Abstract
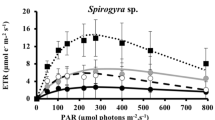
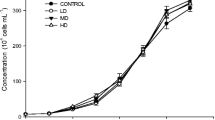
Due to depletion of stratospheric ozone over polar regions of the Northern and Southern Hemispheres UV-B-radiation has increased at the surface of the earth. Measurements of variable chlorophyll fluorescence were conducted to document UV-induced photoinhibition of photosystem II in cultivated macroalgae with different depth distributions in Antarctica. The reactions during artificial UV-exposure were observed on a short time scale (hours) and in light–dark cycles over several days. The nine species of investigated macroalgae show great differences in UV-tolerance of the photosynthetic process. Photosynthesis of the studied green algae was inhibited to a minor degree, while the brown algae showed an intermediate inhibition of photosynthesis. The response of the studied red algae varied with species. The differences in the degree of inhibition and recovery of photosynthetic efficiency and capacity indicate that UV-radiation is one important factor affecting the vertical distribution of macroalgae in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 December 1997 / Accepted: 27 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bischof, K., Hanelt, D. & Wiencke, C. UV-radiation can affect depth-zonation of Antarctic macroalgae. Marine Biology 131, 597–605 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050351
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050351