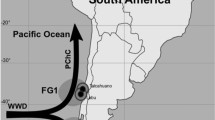
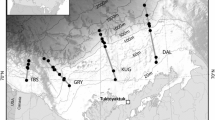
Abstract
Understanding the trophic ecology of deep-sea communities provides valuable insight into deep-water ecosystem functioning, and can help inform fisheries management and conservation initiatives. However, few deep-sea food webs have been studied so far in the Northwest Atlantic. Here, stable isotope, gut content, and morphometric analyses were combined to explore trophic relationships in a deep-water fish assemblage off eastern Canada. While a weak depth effect was found on the isotopic composition of the species analyzed, isotopic and dietary records revealed the existence of two main, strongly coupled trophic pathways. The pelagic pathway either comprised pelagic fishes (e.g., meso- and bathypelagic species), primarily feeding on zooplankton and fish, or benthopelagic predators that showed a more pelagic-oriented diet. Such fishes displayed the lowest values of stable N and C isotope ratios. In contrast, demersal fishes representing the benthic trophic pathway had significantly higher values of δ15N and δ13C, and a taxonomically more benthic-oriented and diverse diet. Furthermore, smaller body sizes, larger mouths, and adaptations (e.g., bioluminescent structures and lures) prevailed in the pelagic species, consistent with living in a relatively food-poor environment. The largest average body sizes were found in the demersal fishes suggesting enhanced food intake and growth investment for the species. Only juvenile individuals of threatened species, such as Coryphaenoides rupestris and Rajella fyllae were caught, providing evidence of the vulnerability of such species to commercial fishing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altabet MA, Pilskaln CP, Thunell R, Pride C, Sigman D, Chavez F, Francois R (1999) The nitrogen isotope biogeochemistry of sinking particles from the margin of the Eastern North Pacific. Deep Sea Res I 46(4):655–679. doi:10.1016/S0967-0637(98)00084-3
Badalamenti F, D’Anna G, Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC (2002) Size-related trophodynamic changes in three target fish species recovering from intensive trawling. Mar Biol 141:561–570. doi:10.1007/s00227-002-0844-3
Bailey DM, King NJ, Priede IG (2007) Cameras and carcasses: historical and current methods for using artificial food falls to study deep-water animals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 350:179–191
Bailey DM, Collins MA, Gordon JDM, Zuur AF, Priede IG (2009) Long-term changes in deep-water fish populations in the Northeast Atlantic: a deeper reaching effect of fisheries? Proc R Soc B 276:1965–1969. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0098
Baillon S, Hamel J-F, Wareham VE, Mercier A (2012) Deep cold-water corals as nurseries for fish larvae. Front Ecol Environ 10(7):351–356. doi:10.1890/120022
Baillon S, Hamel J-F, Mercier A (2014) Diversity, distribution and nature of faunal associations with deep-sea pennatulacean corals in the Northwest Atlantic. PLoS One 9:e111519. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111519
Baker KD, Devine JA, Haedrich RL (2009) Deep-sea fishes in Canada’s Atlantic: population declines and predicted recovery times. Environ Biol Fish 85:79–88. doi:10.1007/s10641-009-9465-8
Baker KD, Haedrich RL, Snelgrove PVR, Wareham VE, Edinger EN, Gilkinson KD (2012) Small-scale patterns of deep-sea fish distributions and assemblages of the Grand Banks, Newfoundland continental slope. Deep Sea Res I 65:171–188. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2012.03.012
Baker R, Buckland A, Sheaves M (2014) Fish gut content analysis: robust measures of diet composition. Fish Fish 15(1):170–177. doi:10.1111/faf.12026
Bergmann M, Dannheim J, Bauerfeind E, Klages M (2009) Trophic relationships along a bathymetric gradient at the deep-sea observatory HAUSGARTEN. Deep Sea Res I 56(3):408–424. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2008.10.004
Bowering WR, Lilly GR (1992) Greenland halibut (Reinhardtius hippoglossoides) off southern Labrador and northeastern Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic) feed primarily on capelin (Mallotus villosus). Neth J Sea Res 29(1–2):211–222. doi:10.1016/0077-7579(92)90021-6
Cabana G, Rasmussen JB (1996) Comparison of aquatic food chain using nitrogen isotopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(20):10844–10847
Campbell N, Neat F, Burns F, Kunzlik P (2011) Species richness, taxonomic diversity, and taxonomic distinctness of the deep-water demersal fish community on the Northeast Atlantic continental slope (ICES Subdivision VIa). ICES J Mar Sci 68(2):365–376. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsq070
