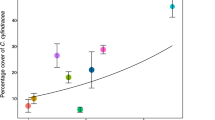
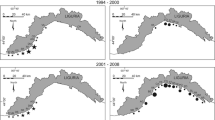
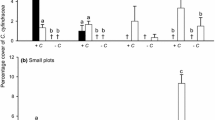
Abstract
The spread of the green macroalga Caulerpa cylindracea is one of the most threatening invasions in the Mediterranean Sea. Many correlative and experimental studies have focused on different aspects of C. cylindracea invasion. This paper aims to evaluate the main factors influencing the spread of this alga through an overview of the results from 47 published papers on this topic; a conceptual model synthesizing the main biotic and abiotic factors that influence C. cylindracea spread was proposed. Mechanical destruction of habitats, enhanced sedimentation rate and nutrients loading directly promote the spread of C. cylindracea. Indirect effects due to factors that foster the spread of turf-forming algae at the expense of canopy-forming species and decrease substrate complexity emerged as an important determinant of the success of C. cylindracea. Ultimately, the spread of C. cylindracea appears to be regulated by a complex net of interactions between abiotic and biotic factors. Our conceptual model represents a general tool for the rapid assessment of the factor underpinning the spread of non-native species, a critical step for the control of non-native species that have successfully established viable populations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airoldi L (2003) The effects of sedimentation on rocky coastal assemblages. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 41:161–203
Airoldi L, Cinelli F (1997) Effect of sedimentation on subtidal macroalgal assemblages: an experimental study from a Mediterranean rocky shore. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 215:271–290
Airoldi L, Balata D, Beck MW (2008) The Gray Zone: relationships between habitat loss and marine diversity and their applications in conservation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 366:8–15
Anderson LW (2007) Control of invasive seaweeds. Bot Mar 50:418–437
Archambault P, Bourget E (1996) Scales of coastal heterogeneity and benthic intertidal species richness, diversity and abundance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 136:111–121
Arenas F, Sánchez I, Hawkins SJ, Jenkins SR (2006) The invisibility of marine algal assemblages: role of functional diversity and identity. Ecology 87:2851–2861
Arevalo R, Pinedo S, Ballesteros E (2007) Changes in the composition and structure of Mediterranean rocky-shore communities following a gradient of nutrient enrichment: descriptive study and test proposed methods to assess water quality regarding macroalgae. Mar Pollut Bull 55:104–113
Balata D, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (2004) A comparison among macroalgal assemblages in areas invaded by Caulerpa taxifolia and C. racemosa on subtidal Mediterranean reefs. P.S.Z.N. Mar Ecol 25:1–13
Balata D, Bulleri F, Piazzi L (2015) Sediment deposition dampens positive effects of substratum complexity on the diversity of macroalgal assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 467:45–51
Ballesteros E (2006) Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages: a synthesis of present knowledge. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 44:123–195
Bavestrello G, Cerrano C, Zanzi D, CattaneoVietti R (1997) Damage by fishing activities in the Gorgonian coral Paramuricea clavata in the Ligurian Sea. Aquat Conserv 7:253–262
Beck MW (2000) Separating the elements of habitat structure: independent effects of habitat complexity and structural components on rocky intertidal gastropods. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 249:29–49
Belton GS, Prud’homme van Reine WF, Huisman JM, Draisma SGA, Gurgel CFD (2014) Resolving Phenotypic Plasticity and species designation in the morphologically challenging Caulerpa racemosa-peltata complex (Caulerpaceae, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 50:32–54
Bernardeau-Esteller J, Ruiz JM, Tomas F, Sandoval-Gil JM, Marín-Guirao L (2015) Photoacclimation of Caulerpa cylindracea: light as a limiting factor in the invasion of native Mediterranean seagrass meadows. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 465:130–141
