Abstract
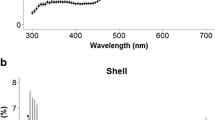
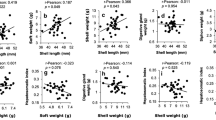
Food sources of the European abalone Haliotis tuberculata throughout its life cycle are still to be clarified in nature. A novel non-destructive method of digital shell color analysis to reveal the diets of European abalone (ormer) was developed in this study. The method was calibrated using ormers reared under experimental conditions in North Western Brittany in 2012 and fed a controlled monospecific diet to define the shell hues associated with various macroalgae (i.e., Rhodophyta, Chlorophyta, and Phaeophyta). General food preferences were established by comparing the shell hue of wild adult ormers and experimental adult ormers. Shell hue corresponds to the color tint in the HSL color space measured on digital pictures of the shell. Experimentally, shell hue values differed according to treatment, with the most yellow-green hue (72°) for ormers fed Saccharina sp. and the coral hue (25°) for ormers fed Palmaria palmata. High variation in shell color of wild ormers was observed according to the sampling site and/or ontogeny. The diet of wild ormers may be related to the abundance of different drifting algae in their respective habitats. Thus, this non-destructive and easy-to-use technique appears to be a promising tool for determining the diet of Haliotis species and, perhaps, other herbivorous mollusks.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin J, Elias JP, Wells RMG, Donovan DA (2007) Energy metabolism in the tropical abalone, Haliotis asinina Linné: comparisons with temperate abalone species. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 342:213–225. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2006.09.005
Barnard W, De Waal D (2006) Raman investigation of pigmentary molecules in the molluscan biogenic matrix. J Raman Spectrosc 37:342–352. doi:10.1002/jrs.1461
Bianchi TS, Kautsky L, Argyrou M (1997) Dominant chlorophylls and carotenoids in macroalgae of the Baltic Sea (Baltic proper): their use as potential biomarkers. Sarsia 82:55–62
Budd A, McDougall C, Green K, Degnan BM (2014) Control of shell pigmentation by secretory tubules in the abalone mantle. Front Zool 11:62. doi:10.1186/s12983-014-0062-0
Caron L, Douady D, De Martino A, Quinet M (2001) Light harvesting in brown algae. Cah Biol 42:109–124
Caut S, Angulo E, Courchamp F (2009) Variation in discrimination factors (δ15N and δ13C): the effect of diet isotopic values and applications for diet reconstruction. J Appl Ecol 46:443–453. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2009.01620.x
Chauvaud L, Lorrain A, Dunbar RB, et al (2005) Shell of the Great Scallop Pecten maximus as a high-frequency archive of paleoenvironmental changes. Geochem Geophys Geosystems 6:1–15. doi:10.1029/2004GC000890
Chauvaud L, Thébault J, Clavier J, et al (2011) What’s hiding behind ontogenetic δ13C variations in mollusk shells? New insights from the Great Scallop (Pecten maximus). Estuaries Coasts 34:211–220. doi:10.1007/s12237-010-9267-4
Cheng H-D, Jiang XH, Sun Y, Wang J (2001) Color image segmentation: advances and prospects. Pattern Recognit 34:2259–2281. doi:10.1016/S0031-3203(00)00149-7
Clavier J, Richard O (1982) Etude expérimentale du déplacement de l’ormeau (Haliotis tuberculata) dans le milieu naturel. Rev Trav Inst Pêch Marit 46:315–326.
