Abstract
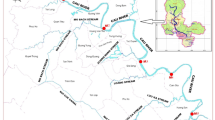
This study provided the first evidence that perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) were widely detected in the Songhua River, China. Seventeen surface water and sediment samples were collected and analyzed for the determination of 14 PFCs. The total concentrations of PFCs (Σ PFCs) ranged from 0.143 to 1.41 ng L−1 in water samples. Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) was detected with the highest detection frequency (%) ranging from below LOQ to 0.678 ng L−1. Σ PFCs were relatively low in sediments, and only four individual homologues were detected. Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and PFOA were detected with the lowest levels in this study compared with other PFCs detected in all the rivers of China in previous studies. The concentrations of PFCs were highly influenced by distribution of wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs). The effluents from WWTPs, which are discharged into the Songhua River, are regarded as the main contamination sources of PFCs in this study. Even though low risk for the concentrations of PFOS and PFOA to aquatic ecosystem of the Songhua River was found in the analysis of potential adverse effect, further experimental studies on occurrence of PFCs and their potential adverse effects to wildlife and humans should be conducted continuously in the Songhua River basin because of the increasing discharge. The mean partition coefficients (log K oc) of PFOS between sediment and water was 4.49 cm3 g−1, which was probably influenced by the sediment characteristics and hydrodynamic parameters. PFCs tend to accumulate in water compared with other persistent organic pollutants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens L (2011) Polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the aquatic environment: a review of their occurrence and fate. J Environ Monit 13:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0em00373e
Ahrens L, Yamashita N, Yeung LWY, Taniyasu S, Horii Y, Lam PKS, Ebinghaus R (2009) Partitioning behavior of per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds between pore water and sediment in two sediment cores from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Environ Sci Technol 43:6969–6975. https://doi.org/10.1021/es901213s
Ahrens L, Taniyasu S, Yeung LWY, Yamashita N, Lam PKS, Ebinghaus R (2010) Distribution of polyfluoroalkyl compounds in water, suspended particulate matter and sediment from Tokyo Bay, Japan. Chemosphere 79:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.01.045
Bao J, Jin Y, Liu W, Ran X, Zhang Z (2009) Perfluorinated compounds in sediments from the Daliao River system of northeast China. Chemosphere 77:652–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.08.018
Bao J, Liu W, Liu L, Jin Y, Ran X, Zhang Z (2010) Perfluorinated compounds in urban river sediments from Guangzhou and Shanghai of China. Chemosphere 80:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.04.008
Bao J, Liu W, Liu L, Jin Y, Dai J, Ran X, Zhang Z, Tsuda S (2011) Perfluorinated compounds in the environment and the blood of residents living near fluorochemical plants in Fuxin, China. Environ Sci Technol 45:8075–8080. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102610x
Bao LJ, Maruya KA, Snyder SA, Zeng EY (2012) China’s water pollution by persistent organic pollutants. Environ Pollut 163:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.12.022
Becker AM, Gerstmann S, Frank H (2008) Perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate in the sediment of the Roter Main river, Bayreuth, Germany. Environ Pollut 156:818–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.05.024
Benskin JP, Ikonomou MG, Gobas FAPC, Begley TH, Woudneh MB, Cosgrove JR (2013) Biodegradation of N-ethyl perfluorooctane sulfonamido ethanol (EtFOSE) and EtFOSE-based phosphate diester (SAmPAP diester) in marine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 47:1381–1389. https://doi.org/10.1021/es304336r
Cai M, Zhao Z, Yin Z, Ahrens L, Huang P, Cai M, Yang H, He J, Sturm R, Ebinghaus R, Xie Z (2012) Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl compounds in surface waters from the North Pacific to the Arctic Ocean. Environ Sci Technol 46:661–668. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2026278
Cao Y, Cao X, Wang H, Wan Y, Wang S (2015) Assessment on the distribution and partitioning of perfluorinated compounds in the water and sediment of Nansi Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4831-9
Chaemfa C, Barber JL, Huber S, Breivik K, Jones KC (2010) Screening for PFOS and PFOA in European air using passive samplers. J Environ Monit 12:1100–1109. https://doi.org/10.1039/b921628f
Cui S, Fu Q, Li YF, Li WL, Li TX, Wang M, Xing ZX, Zhang LJ (2016) Levels, congener profile and inventory of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediment from the Songhua River in the vicinity of cement plant, China: a case study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:15952–15962. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6761-7
Dinglasan MJA, Ye Y, Edwards EA, Mabury SA (2004) Fluorotelomer alcohol biodegradation yields poly- and perfluorinated acids. Environ Sci Technol 38:2857–2864. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0350177