Bordehore C, Ramos-Espla A, Riosmena-Rodrıguez R (2003) Comparative study of two maerl beds with different otter trawling history, southeast Iberian Peninsula. Aquat Conserv 13:43–54
Bourget E, Harvey M (1998) Spatial analysis of recruitment of marine invertebrates on arborescent substrata. Biofouling 12:45–55
Bourget E, DeGuise J, Daigle G (1994) Scales of substratum heterogeneity, structural complexity and the early establishment of a marine epibenthic community. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 181:31–51
Britton-Simmons K (2006) Functional group diversity, resource pre-emption and the genesis of invasion resistance in a community of marine algae. Oikos 113:395–401
Bulleri F, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2008) Facilitation of the introduced green alga, Caulerpa racemosa, by resident algal turfs: experimental evaluation of underlying mechanisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 364:77–86
Bulleri F, Malquori F (2015) High tolerance to simulated herbivory in the clonal seaweed, Caulerpa cylindracea. Mar Environ Res 107:61–65
Bulleri F, Piazzi L (2015) Variations in importance and intensity of competition underpin context-dependency in the effects of an invasive seaweed on resident assemblages. Mar Biol 162:485–489
Bulleri F, Tamburello L, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2009) Loss of consumers alters the effects of resident assemblages on the local spread of an introduced macroalga. Oikos 118:269–279
Bulleri F, Balata D, Bertocci I, Tamburello L, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2010) The seaweed Caulerpa racemosa on Mediterranean rocky reefs: from passenger to driver of ecological changes. Ecology 91:2205–2212
Bulleri F, Alestra T, Ceccherelli G, Tamburello L, Pinna S, Sechi N, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2011) Determinants of Caulerpa racemosa distribution in the north-western Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 431:55–67
Bulleri F, Benedetti-Cecchi L, Jaklin A, Ivesa L (2016) Linking disturbance and resistance to invasion via changes in biodiversity: a conceptual model and an experimental test on rocky reefs. Ecol Evol 6:2010–2021
Capiomont A, Breugnot E, Den Haan M, Meinesz A (2005) Phenology of a deep-water population of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Bot Mar 48:80–83
Caronni S, Calabretti C, Delaria MA, Bernardi G, Navone A, Occhipinti-Ambrogi A, Panzalis P, Ceccherelli G (2015) Consumer depletion alters seagrass resistance to an invasive macroalga. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0115858
Cebrian E, Ballesteros E, Linares C, Tomas F (2011) Do native herbivores provide resistance to Mediterranean marine bioinvasions? a seaweed example. Biol Invasion 13:1397–1408
Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (1997) Short-term effects of nutrient enrichment of the sediment and interactions between the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa and the introduced green alga Caulerpa taxifolia in a Mediterranean bay. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 217:165–177
Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (1999) The role of vegetative spreading in dispersal of the invasive alga Caulerpa taxifolia in the Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 182:299–303
Ceccherelli G, Piazzi L (2001) Dispersal of Caulerpa racemosa fragments in the Mediterranean: lack of detachment time effect on establishment. Bot Mar 44:209–213
Ceccherelli G, Piazzi L (2005) Exploring the success of manual eradication of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta): the effect of habitat. Cryptogam Algol 26:319–328
Ceccherelli G, Piazzi L, Cinelli F (2000) Response of the non-indigenous Caulerpa racemosa (Forsskal) J. Agardh to the native seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile: effect of density of shoots and orientation of edges of meadows. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 243:227–240
