Abstract
Purpose
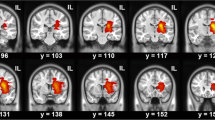
To investigate modifications of Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging (DKI) metrics in lateral white matter (WM) bundles of the cervical spinal cord in patients with previous stroke in the vascular territory of the middle cerebral artery (MCA).
Methods
Twenty consecutive patients with a previous ischemic stroke of the MCA territory and a varying degree of upper motor impairment were enrolled. DKI was centered at the C3C4 and C5C6 intervertebral level.
Results
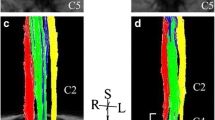
The fractional anisotropy (FA) values in C3C4 and C5C6 were found to be significantly lower in the lateral WM bundles contralateral to the ischemic lesion and thus, in the WM bundle including the affected corticospinal tract (CST) (p = 0.005 and p = 0.008, respectively), as well as mean kurtosis (MK) and axonal water fraction (AWF) values (p = 0.004 and p = 0.04. respectively). FA values correlated significantly with the Global Motor Index (GMI) both for C3C4 (ρ = 0.61, p = 0.004) and C5C6 (ρ = 0.69, p = 0.002). At C3C4, AWF correlated significantly with GMI (ρ = 0.54, p = 0.03). No correlations were found between lateral WM bundle volumes and GMI.
Conclusion
A reduction of anisotropy and microstructural complexity in the affected lateral WM bundle of the cervical spinal cord was observed in patients with previous ischemic stroke involving the CST. The correlations between these metrics and motor performance were statistically significant.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AWF:
-
Axonal water fraction
- CST:
-
Corticospinal tract
- cSC:
-
Cervical spinal cord
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- DKI:
-
Diffusion kurtosis imaging
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- MK:
-
Mean kurtosis
- RK:
-
Radial kurtosis
- AK:
-
Axial kurtosis
- GMI:
-
Global motor index
References
Langhorne P, Coupar F, Pollock A (2009) Motor recovery after stroke: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol 8:741–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422[09]70150-4
Park CH, Kou N, Boudrias MH, Playford ED, Ward NS (2013) Assessing a standardised approach to measuring corticospinal integrity after stroke with DTI. NeuroImage 2:521–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2013.04.002.521-533
Ward NS, Newton JM, Swayne OB et al (2006) Motor system activation after subcortical stroke depends on corticospinal system integrity. Brain 129:809–819. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl002.
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996a) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36(6):893–906
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, Barnett A, Di Chiro G (1996b) Diffusion tensor MR imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201(3):637–648
Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K (2005) Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 53(6):1432–1440. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20508
Panara V, Navarra R, Mattei PA, Piccirilli E, Cotroneo AR, Papinutto N, Henry RG, Uncini A, Caulo M (2017) Spinal cord microstructure integrating phase-sensitive inversion recovery and diffusional kurtosis imaging. Neuroradiology 59(8):819–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1864-5
Van Cauter S, Veraart J, Sijbers J, Peeters RR, Himmelreich U, De Keyzer F et al (2012) Gliomas: diffusion kurtosis MR imaging in grading. Radiology 263(2):492–501
Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2011) MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. 23(7):698–710. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.12110927
Spampinato XMV, Chan XC, Jensen XJH, Helpern XJA Bonilha XL, Kautz XSA et al (2017) Diffusional kurtosis imaging and motor outcome in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR 38(7):1328–1334. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5180
Lindberg G, Bensmail D, Bussel B, Maier MA, Feydy A (2011) Wallerian degeneration in lateral cervical spinal cord detected with diffusion tensor imaging in four chronic stroke patients. J Neuroimaging 21(1):44–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2009.00409.x
Rabadi MH, Rabadi FM (2006) Comparison of the action research arm test and the Fugl-Meyer assessment as measures of upper-extremity motor weakness after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 87:962–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2006.02.036
Taber KH, Herrick RC, Weathers SW, Kumar AJ, Schomer DF, Hayman LA (1998) Pitfalls and artifacts encountered in clinical MR imaging of the spine. Radiographics 18(6):1499–1521. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.18.6.9821197
Kearney H, Yiannakas MC, Abdel-Aziz K, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Altmann DR, Ciccarelli O, Miller DH (2014) Improved MRI quantification of spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 39(3):617–623. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24194
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith RG, Ho S, Gee JC, Gerig G (2006) User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 31(3):1116–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015
Tabesh A, Jensen JH, Ardekani BA, Helpern JA (2011) Estimation of tensors and tensor-derived measures in diffusional kurtosis imaging. Magn Reson Med 65(3):823–836. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22655
