen D, Zeng X, Sheeng Y, Bi X, Gui H, Sheng G, Fu J (2007) The concentrations and distribution of polycyclic musks in a typical cosmetic plant. Chemosphere 66:25–258
Chen F, Gao J, Zhou Q (2011a) Toxicity assessment of simulated urban runoff containing polycylic musks and cadminum in Carassius auratus using oxidative stress. Environ Pollut 162:91–97
Chen C, Xue SG, Zhou QX, Xie XJ (2011b) Multilevel ecotoxicity assessment of polycyclic musk in the earthworm Eisenia fetida using traditional and molecular endpoints. Ecotoxicology 20:1949–1958
Chen G, Jiang R, Qiu J, Cai S, Zhu F, Ouyang G (2015) Environmental fates of synthetic musks in animal and plant: an in vivo study. Chemosphere 138:584–591
Clara M, Gans O, Windhofer G, Krenn U, Hartl W, Braun K, Scharf S, Scheffknech C (2011) Occurrence of polycyclic musks in wastewater and receiving water bodies and fate during wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 82:1116–1123
Dsikowitzky L, Schwarzbauer J (2014) Industrial organic contaminants: identification, toxicity and fate in the environment. Environ Chem Lett 12:371–386
Fazio F, Faggio C, Marafioti S, Torre A, Sanfilippo M, Piccione G (2012) Comparative study of haematological profile on Gobius niger in two different habitat sites: Faro Lake and Tyrrhenian Sea. Cah Biol Mar 53:213–219
Fazio F, Piccione G, Tribulato K, Ferrantelli V, Giangrosso G, Arfuso F, Faggio C (2014) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in blood and tissue of striped mullet in two Italian lakes. J Aquat Anim Health 26:278–284
Flohe L, Gunzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121
Fromme H, Otto T, Pilz K (2001) Polycyclic musk fragrances in different environmental compartments in Berlin (Germany). Water Res 35:121–128
Gao Y, Ji Y, Li G, Mai B, An T (2016) Bioaccumulation and ecotoxicity increase during indirect photochemical transformation of polycyclic musk tonalide: a modeling study. Water Res 105:47–55
Garicano EA, Borkent I, Herments JLM, Vaes WHJ (2003) Removal of two polycyclic musks in sewage treatment plants: freely dissolved and total concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 37:3111–3116
Gooding MP, Newton TJ, Bartsch MR, Hornbuckle KC (2006) Toxicity of synthetic musks to early life stages of the freshwater mussel Lampsilis cardium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:549–558
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jacoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases. First enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Herberer T (2002) Occurrence, fate, and assessment of polycyclic musk residues in the aquatic environment of urban areas: a review. Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 30:227–243
Homem V, Silva JA, Ratola N, Santos L, Alves A (2015) Long lasting perfume: a review of synthetic musks in WWTPs. J Environ Manag 149:168–192
Huang W, Xie Z, Yan W, Mi W, Xu W (2016) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks and organic UV filters from riverine and coastal sediments in the Pearl River estuary of China. Mar Pollut Bull 111:153–159
Kannan K, Reiner JL, Yun SH, Perrotta EE, Tao L, Johnson-Restrepo B, Rodan BD (2005) Polycyclic musk compounds in higher trophic level aquatic organisms and human from the United States. Chemosphere 61:693–700
Lange C, Kuch B, Metzger JW (2015) Occurrence and fate of synthetic musk fragrances in a small German river. J Hazard Mater 282:34–40
Lee IS, Le SH, Oh JE (2010) Occurrence and fate of synthetic musk compounds in water environment. Water Res 44:214–222
Liu S, Zhou Q, Chen Ch (2010) Antioxidant enzyme activities and lipid peroxidation in earthworm Eisenia fetida exposed to 1,3,4,6,7,8-hexahydro-4,6,6,7,8,8-hexamethyl-cyclopenta-γ-2-benzopyran. Environ Toxicol 27:472–479
Lushchak VI (2011) Environmentally induced oxidative stress in aquatic animals. Aquat Toxicol 101:13–30
Lushchak V, Semchyshyn HM (2012) Oxidative stress—molecular mechanisms and biological effects. In Tech, Rijeka, p 362
Lushchak VI, Bagnyukova TV, Lushchak OV, Storey JM, Storey KB (2005) Hypoxia and recovery perturb free radical processes and antioxidant potential in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues antioxidant potential in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:1319–1330
Messina CM, Faggio C, Laudicella AV, Sanfilippo M, Trischitta F, Santulli A (2014) Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) on stress response in the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis): regulatory volume decrease (RVD) and modulation of biochemical markers related to oxidative stress. Aquat Toxicol 157:94–100
Műller J, Bőhmer W, Litz NT (2006) Occurrence of polycyclic musks in sewage sludge and their beahviour in soils and plants. J Soils Sediments 6:231–235
OECD, Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals 215 (2000) Fish, juvenile growth test. OECD, Paris
Osachoff HL, Mahammadali M, Skirrow FC, Hall ER, Brown LLY, van Aggelen GC, Kennedy ChJ, Helbing CC (2014) Evaluating the treatment of a synthetic wastewater containing a pharmaceutical and personal care product chemical cocktail: compound removal efficiency and effects on juvenile rainbow trout. Water Res 62:271–280