Ceccherelli G, Piazzi L, Balata D (2002) Spread of introduced Caulerpa species in macroalgal habitats. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 280:1–11
Ceccherelli G, Campo D, Milazzo M (2007) Short-term response of the slow growing seagrass Posidonia oceanica to simulated anchor impact. Mar Environ Res 63:341–349
Ceccherelli G, Pinna S, Cusseddu V, Bulleri F (2014) The role of disturbance in promoting the spread of the invasive seaweed Caulerpa racemosa in seagrass meadows. Biol Invasion 16:2737–2745
Chisholm JRM, Dauga C, Ageron E, Grimont PAD, Jaubert JM (1996) ‘Roots’ in mixotrophic algae. Nature 381:382
Delgado O, Rodriguez-Prieto C, Gacia E, Ballesteros E (1996) Lack of severe nutrient limitation in Caulerpa taxifolia (Vahl) C. Agardh, an introduced seaweed spreading over the oligotrophic northwestern Mediterranean. Bot Mar 39:61–67
Didham RK, Tylianakis JM, Hutchison MA, Ewers RM, Gemmell NJ (2005) Are invasive species the drivers of ecological change? Trends Ecol Evol 20:470–474
Dukes JS, Mooney HA (1999) Does global change increase the success of biological invaders? Trends Ecol Evol 14:135–139
Dunstan PK, Johnson CR (2007) Mechanisms of invasions: can the recipient community influence invasion rates? Bot Mar 50:361–372
Foster MS (2001) Rhodoliths: between rocks and soft places. J Phycol 37:659–667
Gennaro P, Piazzi L (2011) Synergism between two anthropic impacts: invasion of macroalga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea and seawater nutrient enrichment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 427:59–70
Gennaro P, Piazzi L (2014) The indirect role of nutrients in enhancing the invasion of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Biol Invasion 16:1709–1717
Gennaro P, Piazzi L, Persia E, Porrello S (2015) Nutrients exploitation and competition strategies of the invasive seaweed Caulerpa cylindracea. Eur J Phycol 50:384–394
Giakoumi S, Cebrian E, Kokkoris GD, Ballesteros E, Sala E (2012) Relationships between fish, sea urchins and macroalgae: the structure of shallow rocky sublittoral communities in the Cyclades, Eastern Mediterranean. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 109:1–10
Gianguzza P, Agnetta D, Bonaviri C, Di Trapani F, Visconti G, Gianguzza F, Riggio S (2011) The rise of thermophilic sea urchins and the expansion of barren grounds in the Mediterranean Sea. Chem Ecol 27:129–134
Gollasch S (2007) International collaboration on marine bioinvasions: the ICES response. Mar Pollut Bull 55:353–359
Gonzalez-Correa JM, Baylea JT, Jose T, Sanchez-Lizaso L, Vallea C, Sanchez-Jereza P, Ruiz JM (2005) Recovery of deep Posidonia oceanica meadows degraded by trawling. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 320:65–76
Gorgula SK, Connell SD (2004) Expansive covers of turf-forming algae on human-dominated coast: the relative effects of increasing nutrient and sediment loads. Mar Biol 145:613–619
Gorman D, Russell BD, Connell SD (2009) Land-to-sea connectivity: linking human-derived terrestrial subsidies to subtidal habitat change on open rocky coasts. Ecol Appl 19:1114–1126
Gosselin LA, Bourget E (1989) The performance of an intertidal predator Thais lapillus in relation to structural heterogeneity. J Anim Ecol 58:287–303
Guidetti P, Dulcic J (2007) Relationships among predatory fish, sea urchins and barrens in Mediterranean rocky reefs across a latitudinal gradient. Mar Environ Res 63:168–184
Harris LG, Tyrrell MC (2001) Changing community states in the Gulf of Maine: synergism between invaders, over-fishing and climate change. Biol Invasion 3:9–21
Hewitt CL, Campbell ML (2007) Mechanisms for the prevention of marine bioinvasions for better biosecurity. Mar Pollut Bull 55:395–401
Holon F, Mouquet N, Boissery P, Bouchoucha M, Delaruelle G, Tribot A-S, Deter J (2015) Fine-scale cartography of human impacts along French Mediterranean coasts: a relevant map for the management of marine ecosystems. PLoS One 10(8):e0135473. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0135473
Incera M, Bertocci I, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2010) Effects of mean intensity and temporal variability of disturbance on the invasion of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales) in rock pools. Biol Invasion 12:501–514