Churchill DA, Heithaus MR, Vaudo JJ, Grubbs RD, Gastrich K, Castro JI (2015) Trophic interactions of common elasmobranchs in deep-sea communities of the Gulf of Mexico revealed through stable isotope and stomach content analysis. Deep Sea Res II 115:92–102. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.10.011
Clarke MW, Kelly CJ, Connolly PL, Molloy JP (2003) A life history approach to the assessment and management of deepwater fisheries in the Northeast Atlantic. J Northwest Atl Fish Sci 31:401–411
Clarke J, Milligan RJ, Bailey DM, Neat FC (2015) A scientific basis for regulating deep-sea fishing by depth. Curr Biol 25:2425–2429. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2015.07.070
Coad BW, Reist JD (2004) Annotated list of the Arctic marine fishes of Canada. Can Manuscr Rep Fish Aquat Sci 2674:112
Conley WJ, Hopkins TL (2004) Feeding ecology of lanternfish (Pisces: Myctophidae) larvae: prey preferences as a reflection of morphology. Bull Mar Sci 75(3):361–379
COSEWIC (Committee on the Status of Endangered Wildlife in Canada) (2016) Canadian species at risk. https://www.registrelep-sararegistry.gc.ca/sar/assessment/status_e.cfm. Accessed Mar 2017
Devine JA, Baker KD, Haedrich RL (2006) Fisheries: deep-sea fishes qualify as endangered. Nature 439:29. doi:10.1038/439029a
Drazen JC, Haedrich RL (2012) A continuum of life histories in deep-sea demersal fishes. Deep Sea Res I 61:34–42. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2011.11.002
Drazen JC, Sutton TT (2017) Dining in the deep: the feeding ecology of deep-sea fishes. Annu Rev Mar Sci 9:337–366. doi:10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060543
Drazen JC, Popp BN, Choy AC, Clemente T, De Forest L, Smith KL Jr (2008) Bypassing the abyssal benthic food web: macrourid diet in the eastern North Pacific inferred from stomach content and stable isotope analyses. Limnol Oceanogr 53(6):2644–2654. doi:10.4319/lo.2008.53.6.2644
Ebeling AW, Cailliet GM (1974) Mouth size and predator strategy of midwater fishes. Deep Sea Res Oceanogr Abstr 21(11):959–968. doi:10.1016/0011-7471(74)90028-X
Eliassen J-E, Jobling M (1985) Food of the roughhead grenadier, Macrourus berglax, Lacepede in North Norwegian waters. J Fish Biol 26(3):367–376. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1985.tb04276.x
Froese R, Pauly D (2016) FishBase. http://www.fishbase.org. Accessed Mar 2017
Gale KSP, Hamel J-F, Mercier A (2013) Trophic ecology of deep-sea Asteroidea (Echinodermata) from eastern Canada. Deep Sea Res I 80:25–36. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2013.05.016
Galván DE, Sweeting CJ, Reid WDK (2010) Power of stable isotope techniques to detect size-based feeding in marine fishes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 407:271–278. doi:10.3354/meps08528
Gartner JV Jr, Crabtree RE, Sulak KJ (1997) Feeding at depth. In: Randall DJ, Farrell AP (eds) Deep sea fishes. Academic Press, New York, pp 115–194
Gerringer ME, Popp BN, Linley TD, Jamieson AJ, Drazen JC (2017) Comparative feeding ecology of abyssal and hadal fishes through stomach content and amino acid isotope analysis. Deep Sea Res II 121:110–120. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2017.01.003
Godbold JA, Bailey DM, Collins MA, Gordon JDM, Spallek WA, Priede IG (2013) Putative fishery-induced changes in biomass and population size structures of demersal deep-sea fishes in ICES Sub-area VII, Northeast Atlantic Ocean. Biogeosciences 10:529. doi:10.5194/bg-10-529-2013
Gonzáles C, Román E, Paz X, Ceballos E (2006) Feeding habits and diet overlap of skates (Amblyraja radiata, A. hyperborea, Bathyraja spinicauda, Malacoraja senta and Rajella fyllae) in the North Atlantic. Report, NAFO SCR Doc 06/53, Ser N5285
Gordon JDM, Mauchline J (1996) The distribution and diet of the dominant, slope-dwelling eel, Synaphobranchus kaupi, of the Rockall Trough. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 76(2):493–503. doi:10.1017/S0025315400030691
Haedrich RL (1996) Deep-water fishes: evolution and adaptation in the earth’s largest living spaces. J Fish Biol 49:40–53. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1996.tb06066.x
Hoffman JC, Sutton TT (2010) Lipid correction for carbon stable isotope analysis of deep-sea fishes. Deep Sea Res I 57(8):956–964. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2010.05.003
Hulley P (2015) Alepocephalus bairdii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T15147740A15147743. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T15147740A15147743.en. Accessed Mar 2017
Hussey NE, MacNeil MA, Olin JA, McMeans BC, Kinney MJ, Chapman DD, Fisk AT (2012) Stable isotopes and elasmobranchs: tissue types, methods, applications and assumptions. J Fish Biol 80(5):1449–1484. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2012.03251.x