Clavier J, Richard O (1986) Growth of juvenile Haliotis tuberculata (Mollusca: Gastropoda) in their natural environment. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 66:497–503
Comfort A (1951) The pigmentation of molluscan shells. Biol Rev 26:285–301
Day RW, Cook P (1995) Bias towards brown algae in determining diet and food preferences: the South African abalone Haliotis midae. Mar Freshw Res 46:623–627. doi:10.1071/MF9950623
de Oliveira LN, de Oliveira VE, D’ávila S et al (2013) Raman spectroscopy as a tool for polyunsaturated compound characterization in gastropod and limnic terrestrial shell specimens. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 114:541–546. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2013.05.095
Dethier MN, Sosik E, Galloway AW et al (2013) Addressing assumptions: variation in stable isotopes and fatty acids of marine macrophytes can confound conclusions of food web studies. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 478:1–14. doi:10.3354/meps10310
Emmery A, Lefebvre S, Alunno-Bruscia M, Kooijman S (2011) Understanding the dynamics of δ13C and δ15N in soft tissues of the bivalve Crassostrea gigas facing environmental fluctuations in the context of Dynamic Energy Budgets (DEB). J Sea Res 66:361–371. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2011.08.002
Fox DL (1966) Pigmentation of molluscs. In: Wilbur KM, Yonge CM (eds) Physiology of mollusca. Academic press, New York, pp 249–274
Gallardo WG, Bautista-Teruel MN, Fermin AC, Marte CL (2003) Shell marking by artificial feeding of the tropical abalone Haliotis asinina Linne juveniles for sea ranching and stock enhancement. Aquac Res 34:839–842. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2109.2003.00890.x
Ge J, Li Q, Yu H, Kong L (2015) Mendelian inheritance of golden shell color in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquaculture 441:21–24. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.01.031
Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (2008) Color image processing. In: Gonzalez RC, Woods RE (eds) Digital image processing, 3rd edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey, pp 394–460
Grossman EL, Ku TL (1986) Oxygen and carbon isotope fractionation in biogenic aragonite: temperature effects. Chem Geol Isot Geosci Sect 59:59–74.
Guest MA, Nichols PD, Frusher SD, Hirst AJ (2008) Evidence of abalone (Haliotis rubra) diet from combined fatty acid and stable isotope analyses. Mar Biol 153:579–588. doi:10.1007/s00227-007-0831-9
Hancz C, Magyary I, Molnar T et al (2003) Evaluation of color intensity enhanced by paprika as feed additive in goldfish and koi carp using computer-assisted image analysis. Fish Sci 69:1158–1161.
Hedegaard C, Bardeau J-F, Chateigner D (2006) Molluscan shell pigments: an in situ resonance Raman study. J Molluscan Stud 72:157–162. doi:10.1093/mollus/eyi062
Hoang TH, Qin JG, Stone DA et al (2016) Colour changes of greenlip abalone (Haliotis laevigata Donovan) fed fresh macroalgae and dried algal supplement. Aquaculture 456:16–23. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.01.022
Jackson DJ, McDougall C, Green K et al (2006) A rapidly evolving secretome builds and patterns a sea shell. BMC Biol 4:40. doi:10.1186/1741-7007-4-40
Jeffrey SW, Mantoura RFC, Wright SW (1997) Phytoplankton pigments in oceanography: guidelines to modern methods. UNESCO, Paris
Jolivet A, Chauvaud L, Huchette S et al (2015) The ormer (Haliotis tuberculata): A new, promising paleoclimatic tool. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 427:32–40. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.03.032
Karcher DE, Richardson MD (2003) Quantifying turfgrass color using digital image analysis. Crop Sci 43:943–951
Kawamura T, Takami H (1995) Analysis of feeding and growth rate of newly metamorphosed abalone Haliotis discus hannai fed on four species of benthic diatom. Fish Sci 61:357–358.
Kawamura T, Roberts RD, Takami H (1998) A review of the feeding and growth of postlarval abalone. J Shellfish Res 17:615–625
Koike Y (1978) Biological and ecological studies on the propagation of the ormer, Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus. I. Larval development and growth of juveniles. La mer 16:124–136
Leighton DL (1961) Observations of the effect of diet on shell coloration in the red abalone, Haliotis rufescens Swainson. Veliger 4:29–32.