Dreyer A, Weinberg I, Temme C, Ebinghaus R (2009) Polyfluorinated compounds in the atmosphere of the Atlantic and Southern Oceans: evidence for a global distribution. Environ Sci Technol 43:6507–6514. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9010465
Ellis DA, Martin JW, Silva AOD, Mabury SA, Hurley MD, Andersen MPS, Wallington TJ (2004) Degradation of fluorotelomer alcohols: a likely atmospheric source of perfluorinated carboxylic acids. Environ Sci Technol 38:3316–3321. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049860w
Gao D, Li Z, Wen Z, Ren N (2014) Occurrence and fate of phthalate esters in full-scale domestic wastewater treatment plants and their impact on receiving waters along the Songhua River in China. Chemosphere 95:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.009
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2001) Global distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate in wildlife. Environ Sci Technol 35:1339–1342. https://doi.org/10.1021/es001834k
Giesy JP, Kannan K (2002) Peer reviewed: perfluorochemical surfactants in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 36:146A–152A. https://doi.org/10.1021/es022253t
Giesy J, Naile J, Khim J, Jones P, Newsted J (2010) Aquatic toxicology of perfluorinated chemicals, reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology. Springer, New York, pp 1–52
Hawthorne SB, Grabanski CB, Miller DJ (2006) Measured partitioning coefficients for parent and alkyl polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in 114 historically contaminated sediments: part 1. K oc values. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2901–2911. https://doi.org/10.1897/06-115r.1
Higgins CP, Luthy RG (2006) Sorption of perfluorinated surfactants on sediment. Environ Sci Technol 40:7251–7256. https://doi.org/10.1021/es061000n
Hodson J, Williams NA (1988) The estimation of the adsorption coefficient (K oc) for soils by high performance liquid chromatography. Chemosphere 17:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(88)90045-8
Houde M, Martin JW, Letcher RJ, Solomon KR, Muir DC (2006) Biological monitoring of polyfluoroalkyl substances: a review. Environ Sci Technol 40:3463–3473. https://doi.org/10.1021/es052580b
Hu J, Liu C, Guo Q, Yang J, Okoli CP, Liang Y, Zhao Z, Li S, Liu B, Song G (2017) Characteristics, source, and potential ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Songhua River Basin, Northeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:17090–17102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9057-7
Huset CA, Chiaia AC, Barofsky DF, Jonkers N, Kohler HP, Ort C, Giger DW, Field JA (2008) Occurrence and mass flows of fluorochemicals in the Glatt Valley watershed, Switzerland. Environ Sci Technol 42:6369–6377. https://doi.org/10.1021/es703062f
Kannan K, Corsolini S, Falandysz J, Fillmann G, Kumar KS, Loganathan BG, Mohd MA, Olivero J, Van Wouwe N, Yang JH, Aldous KM (2004) Perfluorooctanesulfonate and related fluorochemicals in human blood from several countries. Environ Sci Technol 38:4489–4495. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0493446
Kim EJ, Park YM, Park JE, Kim JG (2014) Distributions of new Stockholm convention POPs in soils across South Korea. Sci Total Environ 476–477:327–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.01.034
Kissa E (2001) Fluorinated surfactants and repellents. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York
Kwok KY, Yamazaki E, Yamashita N, Taniyasu S, Murphy MB, Horii Y, Petrick G, Kallerborn R, Kannan K, Murano K, Lam PK (2013) Transport of perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) froman arctic glacier to downstream locations: implications for sources. Sci Total Environ 447:46–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.10.091
Lau C, Butenhoff JL, Rogers JM (2004) The developmental toxicity of perfluoroalkyl acids and their derivatives. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2003.11.031
Li F, Sun H, Hao Z, He N, Zhao L, Zhang T (2011a) Perfluorinated compounds in Haihe River and Dagu Drainage Canal in Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 84:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.060
Li J, Vento SD, Schuster J, Zhang G, Chakraborty P, Kobara Y, Jones KC (2011b) Perfluorinated compounds in the Asian atmosphere. Environ Sci Technol 45:7241–7248. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201739t
Liu J, Lee LS (2005) Solubility and sorption by soils of 8:2 fluorotelomer alcohol in water and cosolvent systems. Environ Sci Technol 39:7535–7540. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051125c
Liu B, Zhang H, Xie L, Li J, Wang X, Zhao L, Wang Y, Yang B (2015a) Spatial distribution and partition of perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in rivers of the Pearl River Delta, southern China. Sci Total Environ 524–525:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.04.004
Liu B, Zhang H, Yao D, Li J, Xie L, Wang X, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang B (2015b) Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in the atmosphere of Shenzhen, China: spatial distribution, sources and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 138:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.07.012