Hussey NE, Macneil MA, McMeans BC, Olin JA, Dudley SFJ, Cliff G, Wintner SP, Fennessy ST, Fisk AT (2014) Rescaling the trophic structure of marine food webs. Ecol Lett 17(2):239–250. doi:10.1111/ele.12226
Hynes HBN (1950) The food of fresh-water sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus and Pygosteus pungitius), with a review of methods used in studies of the food of fishes. J Anim Ecol 19:36–58
Iken K, Brey T, Wand U, Voigt J, Junghans P (2001) Food web structure of the benthic community at the Porcupine Abyssal Plain (NE Atlantic): a stable isotope analysis. Prog Oceanogr 50:383–405. doi:10.1016/S0079-6611(01)00062-3
Iken K, Bluhm BA, Gradinger R (2005) Food web structure in the high Arctic Canada Basin: evidence from δ13C and δ15N analysis. Polar Biol 28(3):238–249. doi:10.1007/s00300-004-0669-2
Iwamoto T (2015) Coryphaenoides rupestris. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2015: e.T15522149A15603540. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T15522149A15603540.en. Accessed Mar 2017
Kim SL, Koch PL (2012) Methods to collect, preserve, and prepare elasmobranch tissues for stable isotope analysis. Environ Biol Fish 95(1):53–63. doi:10.1007/s10641-011-9860-9
Kulka DW, Barker AS, Orlov A, Pasolini P (2009) Rajella fyllae. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2009: e.T161587A5458368. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009-2.RLTS.T161587A5458368.en. Accessed Mar 2017
Layman CA, Albrey Arrington D, Montana CG, Post DM (2007) Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88(1):42–48
Mauchline J, Gordon JDM (1983) Diets of clupeoid, stomiatoid and salmonoid fish of the Rockall Trough, northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Mar Biol 77(1):67–78. doi:10.1007/BF00393211
Mauchline J, Gordon JDM (1984a) Occurrence and feeding of berycomorphid and percomorphid teleost fish in the Rockall Trough. ICES J Mar Sci 41(3):239–247. doi:10.1093/icesjms/41.3.239
Mauchline J, Gordon JDM (1984b) Diets and bathymetric distributions of the macrourid fish of the Rockall Trough, northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Mar Biol 81(2):107–121. doi:10.1007/BF00393109
Mauchline J, Gordon JDM (1985) Trophic diversity in deep-sea fish. J Fish Biol 26(5):527–535. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1985.tb04293.x
McConnaughey T, McRoy CP (1979) Food-web structure and the fractionation of carbon isotopes in the Bering sea. Mar Biol 53:257–262. doi:10.1007/BF00952434
Minagawa M, Wada E (1984) Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: further evidence and the relation between δ15N and animal age. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48(5):1135–1140
Mindel BL, Webb TJ, Neat FC, Blanchard JL (2015) A trait-based metric sheds new light on the nature of the body size–depth relationship in the deep-sea. J Anim Ecol 85(2):427–436. doi:10.1111/1365-2656.12471
Mindel BL, Neat FC, Trueman CN, Webb TJ, Blanchard JL (2016) Functional, size and taxonomic diversity of fish along a depth gradient in the deep sea. PeerJ 4:e2387. doi:10.7717/peerj.2387
Mintenbeck K, Jacob U, Knust R, Arntz WE, Brey T (2007) Depth-dependence in stable isotope ratio δ15N of benthic POM consumers: the role of particle dynamics and organism trophic guild. Deep Sea Res I 54(6):1015–1023. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2007.03.005
Murillo FJ, Muñoz PD, Altuna A, Serrano A (2011) Distribution of deep-water corals of the Flemish Cap, Flemish Pass, and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic Ocean): interaction with fishing activities. ICES J Mar Sci 68(2):319–332. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsq071
Murillo FJ, Muñoz PD, Cristobo J, Ríos P, González C, Kenchington E, Serrano A (2012) Deep-sea sponge grounds of the Flemish Cap, Flemish Pass and the Grand Banks of Newfoundland (Northwest Atlantic Ocean): distribution and species composition. Mar Biol Res 8:842–854. doi:10.1080/17451000.2012.682583
Polunin NVC, Morales-Nin B, Pawsey WE, Cartes JE, Pinnegar JK, Moranta J (2001) Feeding relationships elucidated by stable nitrogen and carbon isotope data. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 220:13–23. doi:10.3354/meps220013
Post DM, Layman CA, Albrey Arrington D, Takimoto G, Quattrochi J, Montaña CG (2007) Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia 152:179–189. doi:10.1007/s00442-006-0630-x
Reece JS, Metha RS (2013) Evolutionary history of elongation and maximum body length in moray eels (Anguilliformes: Murenidae). Biol J Linn Soc 109(4):861–875. doi:10.1111/bij.12098