Leighton D, Boolootian RA (1963) Diet and growth in the black abalone, Haliotis cracerodii. Ecology 44:228–238
Lindberg DR, Pearse JS (1990) Experimental manipulation of shell color and morphology of the limpets Lottia asmi (Middendorff) and Lottia digitalis (Rathke)(Mollusca: Patellogastropoda). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 140:173–185
Liu X, Wu F, Zhao H et al (2009) A novel shell color variant of the Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino subject to genetic control and dietary influence. J Shellfish Res 28:419–424. doi:10.2983/035.028.0226
Mai K, Mercer JP, Donlon J (1996) Comparative studies on the nutrition of two species of abalone, Haliotis tuberculata L. and Haliotis discus hannai Ino. V. The role of polyunsaturated fatty acids of macroalgae in abalone nutrition. Aquaculture 139:77–89. doi:10.1016/0044-8486(95)01158-7
Manríquez PH, Lagos NA, Jara ME, Castilla JC (2009) Adaptive shell color plasticity during the early ontogeny of an intertidal keystone snail. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:16298–16303. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908655106
Maoka T (2011) Carotenoids in marine animals. Mar Drugs 9:278–293. doi:10.3390/md9020278
Marchais V, Richard J, Jolivet A et al (2015) Coupling experimental and field-based approaches to decipher carbon sources in the shell of the great scallop, Pecten maximus (L.). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 168:58–69. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2015.07.010
Matile P, Hörtensteiner S, Thomas H (1999) Chlorophyll degradation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50:67–95. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.67
McShane PE, Gorfine H, Knuckey I (1994) Factors influencing food selection in the abalone Haliotis rubra (Mollusca: Gastropoda). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 176:27–37
Mercer JP, Mai K-S, Donlon J (1993) Comparative studies on the nutrition of two species of abalone, Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus and Haliotis discus hannai Ino I. Effects of algal diets on growth and biochemical composition. Invertebr Reprod Dev 23:75–88. doi:10.1080/07924259.1993.9672298
Mgaya YD (1995) Synopsis of biological data on the European abalone (ormer), Haliotis tuberculata Linnaeus, 1758 (Gastropoda: Haliotidae). Food and agriculture organisation of the United Nations, Rome
Moss B (1968) Studies on the degradation of chlorophyll a and carotenoids in freshwaters. New Phytol 67:49–59. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1968.tb05453.x
Nakamura K, Archdale MV (2001) Activity patterns of abalone under experimental conditions. Aquac Res 32:169–179. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2109.2001.00537.x
Nash CE (1991) The production of abalone. In: Nash CE (ed) Production of aquatic animals: crustaceans, molluscs, amphibians and reptiles. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 173–181
Neitz J, Jacobs GH (1986) Polymorphism of the long-wavelength cone in normal human colour vision. Nature 323:623–625. doi:10.1038/323623a0
Olsen DA (1968a) Banding patterns in Haliotis rufescens. II. Some behavioral considerations and the effect of diet on shell coloration for Haliotis rufescens, Haliotis corrugata, Haliotis sorenseni, and Haliotis assimilis. Veliger 11:135–139.
Olsen DA (1968b) Banding patterns of Haliotis rufescens as indicators of botanical and animal succession. Biol Bull 11:139–147
Onitsuka T, Kawamura T, Ohashi S et al (2004) Morphological changes in the radula of abalone Haliotis diversicolor aquatilis from post-larva to adult. J Shellfish Res 23:1079–1086
R Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Raven JA, Johnston AM, Kübler JE et al (2002) Mechanistic interpretation of carbon isotope discrimination by marine macroalgae and seagrasses. Funct Plant Biol 29:355–378. doi:10.1071/PP01201
Roussel S, Huchette S, Clavier J, Chauvaud L (2011) Growth of the European abalone (Haliotis tuberculata L.) in situ: seasonality and ageing using stable oxygen isotopes. J Sea Res 65:213–218. doi:10.1016/j.seares.2010.10.001
Roussel V, Charreyron J, Labarre S et al (2013) First steps on technological and genetic improvement of European abalone (Haliotis tuberculata) based on investigations in full-sib families. Open J Genet 3:224–233. doi:10.4236/ojgen.2013.33025