Loganathan BG, Sajwan KS, Sinclair E, Kumar KS, Kannan K (2007) Perfluoroalkyl sulfonates and perfluorocarboxylates in two wastewater treatment facilities in Kentucky and Georgia. Water Res 41:4611–4620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.06.045
Nakayama S, Harada K, Inoue K, Sasaki K, Seery B, Saito N, Koizumi A (2005) Distributions of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in Japan and their toxicities. Environ Sci 12:293–313 PMID: 16609670
Olsen GW, Church TR, Miller JP, Burris JM, Hansen KJ, Lundberg JK, Armitage JB, Herron RM, Medhdizadehkashi Z, Nobiletti JB, O’Neil EM, Mandel JH, Zobel LR (2003) Perfluorooctanesulfonate and other fluorochemicals in the serum of American Red Cross adult blood donors. Environ Health Perspect 111:1892–1901. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6316
Pan G, You C (2010) Sediment–water distribution of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in Yangtze River Estuary. Environ Pollut 158:1363–1367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.011
Pan G, Zhou Q, Luan X, Fu QS (2014) Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in Lake Taihu (China): impact to human health and water standards. Sci Total Environ 487:778–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.100
Paul AG, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ (2009) A first global production, emission, and environmental inventory for perfluorooctane sulfonate. Environ Sci Technol 43:386–392. https://doi.org/10.1021/es802216n
Post GB, Louis JB, Lee LR, Procopio NA (2013) Occurrence of perfluorinated compounds in raw water from New Jersey public drinking water systems. Environ Sci Technol 47:13266–13275. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402884x
Prevedouros K, Cousins IT, Buck RC, Korzeniowski SH (2006) Sources, fate and transport of perfluorocarboxylates. Environ Sci Technol 40:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0512475
Rayne S, Forest K (2009) Perfluoroalkyl sulfonic and carboxylic acids: a critical review of physicochemical properties, levels and patterns in waters and wastewaters, and treatment methods. J Environ Sci Health A 44:1145–1199. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520903139811
Schröder HF, Meesters RJW (2005) Stability of fluorinated surfactants in advanced oxidation processes—a follow up of degradation products using flow injection-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-multiple stage mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1082:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2005.02.070
Schultz MM, Barofsky DF, Field JA (2006) Quantitative determination of fluorinated alkyl substances by large-volume-injection liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry—characterization of municipal wastewaters. Environ Sci Technol 40:289–295. https://doi.org/10.1021/es051381p
Shivakoti BR, Tanaka S, Fujii S, Kunacheva C, Boontanon SK, Musirat C, Seneviratne ST, Tanaka H (2010) Occurrences and behavior of perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in several wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in Japan and Thailand. J Environ Monit 12:1255–1264. https://doi.org/10.1039/b927287a
Simcik MF, Dorweiler KJ (2005) Ratio of perfluorochemical concentrations as a tracer of atmospheric deposition to surface waters. Environ Sci Technol 39:8678–8683. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0511218
So MK, Taniyasu S, Yamashita N, Giesy JP, Zheng J, Fang Z, Im SH, Lam PKS (2004) Perfluorinated compounds in coastal waters of Hong Kong, South China, and Korea. Environ Sci Technol 38:4056–4063. https://doi.org/10.1021/es049441z
So MK, Miyake Y, Yeung WY, Ho YM, Taniyasu S, Rostkowski P, Yamashita N, Zhou BS, Shi XJ, Wang JX, Giesy JP, Yu H, Lam PKS (2007) Perfluorinated compounds in the Pearl River and Yangtze River of China. Chemosphere 68:2085–2095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.008
Tomy GT, Tittlemier SA, Palace VP, Budakowski WR, Braekevelt E, Brinkworth L, Friesen K (2004) Biotransformation of Nethyl perfluorooctanesulfonamide by rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mykiss) liver microsomes. Environ Sci Technol 38:758–762. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034550j
UNEP (2009) The conference of the parties 4 of the Stockholm Convention (COP-4) in Geneva placed perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctane sulfonyl fluoride (PFOS and PFOSF) in Annex B. Stoekholm convention on persistent organic pollutants (POPs). http://www.pops.int
US Environmental Protection Agency (1995) Final water quality guidance for the Great Lakes system. http://www.epa.gov/EPA-WATER/1995/March/Day-23/pr-82DIR/Facts/Fact_Sheet.pdf
Wang C, Feng YJ, Gao P, Ren NQ, Li BL (2012) Simulation and prediction of phenolic compounds fate in Songhua River, China. Sci Total Environ 431:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.047
Wang B, Cao M, Zhu H, Chen J, Wang L, Liu G, Gu X, Lu X (2013a) Distribution of perfluorinated compounds in surface water from Hanjiang River in Wuhan, China. Chemosphere 93:468–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.014
Wang P, Wang T, Giesy JP, Lu Y (2013b) Perfluorinated compounds in soils from Liaodong bay with concentrated fluorine industry parks in China. Chemosphere 91:751–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.017