Pablos MV, Jimenez MA, Segundo LS, Martini F, Beltran E, Fernandez C (2016) Effects of dietary exposure of polycyclic musk HHCB on the metamorphosis of Xenopus laevis. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:1428–1435
Pagano M, Capillo G, Sanfilippo M, Palato S, Trischitta F, Manganaro A, Faggio C (2016) Evaluation of functionality and biological responses of Mytilus galloprovincialis after exposure to quaternium-15 (methenamine 3-chloroallylochloride). Molecules 21:144
Parolini M, Magni S, Traversi I, Villa S, Finizio A (2015) Environmentally relevant concentrations of galaxolide (HHCB) and tonalide (AHTN) induced oxidative and genetic damage in Dreissena polymorpha. J Hazard Mater 285:1–10
Prichard E, Granek EF (2016) Effects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products on marine organisms: from single-species studies to an ecosystem-based approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:22365–22384
Rimkus GG (1999) Polycyclic musk fragrances in the aquatic environment. Toxicol Lett 20:37–56
Rüdel H, Böhmer W, Schröter-Kermani Ch (2006) Retrospective monitoring of synthetic musk compounds in aquatic biota from German rivers and coastal areas. J Environ Monit 8:812–823
Sadekarpawar S, Mansoori R, Upadhyay A, Parikh PH (2015) Biochemical and oxidative stress response of plant nutrient Liebrel TM in Orechromis mossambicus and Labeo rohita. Int J Adv Res 3:1587–1596
Sang W, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Ma L, Sun X (2012) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks in surface sediments of Liangtan River, West China. Environ Eng Sci 29:19–25
Saraiva M, Cavalheiro J, Lanceleur L, Monperrus M (2016) Synthetic musk in seafood products form south Europe using a quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction method. Food Chem 200:330–335
Satinder A (2013) Monitoring water quality: pollution assessment, analysis and remediation. Elsevier, Waltham
Schnell S, Martin-Skilton R, Fernandes D, Porte C (2009) The interference of nitro- and polycyclic musks with endogenous and xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in carp: an in vitro study. Environ Sci Technol 43:9458–9464
Schreurs RHMM, Legler J, Artola-Garicano E, Sinnige TL, Lanser PH, Seinen W, van der Burg B (2004) In vitro and in vivo antiestrogenic effects of polycyclic musk in zebrafish. Environ Sci Technol 38:997–1002
Sehonova P, Plhalova L, Blahova J, Berankova P, Doubkova V, Prokes M, Tichy F, Vecerek V, Svobodova Z (2016) The effect of tramadol hydrochloride on early life stages of fish. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 44:151–157
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Subedi B, Du B, Chambliss CK, Koschorreck J, Rűdel H, Quack M, Brooks BW, Usenko S (2012) Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in German fish tissue: a national study. Environ Sci Technol 46:9047–9054
Valavanidis A, Vlahogianni T, Dassenakis M, Scoullos M (2006) Molecular biomarkers of oxidative stress in aquatic organisms in relation to toxic environmental pollutant. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 64:178–189
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 13:57–149
Wang Q, Kelly BC (2017) Occurrence and distribution of synthetic musks, triclosan and methyl triclosan in a tropical urban catchment: influence of land-use proximity, rainfall and physicochemical properties. Sci Total Environ 574:1439–1447
Wollenberger L, Breitholtz M, Kusk KO, Bengtsson BE (2003) Inhibition of larval development of marine copepod Acartia tonsa by four synthetic musk substances. Sci Total Eviron 305:53–64
Yamauchi R, Ishibashi H, Hirano M, Mori T, Kim J, Arizono K (2008) Effects of synthetic polycyclic musks on estrogen receptor, vitellogenin, pregnane X receptor, and cytochrome P450 3A gene expression in the liver of male medaka (Oryzias latipes). Aquat Toxicol 90:261–268
Yancheva V, Velcheva I, Georgieva E (2016) Histological biomarkers in fish as a tool in ecological risk assessment and monitoring programs: a review. Appl Ecol Environ Res 14:47–75
Yang JJ, Metcalfe ChD (2006) Fate of synthetic musks in a domestic wastewater treatment plant and in an agricultural field amended with biosolids. Sci Total Environ 363:149–165
Zhang X, Yao Y, Zeng X, Qian G, Guo Y, Wu M (2008) Synthetic musks in the aquatic environment and personal care products in Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 72:1553–1558
Zhang L, Jing AN, Zhou Q (2012) Single and joint effects of HHCB and cadmium on zebrafish (Danio rerio) in feculent water containing bedloads. Front Environ Sci Eng 6:360–373
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a Grant from the University of Veterinary and Pharmaceutical Sciences Brno (IGA VFU 248/2015/FVHE). The authors thank Mr. Matthew Nicholls for paper improvement and English correction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blahova, J., Divisova, L., Plhalova, L. et al. Multibiomarker Responses of Juvenile Stages of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) to Subchronic Exposure to Polycyclic Musk Tonalide. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74, 568–576 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0484-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0484-8