Abstract.
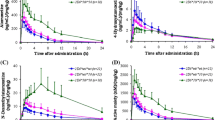
Objectives: To address the relevance of cytochrome P-450 (CYP) 2C19 polymorphism for the pharmacokinetics and dynamics of selegiline and its two known primary metabolites, desmethylselegiline and l-methamphetamine. Methods: Six extensive (mephenytoin S/R ratio <0.3; EM) and six poor (mephenytoin S/R ratio >0.8; PM) hydroxylators of S-mephenytoin ingested a single 10-mg oral dose of selegiline hydrochloride. Serum concentrations of selegiline, desmethylselegiline and l-methamphetamine were measured by gas chromatography – mass spectrometry for up to 48 h. In addition, the platelet monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) activity was measured for 14 days to describe possible differences in the pharmacodynamics of selegiline and its metabolites between EM and PM. Results: The CYP2C19 phenotype had no significant effects on the pharmacokinetic variables of selegiline. PM of S-mephenytoin had 68% higher mean AUC of desmethylselegiline (P=0.0017) than EM, but no significant differences were observed in other pharmacokinetic parameters of desmethylselegiline. Contrary to desmethylselegiline, the serum l-methamphetamine concentrations were slightly lower in PM, but no statistically significant differences were observed in l-methamphetamine pharmacokinetics between the two CYP2C19 phenotypes. Accordingly, the magnitude of MAO-B inhibition showed no significant differences between the study groups. Conclusions: CYP2C19 polymorphism does not seem to be crucial for the metabolism or clinical effects of selegiline.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted in revised form: 12 February 2001
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laine, K., Anttila, M., Nyman, L. et al. CYP2C19 polymorphism is not important for the in vivo metabolism of selegiline. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 57, 137–142 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280100289
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002280100289