Wang Y, Wang P, Bai YJ, Tian ZX, Li JW, Shao X, Mustavich LF, Li BL (2013c) Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: a case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China. J Hydro Environ Res 7:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2012.10.003
Wang W, Wang H, Zhang W, Liang H, Gao D (2017) Occurrence, distribution, and risk assessment of antibiotics in the Songhua River in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19282–19292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9471-x
Xiao F, Halbach TR, Simcik MF, Gulliver JS (2012a) Input characterization of perfluoroalkyl substances in wastewater treatment plants: source discrimination by exploratory data analysis. Water Res 46:3101–3109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.027
Xiao F, Simcik MF, Gulliver JS (2012b) Perfluoroalkyl acids in urban stormwater runoff: influence of land use. Water Res 46:6601–6608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.029
Xie S, Wang T, Liu S, Jones KC, Sweetman AJ, Lu Y (2013) Industrial source identification and emission estimation of perfluorooctane sulfonate in China. Environ Int 52:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.11.004
Xu L, Krenitsky DM, Seacat AM, Butenhoff JL, Anders MW (2004) Biotransformation of N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)perfluorooctanesulfonamide by rat liver microsomes, cytosol, and slices and by expressed rat and human cytochromes P450. Chem Res Toxicol 17:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx034222x
Yamashita N, Kannan K, Taniyasu S, Horii Y, Petrick G, Gamo T (2005) A global survey of perfluorinated acids in oceans. Mar Pollut Bull 51:658–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.04.026
Yang L, Zhu L, Liu Z (2011) Occurrence and partition of perfluorinated compounds in water and sediment from Liao River and Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 83:806–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.075
You C, Jia C, Pan G (2010) Effect of salinity and sediment characteristics on the sorption and desorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate at sediment–water interface. Environ Pollut 158:1343–1347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.01.009
Young CJ, Furdui VI, Franklin J, Koerner RM, Muir DCG, Mabury SA (2007) Perfluorinated acids in arctic snow: new evidence for atmospheric formation. Environ Sci Technol 41:3455–3461. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0626234
Yu J, Hu JY, Tanaka S, Fujii S (2009) Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in sewage treatment plants. Water Res 43:2399–2408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.009
Zhang Y, Meng W, Guo C, Xu J, Yu T, Fan W, Li L (2012) Determination and partitioning behavior of perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids and perfluorooctanesulfonate in water and sediment from Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere 88:1292–1299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.103
Zhang Y, Lai S, Zhao Z, Liu F, Chen H, Zou S, Xie Z, Ebinghaus R (2013) Spatial distribution of perfluoroalkyl acids in the Pearl River of Southern China. Chemosphere 93:1519–1525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.060
Zhang Z, Ren N, Kannan K, Nan J, Liu L, Ma W, Qi H, Li Y (2014) Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting phenols and estrogens in water and sediment of the Songhua river, northeastern China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:361–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-9998-5
Zhang C, Yan H, Li F, Zhou Q (2015) Occurrence and fate of perfluorinated acids in two wastewater treatment plants in Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1804–1811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2044-8
Zhao Z, Tang J, Xie Z, Chen Y, Pan X, Zhong G, Sturm R, Zhang G, Ebinghaus R (2013) Perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs) in riverine and coastal sediments of Laizhou Bay, North China. Sci Total Environ 447:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.095
Zhao X, Ding J, You H (2014) Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environ Geochem Health 36:131–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9524-0
Zhu Z, Wang T, Meng J, Wang P, Li Q, Lu Y (2015) Perfluoroalkyl substances in the Daling River with concentrated fluorine industries in China: seasonal variation, mass flow, and risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:10009–10018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4189-0
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31200407), the Science and Technology Research Project of the Education Department of Jilin Province, China (Nos. 2014518 and 2015357), the National Natural Science Foundation of Changchun Normal University (No. 2015003), and the Project of Sci-tech Innovation Teams in Changchun Normal University (No. T2013-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, W., Liu, B., Song, Y. et al. Occurrence and Partition of Perfluorinated Compounds (PFCs) in Water and Sediment from the Songhua River, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 74, 492–501 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0474-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-017-0474-x