Reid WDK, Wigham BD, McGill RAR, Polunin NVC (2012) Elucidating trophic pathways in benthic deep-sea assemblages of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge north and south of the Charlie–Gibbs Fracture Zone. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 463:89–103. doi:10.3354/meps09863
Reid WDK, Sweeting CJ, Wigham BD, McGill RAR, Polunin NVC (2013) High variability in spatial and temporal size-based trophodynamics of deep-sea fishes from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge elucidated by stable isotopes. Deep Sea Res II 98:412–420. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.01.020
Reiner F (1996) Catálogo dos peixes do arquipélago de Cabo Verde. Instituto Português de Investigação Marítima, Publicações Avulsas do IPIMAR, Lisbon, p 339
Ribeiro MDO, Barreto Teresa F, Casatti L (2016) Use of functional traits to assess changes in stream fish assemblages across a habitat gradient. Neotrop Ichthyol 14:e140185. doi:10.1590/1982-0224-20140185
Rombouts I, Beaugrand G, Fizzala X, Gaill F, Greenstreet SPR, Lamare S, Le loc’h F, McQuatters-Gollop A, Mialet B, Niquil N (2013) Food web indicators under the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: from complexity to simplicity? Ecol Indic 29:246–254. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.12.021
Scharf FS, Juanes F, Rountree RA (2000) Prey size relationships of marine fish predators: interspecific variation and effects of ontogeny and body size on trophic-niche breadth. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 208:229–248. doi:10.3354/meps208229
Sherwood GD, Rose GA (2005) Stable isotope analysis of some representative fish and invertebrates of the Newfoundland and Labrador continental shelf food web. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 63(4):537–549. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2004.12.010
Sherwood OA, Jamieson RE, Edinger EN, Wareham VE (2008) Stable C and N isotopic composition of cold-water corals from the Newfoundland and Labrador continental slope: examination of trophic, depth and spatial effects. Deep Sea Res I 55(10):1392–1402. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2008.05.013
Smith D, Gordon JDM, Priede IG (2010) Synaphobranchus kaupii. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T155246A4756653. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T155246A4756653.en. Accessed Mar 2017
Snelgrove P, Haedrich R (1985) Structure of the deep demersal fish fauna off Newfoundland. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 27:99–107. doi:10.3354/meps027099
Trueman CN, Johnston G, O’Hea B, MacKenzie KM (2014) Trophic interactions of fish communities at midwater depths enhance long-term carbon storage and benthic production on continental slopes. Proc R Soc B 281:20140669. doi:10.1098/rspb.2014.0669
Valls M, Sweeting CJ, Olivar MP, Fernández de Puelles ML, Pasqual C, Polunin NVC, Quetglas A (2014) Structure and dynamics of food webs in the water column on shelf and slope grounds of the western Mediterranean. J Mar Syst 138:171–181. doi:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.04.002
Walsh SJ, McCallum BR (1997) Performance of the Campelen 1800 shrimp trawl during the 1995 Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Centre autumn groundfish survey. NAFO Sci Coun Stud 29:105–116
Ward AB, Mehta RS (2010) Axial elongation in fishes: using morphological approaches to elucidate developmental mechanisms in studying body shape. Integr Comp Biol 50(6):1106–1119. doi:10.1093/icb/icq029
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) Discovery Grant (Grant no. 311406 to A. Mercier and 105379 to C.C. Parrish) and Canada Foundation for Innovation (CFI) Leaders Opportunity Fund (Grant no. 11231 to A. Mercier). The authors also want to thank the associate editor C. Harrod and the reviewers for their insightful comments and great contributions to this manuscript; the DFO staff, in particular D. Stansbury, K. Tipple, D. Pittman, V.E. Wareham, and M. Koen-Alonso for help with logistics and species identification; E. Montgomery for sample collection; A. Pye, J. Wells, U. Tilves, N. Ӧzdemír, K.S.P. Gale, L. Cárreon-Palau, R. Belley, and J. Ammendolia for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors, CP, CCP, J-FH, AM, have approved the manuscript submitted and declared they have no conflicts of interest in regard to this work.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: C. Harrod.
Reviewed by C. Trueman and an undisclosed expert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parzanini, C., Parrish, C.C., Hamel, JF. et al. Trophic ecology of a deep-sea fish assemblage in the Northwest Atlantic. Mar Biol 164, 206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3236-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3236-4