Chang LC, Jones DK, Pierpaoli C (2005) RESTORE: robust estimation of tensors by outlier rejection. Magn Reson Med 53(5):1088–1095. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20426
Fieremans E, Jensen JH, Helpern JA (2011) White matter characterization with diffusional kurtosis imaging. NeuroImage 58(1):177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.006
De Leener B, Kadoury S, Cohen-Adad J (2014) Robust, accurate and fast automatic segmentation of the spinal cord. NeuroImage 98:528–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.051
Levy S, Benhamou M, Naaman C, Rainville P, Callot V, Cohen- Adad J (2015) White matter atlas of the human spinal cord with estimation of partial volume effect. NeuroImage 119:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.06.040
Fugl-Meyer AR, Jaasko L, Leyman I, Olsson S, Steglind S (1975) The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. 1. a method for evaluation of physical performance. Scand J Rehabil Med 7(1):13–31
Collin C, Wade D (1990) Assessing motor impairment after stroke: a pilot reliability study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53(7):576–579
Mathiowetz V, Volland G, Kashman N, Weber K (1985) Adult norms for the box and block test of manual dexterity. Am J Occup Ther 39(6):386–391
Rothman KJ (1990) No adjustment are needed for multiple comparisons. Epidemiology 1(1):43–46
Lindenberg R, Renga V, Zhu LL, Betzler F, Alsop D (2010) Structural integrity of corticospinal motor fibers predicts motor impairment in chronic stroke. Neurology 74:280–287. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181ccc6d9
Pineiro R, Pendlebury ST, Smith S, Flitney D, Blamire AM, Styles P, Matthews PM (2000) Relating MRI changes to motor deficit after ischemic stroke by segmentation of functional motor pathways. Stroke 31:672–679
Schiemanck SK, Kwakkel G, Post MW, Kappelle LJ, Prevo AJ (2008) Impact of internal capsule lesions on outcome of motor hand function at one year post-stroke. J Rehabil Med 40:96–101. https://doi.org/10.2340/16501977-0130
Jin R, Liu L, Zhang S, Nanda A, Li G (2013) Role of inflammation and its mediators in acute ischemic stroke. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 6(5):834–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-013-9508-6
Choudhury GR, Ding S (2016) Reactive astrocytes and therapeutic potential in focal ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis 85:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.05.003
Virta A, Barnett AL, Pierpaoli C (1999) Visualizing and characterizing white matter fiber structure and architecture in the human pyramidal tract using diffusion tensor MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 17(8):1121–1133
Pierpaoli C, Barnett A, Pajevic S, Chen R, Penix LR, Virta A, Basser P (2001) Water diffusion changes in Wallerian degeneration and their dependence on white matter architecture. NeuroImage 13:1174–1185. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0765
Prados F, Ashburner J, Blaiotta C, Brosch T, Carballido-Gamio J, Cardoso MJ, Conrad BN, Datta E, David G, De Leener B, Duponte SM, Freund P, Wheeler-Kingshott C, Grussu F, Henry R, Landman BA, Ljungberg E, Lyttle B, Ourselin B, Papinutto N, Saporito S, Schlaeger R, Smith SA, Summers P, Tami R, Yiannakas MC, Zhu A, Cohen-Adad (2017) Spinal cord grey matter segmentation challenge. NeuroImage 152:312–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.010
Papinutto N, Schlaeger R, Panara V, Caverzasi E, Ahn S, Johnson KJ, Zhu AH, Stern WA, Laub G, Hauser SL, Henry RG (2015) 2D phase-sensitive inversion recovery imaging to measure in vivo spinal cord gray and white matter areas in clinically feasible acquisition times. J Magn Reson Imaging 42(3):698–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24819
Papinutto N, Schlaeger R, Panara V, Zhu AH, Caverzasi E, Stern WA, Hauser SL, Henry RG (2015) Age, gender and normalization covariates for spinal cord gray matter and total cross-sectional areas at cervical and thoracic levels: a 2D phase sensitive inversion recovery imaging study. PLoS One 10(3):e0118576. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118576 Published online 2015 Mar 17
Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Panara V, Bevan C, Lobach IV, Bucci M, Caverzasi E, Gelfand JM, Green AJ, Jordan KM, Stern WA, von Büdingen HC, Waubant E, Zhu AH, Goodin DS, Cree BA, Hauser SL, Henry RG (2014) Spinal cord gray matter atrophy correlates with multiple sclerosis disability. Ann Neurol 76(4):568–580. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24241
Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, Lobach IV, Bevan CJ, Bucci M, Castellano A, Gelfand JM, Graves JS, Green AJ, Jordan KM, Keshavan A, Panara V, Stern WA, von Büdingen HC, Waubant E, Goodin DS, Cree BA, Hauser SL, Henry RG (2015) Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 72(8):897–904. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.0993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panara, V., Navarra, R., Mattei, P.A. et al. Correlations between cervical spinal cord magnetic resonance diffusion tensor and diffusion kurtosis imaging metrics and motor performance in patients with chronic ischemic brain lesions of the corticospinal tract. Neuroradiology 61, 175–182 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2139-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-018-2139-5