Abstract
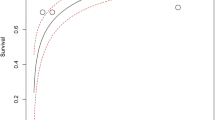
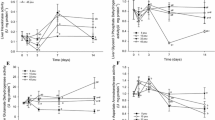
Juvenile lesser blue crabs, Callinectes similis Williams, were exposed to a range of salinities for measurement of survival and bioenergetics. Effects of salinity on survival were determined by exposing juvenile crabs to salinity treatments ranging from 0 to 74‰. All crabs survived 21 d of exposure to 5 and 45‰S. The 21 d LC50 values for salinity tolerance (calculated from survival data) were 2.6 and 60.8‰S at low and high salinities, respectively. Energy-budget components and scope for growth were determined for crabs exposed to 2.5, 10, 25, 35 and 50‰S. Energetic absorption rates were highest at 2.5 and 35‰S. Energetic expenditure rates (energy lost to respiration and excretion) were greatest at 2.5‰S, and decreased as salinity increased. Respiration constituted the majority of energetic expenditure at all salinities (92.3% average). Scope for growth was significantly affected by salinity and was highest in crabs exposed to 35‰S. Increased respiration at low salinity may indicate that C. similis incurs greater costs due to osmoregulation. The results of this study indicate that C. similis is capable of surviving and growing in waters with salinities as low as 10‰.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 January 1997 / Accepted: 11 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerin, J., Stickle, W. Effect of salinity on survival and bioenergetics of juvenile lesser blue crabs, Callinectes similis . Marine Biology 129, 63–69 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050146
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050146