Infantes E, Terrados J, Orfila A (2011) Assessment of substratum effect on the distribution of two invasive Caulerpa (Chlorophyta) species. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 91:434–444
Irving AD, Connell SD (2002) Interactive effects of sedimentation and microtopography on the abundance of subtidal turf-forming algae. Phycologia 41:517–522
Irving AD, Connell SD (2006) Physical disturbance by kelp abrades erect algae from the understorey. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 324:127–137
Ivesa L, Djakovac T, Devescovi M (2015) Spreading patterns of the invasive Caulerpa cylindracea Sonder along the west Istrian Coast (northern Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Mar Environ Res 107:1–7
Katsanevakis S, Issaris Y, Poursanidis D, Thessalou-Legaki M (2010) Vulnerability of marine habitats to the invasive green alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea within a marine protected area. Mar Environ Res 70:210–218
Klein J, Verlaque M (2008) The Caulerpa racemosa invasion: a critical review. Mar Pollut Bull 56:205–225
Klein JC, Verlaque M (2009) Macroalgal assemblages of disturbed coastal detritic bottoms subject to invasive species. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:461–468
Klein JC, Verlaque M (2011) Experimental removal of the invasive Caulerpa racemosa triggers partial assemblage recovery. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 91:117–125
Lapointe L, Bourget E (1999) Influence of substratum heterogeneity scales and complexity on a temperate epibenthic marine community. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 189:159–170
MacDougall AS, Turkington R (2005) Are invasive species the drivers or passengers of change in degraded ecosystems? Ecology 86:42–55
Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, Bazzaz FA (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol Appl 10:689–710
Marin-Guirao L, Bernardeau-Esteller J, Ruiz JM, Sandoval-Gil JM (2015) Resistance of Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows to the spread of the introduced green alga Caulerpa cylindracea: assessment of the role of light. Biol Invasion 17:1989–2009
Micheli F, Benedetti-Cecchi L, Gambaccini S, Bertocci I, Borsini C, Osio CG, Romano F (2005) Cascading human impacts, marine protected areas and the structure of Mediterranean rocky-reef assemblages. Ecol Monogr 75:81–102
Milazzo M, Badalamenti F, Ceccherelli G, Chemello R (2004) Boat anchoring on Posidonia oceanica beds in a marine protected area (Italy, Western Mediterranean): effect of anchor types in different anchoring stages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 299:51–62
Montefalcone M, Lasagna R, Bianchi CN, Morri C, Albertelli G (2006) Anchoring damage on Posidonia oceanica meadow cover: a case study in Prelo cove (Ligurian Sea, NW Mediterranean). Chem Ecol 22:207–217
Montefalcone M, Albertelli G, Morri C, Bianchi CN (2010) Pattern of wide-scale substitution within Posidonia oceanica meadows of NW Mediterranean Sea: invaders are stronger than natives. Aquat Conserv Mar Freshw Ecosyst 20:507–515
Montefalcone M, Vassallo P, Gatti G, Parravicini V, Paoli C, Morri C, Bianchi CN (2015a) The exergy of a phase shift: ecosystem functioning loss in seagrass meadows of the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 156:186–194
Montefalcone M, Morri C, Parravicini V, Bianchi CN (2015b) A tale of two invaders: divergent spreading kinetics of the alien green algae Caulerpa taxifolia and Caulerpa cylindracea. Biol Invasion 17:2717–2728
Pacciardi L, De Biasi AM, Piazzi L (2011) Effects of Caulerpa racemosa invasion on soft-bottom assemblages in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Biol Invasion 13:2677–2690
Pedersen MF, Borum J (1997) Nutrient control of estuarine macroalgae: growth strategy and the balance between nitrogen requirement and uptake. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 161:155–163
