Abstract.
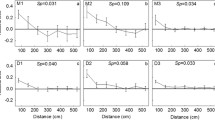
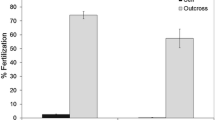
This study examined the occurrence and effects of inbreeding in the sessile, colonial hermaphrodite Celleporella hyalina. The results are discussed with regard to theoretical explanations for the prevalence of hermaphroditism in sessile clonal organisms. C. hyalina exhibited inbreeding depression at all stages, including the pre-zygotic. Outcrossing, sib and half-sib matings produced offspring but selfing did not. There was inbreeding depression in embryo production and survival. Inbred colonies showed slower growth and later maturation, with fewer reproductive zooids. The relative numbers of male and female zooids were affected by inbreeding; increased production of males is a sign of stress in C. hyalina. When mated with an outbred non-relative, inbred colonies had lower success both as males and as females in embryo production and offspring survivorship. The low survivorship of embryos fathered by inbred colonies is a clear effect of inbreeding on the F2 generation. These results indicate that C. hyalina is unlikely to inbreed in the wild, supporting the "space-limited" model of hermaphroditism for this species. This study indicates that hermaphroditism, by avoiding much of the cost of sex, can confer optimal reproductive fitness for sessile brooding animals in a space-limited habitat even in the absence of inbreeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoare, .K., Hughes, .R. Inbreeding and hermaphroditism in the sessile-brooding bryozoan Celleporella hyalina. Marine Biology 139, 147–162 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270100566
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270100566