Abstract
Introduction
To evaluate the hypothesis that flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (FAIR) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging can detect retrograde cortical venous drainage (RCVD) in patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF).
Methods
Seven patients with angiographically confirmed DAVF with RCVD and two DAVF patients without RCVD underwent examinations with conventional MR imaging and FAIR, five of these seven patients with RCVD also underwent examination with dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR imaging. The ability of FAIR to depict prominent cerebral veins was evaluated, and FAIR was compared with the relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) maps created with DSC.
Results
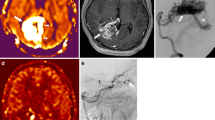
In all DAVF patients with RCVD, FAIR clearly showed prominent veins on the surface of the brain in affected hemisphere, and FAIR corresponded well with the areas of increased rCBV. In all DAVF patients without RCVD, FAIR showed no prominent veins.
Conclusion
FAIR can detect RCVD in patients with DAVF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lasjaunias P, Chiu M, TerBrugge K, Tolia A, Hurth M, Bernstein M (1986) Neurorogical manifestations of intracranial dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64:724–730
Hurst RW, Bagley LJ, Galetta S (eds) (1998) Dementia resulting from dural arteriovenous fistulas: the pathologic findings of venous hypertensive encephalopathy. AJNR 19:1267–1273
Awad I, Little J, Akrawi W, Ahl J (1990) Intracranial dural aeteriovenous malformations: factors predisposing to an aggressive neurological course. J Neurosurg 72:839–850
Malik GM, Pearce JE, Ausman JI, Mehta B (1984) Dural arteriovenous malformations and intracranial hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 15:332–339
Vinuela F, Fox AJ, Pelz DM, Drake CG (1986) Unusual clinical manifestations of dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 64:554–558
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA (1995) A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82:166–179
Cognard C, Gobin Y, Pierot L (eds) (1995) Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology 194:671–680
van Dijk JM, terBrugge KG, Willinsky RA, Wallace MC (2002) Clinical cource of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with long-term persistent cortical venous reflux. Stroke 33:1233–1236
Willinsky R, Goyal M, terBrugge K, Montanera W (1999) Tortous, enlarged pial veins in intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: correlations with presentation, location, and MR findings in 122 patients. AJNR 20:1031–1036
DeMarco K, Dillon WP, Halbach VV, Tsuruda JS (1990) Dural arteriovenous fistula: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 175:193–199
Chen JC, Tsuruda JS, Halbach VV (1992) Suspected dural arteriovenous fistula: results with screening MR angiography in seven patients. Radiology 183:265–271
Willinsky R, terBrugge K, Montanera W, Mikulis D, Wallace C (1994) Venous congestion: an MR finding in dural arteriovenous malformations with cortical venous drainage. AJNR 15:1501–1507
Noguchi K, Kubo M, Kuwayama N (eds) (2006) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with retrograde cortical venous drainage: assessment with cerebral blood volume by dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging. AJNR 27:1252–1256
Kim SG, Tsekos NV (1997) Perfusion imaging by a flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (FAIR) technique: application to functional brain imaging. Magn Reson Med 37:425–435
Alsop DC, Detre JA (1998) Multisection cerebral blood flow MR imaging with continuous arterial spin labeling. Radiology 208:410–416
Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA (2008) Arterial spin labeling in routine clinical practice, part 1: technique and artifacts. AJNR 29:1228–1234
Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA (2008) Arterial spin labeling in routine clinical practice, part 2: hypoperfusion patterns. AJNR 29:1235–1241
Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA (2008) Arterial spin labeling in routine clinical practice, part 3: hyperperfusion patterns. AJNR 29:1428–1435
Wolf RL, Wang J, Detre JA, Zager EL, Hurst RW (2008) Arteriovenous shunt visualization in arteriovenous malformations with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. AJNR 29:681–687
Noguchi K, Melhem ER, Kanazawa T, Kubo M, Kuwayama N, Seto H (2004) Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with combined 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and MR digital subtraction angiography. AJR 182:183–190
Coley SC, Romanowski CAJ, Hodgson TJ, Griffiths PD (2002) Dural arteriovenous fistulae: noninvasive diagnosis with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR 23:404–407
Horie N, Morikawa M, Kitigawa N, Tsutsumi K, Kaminogo M, Nagata I (2006) 2D Thick-section mr digital subtraction angiography for the assessment of dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR 27:264–269
Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Johnstone DM, teBrugge KG (2009) Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and classification with time-resolved MR angiography at 3 T. AJNR 30:1546–1551
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A (eds) (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3 T. AJNR 31:80–85
Noguchi K, Kuwayama N, Kubo M (eds) (2007) Dural arteriovenous fistula involving the transverse sigmoid sinus after treatment: assessment with magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 49:639–643
Kitajima M, Hirai T, Korogi Y, Yamura M, Kawanaka K, Ikushima I, Hayashida Y, Yamashita Y, Kuratsu J (2005) Retrograde cortical and deep venous drainage in patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: comparison of MR imaging and angiographic findings. AJNR 26:1532–1538
Wang J, Alsop DC, Li L, Listerud J, Gonzalez-At JB, Schnall MD, Detre JA (2002) Comparison of quantitative perfusion imaging using arterial spin labeling at 1.5 and 4.0 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 8:242–254
Boss A, Martirosian P, Klose U, Nägele T, Claussen CD, Schick F (2007) FAIR-TrueFISP imaging of cerebral perfusion in areas of high magnetic susceptibility differences at 1.5 and 3 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 25:924–931
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, K., Kuwayama, N., Kubo, M. et al. Flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (fair) imaging for retrograde cortical venous drainage related to intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula. Neuroradiology 53, 153–158 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0711-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0711-8