Piazzi L, Balata D (2008) The spread of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the Mediterranean Sea: an example of how biological invasions can influence beta diversity. Mar Environ Res 65:50–61
Piazzi L, Balata D (2009) Invasion of alien macroalgae in different Mediterranean habitats. Biol Invasion 11:193–204
Piazzi L, Ceccherelli G (2002) Effects of competition between two introduced Caulerpa. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 225:189–195
Piazzi L, Ceccherelli G (2006) Persistence of biological invasion effects: recovery of macroalgal assemblages after removal of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 68:455–461
Piazzi L, Balata D, Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (2001a) Comparative study of the growth of the two co-occurring introduced green algae Caulerpa taxifolia and Caulerpa racemosa along the Tuscan coast (Italy, western Mediterranean. Cryptogam Algol 22:459–466
Piazzi L, Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (2001b) Threat to macroalgal diversity: effects of the introduced green alga Caulerpa racemosa in the Mediterranean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 210:149–159
Piazzi L, Balata D, Cecchi E, Cinelli F (2003a) Co-occurrence of Caulerpa taxifolia and C. racemosa in the Mediterranean Sea: interspecific interactions and influence on native macroalgal assemblages. Cryptogam Algol 24:233–243
Piazzi L, Ceccherelli G, Balata D, Cinelli F (2003b) Early patterns of Caulerpa racemosa recovery in the Mediterranean Sea: the influence of algal turfs. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 83:27–29
Piazzi L, Balata D, Ceccherelli G, Cinelli F (2005a) Interactive effect of sedimentation and Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea invasion on macroalgal assemblages in the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64:467–474
Piazzi L, Meinesz A, Verlaque M, Akçali B, Antolić B, Argyrou M, Balata D, Ballesteros E, Calvo S, Cinelli F, Cirik S, Cossu A, D’Archino R, Djellouli SA, Javel F, Lanfranco E, Mifsud C, Pala D, Panayotidis P, Peirano A, Pergent G, Petrocelli A, Ruitton S, Žuljević A, Ceccherelli G (2005b) Invasion of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea: an assessment of the early stages of spread. Cryptogam Algol 26:189–202
Piazzi L, Balata D, Cinelli F (2007a) Invasions of alien macroalgae in Mediterranean coralligenous assemblages. Cryptogam Algol 28:289–301
Piazzi L, Balata D, Foresi L, Cristaudo C, Cinelli F (2007b) Sediment as a constituent of Mediterranean benthic communities dominated by Caulerpa racemosa var cylindracea. Sci Mar 71:129–135
Piazzi L, Gennaro P, Balata D (2012) Threats to macroalgal coralligenous assemblages in the Mediterranean Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2623–2629
Piazzi L, Gennaro P, Ceccherelli G (2014) Il ruolo di stress antropici nel favorire l’invasione di Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea. Biol Mar Medit 21:125–126
Pimentel D, McNair S, Janecka J, Wightman J, Simmonds C, O’Connell C, Wong E, Russel L, Zern J, Aquino T, Tsomondo T (2001) Economic and environmental threats of alien plant, animal, and microbe invasions. Agric Ecosyst Environ 84:1–20
Piola RF, Johnston EL (2008) Pollution reduces native diversity and increases invader dominance in marine hard-substrate communities. Div Distrib 14:329–342
Ruitton S, Verlaque M, Boudoresque CF (2005a) Seasonal changes of the introduced Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) at the northwest limit of its Mediterranean range. Aquat Bot 82:55–70
Ruitton S, Javel F, Culioli JM, Meinesz A, Pergent G, Verlaque M (2005b) First assessment of the Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) invasion along the French Mediterranean coast. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1061–1068
Ruitton S, Verlaque M, Aubin G, Boudouresque CF (2006) Grazing on Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea (Caulerpales, Chlorophyta) in the Mediterranean Sea by herbivorous fishes and sea urchins. Vie et Milieu 56:33–42