Shepherd SA (1973) Studies on southern Australian abalone (genus Haliotis). I. Ecology of five sympatric species. Mar Freshw Res 24:217–258. doi:10.1071/MF9730217
Shepherd SA, Steinberg PD (1992) Food preferences of three Australian abalone species with a review of the algal food of abalone. In: Shepherd SA, Tegner MJ, Guzmand del Proo SA (eds) Abalone of the world: biology, fisheries and culture. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 169–181
Shepherd SA, Turner JA (1985) Studies on southern Australian abalone (genus Haliotis). VI. Habitat preference, abundance and predators of juveniles. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 93:285–298. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(85)90245-X
Stemmer K, Nehrke G (2014) The distribution of polyenes in the shell of Arctica islandica from North Atlantic localities: a confocal Raman microscopy study. J Molluscan Stud 80:365–370. doi:10.1093/mollus/eyu033
Stott A, Takeuchi T, Koike Y, et al (2002) Using micro particle diets to replace diatoms for feeding postlarval abalone Haliotis discus discus (Reeve.). Fish Sci 68:1088–1093. doi:10.1046/j.1444-2906.2002.00536.x
Takami H, Kawamura T (2003) Dietary changes in the abalone, Haliotis discus hannai, and relationship with the development of the digestive organ. Jpn Agric Res Q 37:89–98. doi:10.6090/jarq.37.89
Tlusty M (2005) Use of digital colour analysis to assess variation within individual adult American lobsters (Homarus americanus) and the process of addition of colour in white lobsters. N Z J Mar Freshw Res 39:571–580. doi:10.1080/00288330.2005.9517336
Travis D (1991) Effective color displays. Theory and practice. Academic press, London
Tutschulte TC, Connell JH (1988) Feeding behavior and algal food of three species of abalones (Haliotis) in southern California. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 49:57–64
Underwood AJ, Creese RG (1976) Observations on the biology of the trochid gastropod Austrocochlea constricta (Lamarck) (Prosobranchia). II. The effects of available food on shell-banding pattern. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 23:229–240. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(76)90022-8
Vander Zanden MJ, Rasmussen JB (2001) Variation in 15N and 13C trophic fractionation: implications for aquatic food web studies. Limnol Oceanogr 46:2061–2066. doi:10.4319/lo.2001.46.8.2061
Wilbur KM, Saleuddin ASM (1983) Shell Formation. In: Saleuddin ASM, Wilbur KM (eds) The Mollusca. Academic Press, New York, pp 235–287
Winkler FM, Estevez BF, Jollan LB, Garrido JP (2001) Inheritance of the general shell color in the scallop Argopecten purpuratus (Bivalvia: Pectinidae). J Hered 92:521–525. doi:10.1093/jhered/92.6.521
Won N-I, Kawamura T, Takami H et al (2010) Ontogenetic changes in the feeding habits of the abalone Haliotis discus hannai: field verification by stable isotope analyses. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 67:347–356. doi:10.1139/F09-187
Wood AD, Buxton CD (1996) Aspects of the biology of the abalone Haliotis midae (Linne, 1758) on the east coast of South Africa. 1. Feeding biology. South Afr J Mar Sci 17:61–68.
Yue X, Nie Q, Xiao G, Liu B (2015) Transcriptome Analysis of Shell Color-Related Genes in the Clam Meretrix meretrix. Mar Biotechnol 17:364–374. doi:10.1007/s10126-015-9625-0
Acknowledgements
We thank the team at the France Haliotis hatchery and their interns for the care of the animals and assistance during the experiment. Many thanks to all of the people who contributed to sampling macroalgae on foreshore. The authors also thank the scuba divers for sampling wild abalones, and Sylvain Huchette for contributing to this experiment and his feedback. We would like to thank the three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The project was supported by the National Research Agency, French Government, with regard to investment expenditure program PIA-ANR IDEALG BTBR-10-04 and the CHIVAS (ANR-Blanc) program. V. Marchais was supported by a doctoral grant from the Université de Bretagne Occidentale. All applicable international and national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: A.G. Checa.
Reviewed by Undisclosed experts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchais, V., Jolivet, A., Hervé, S. et al. New tool to elucidate the diet of the ormer Haliotis tuberculata (L.): Digital shell color analysis. Mar Biol 164, 71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3103-3