Soltan D, Verlaque M, Boudouresque CF, Francour P (2001) Changes in macroalgal communities in the vicinity of a Mediterranean sewage outfall after the setting up of a treatment plant. Mar Pollut Bull 42:59–70
Stachowicz JJ, Fried H, Osman RW, Whitlatch RB (2002) Biodiversity, invasion resistance and marine ecosystem function: reconciling pattern and process. Ecology 83:2575–2590
Tamburello L, Benedetti-Cecchi L, Masini L, Bulleri F (2013) Habitat heterogeneity promotes the coexistence of exotic seaweeds. Oecologia 172:505–513
Tamburello L, Bulleri F, Balata D, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2014) The role of overgrazing and anthropogenic disturbance in shaping spatial patterns of distribution of an invasive seaweed. J Appl Ecol 51:406–414
Teichberg M, Fox SE, Aguila C, Olsen YS, Valiela I (2008) Macroalgal responses to experimental nutrient enrichment in shallow coastal waters: growth, internal nutrient pools, and isotopic signatures. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 368:117–126
Terlizzi A, Felline S, Lionetto MG, Caricato R, Perfetti V, Cutignano A, Mollo E (2011) Detrimental physiological effects of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa on the Mediterranean white seabream Diplodus sargus. Aquat Biol 12:109–117
Tomas F, Box A, Terrados J (2011a) Effects of invasive seaweeds on feeding preference and performance of a keystone Mediterranean herbivore. Biol Invasion 13:1559–1570
Tomas F, Cebrian E, Ballesteros E (2011b) Differential herbivory of invasive algae by native fish in the Mediterranean Sea. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 92:27–34
Valentine JP, Magierowski RH, Johnson CR (2007) Mechanisms of invasion: establishment, spreadand persistence of introduced seaweed populations. Bot Mar 50:351–360
Vaselli S, Bulleri F, Benedetti-Cecchi L (2008) Hard coastal-defence structures as habitats for native and exotic rocky-bottom species. Mar Environ Res 66:395–403
Vázquez-Luis M, Sanchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT (2008) Changes in amphipod (Crustacea) assemblages associated with shallow-water algal habitats invaded by Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea in the western Mediterranean Sea. Mar Environ Res 65:416–426
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Westbrooks M (1996) Biological invasions as global environmental change. Am Sci 84:468–478
Vitousek PM, D’Antonio CM, Loope LL, Rejmànek M, Westbrooks M (1997) Introduced species: a significant component of human-caused global change. NZ J Ecol 21:1–16
Wasson K, Fenn K, Pearse JS (2005) Habitat differences in marine invasions of central California. Biol Invasion 7:935–948
Welden CW, Slauson WL (1986) The intensity of competition versus its importance: an overlooked distinction and some implications. Q Rev Biol 61:23–44
Žuljević A, Nikolic V, Despalatovic M, Antolić B (2008) Experimental in situ feeding of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus with invasive algae Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea and Caulerpa taxifolia in the Adriatic Sea. Fresenius Environ Bull 17:2098–2102
Žuljević A, Thibaut T, Despalatovic M, Cottalorda J-M, Nikolic V, Cvitkovic I, Antolić B (2011) Invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea makes a strong impact on the Mediterranean sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Biol Invasion 13:2303–2308
Acknowledgments
L. Piazzi was funded by ‘Desertificazione marina da sovrapascolo di ricci: indagine sulla transizione di stadi stabili bentonici alternativi’ project financed by P.O.R. SARDEGNA F.S.E. 2007–2013—Obiettivo competitività regionale e occupazione, Asse IV Capitale umano, Linea di Attività l.3.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: K. Bischof.
Reviewed by Ch. Hewitt and an undisclosed expert.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Invasive Species.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piazzi, L., Balata, D., Bulleri, F. et al. The invasion of Caulerpa cylindracea in the Mediterranean: the known, the unknown and the knowable. Mar Biol 163, 161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2937-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2937-4