Abstract
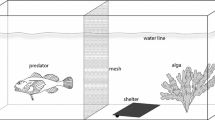
Amphipod assemblages that inhabit Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows are potentially relevant trophic resources for ichthyofauna. However, the effects of fish predation on amphipod assemblages in this system have received little attention. To address this gap in knowledge, experimental manipulations of predation intensity (exclusion and inclusion cages) were conducted at two sites in a Mediterranean marine protected area, where different levels of fish predation were expected to occur. We found that in the absence of predatory fishes (exclusion cages), total amphipod density and biomass were higher than in uncaged areas and partially controlled cages. At the species level, Caprella acanthifera and Iphimedia minuta responded to caging with increased abundance, while in most cases different species did not exhibit differences in density or biomass between treatments. The presence of one enclosed labrid fish predator (inclusion cages) resulted in a lower density and biomass of Aora spinicornis and a lower biomass of Phtisica marina, although total amphipod density and biomass were unchanged. In the inclusion cages, a size-frequency analysis revealed that predators mainly targeted large A. spinicornis and Apherusa chiereghinii individuals. Our results suggest that predation by fish may be an important factor in controlling amphipod abundances and biomasses in P. oceanica meadows. Overall, amphipod community composition was not affected by exclusion or inclusion of fish predators. However, some significant effects at the species level point to more complex interactions between some amphipods and fish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ, Gorley RN, Clarke KR (2008) PERMANOVA + for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Andersson S, Persson M, Moksnes PO, Baden S (2009) The role of the amphipod Gammarus locusta as a grazer on macroalgae in Swedish seagrass meadows. Mar Biol 156:969–981
Aoki M (1999) Morphological characteristics of young, maternal care behaviour and microhabitat use by caprellid amphipods. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 79:629–638
Bell JD, Harmelin-Vivien ML (1983) Fish fauna of French Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows. 2. Feeding habits. Tethys 11:1–14
Bellan-Santini D (1998) Ecology. In: Ruffo S (ed) The Amphipoda of the Mediterranean, Part 4. Mémoires de l’Institut océanographique no. 13, Monaco, pp 869–893
Bellan-Santini D (1999). Ordre des Amphipodes (Amphipoda Latreille, 1816). In: Forest J et al. (eds) Traité de zoologie: anatomie, systématique, biologie: 7. Crustacés: 3A. Péracarides. Mémoires de l’Institut océanographique no. 19, Monaco, pp 93–176
Boudouresque CF, Caltagirone A, Lefevre JR, Rico V, Semroud R (1992) Macrozoobenthos de la réserve naturelle de Scandola (Corse, Méditerranée nord-occidentale). Analyse pluriannuelle de « l’effet réserve » . In: Olivier J, Gérardin N, Jeudy de Grissac A (eds) Impact économique des espaces côtiers protégés de Méditerranée. MedPAN News 3, Ajaccio, pp 15–20
Boudouresque CF, Bernard G, Bonhomme P, Charbonnel E, Diviacco G, Meinesz A, Pergent G, Pergent-Martini C, Ruitton S, Tunesi L (2006) Préservation et conservation des herbiers à Posidonia oceanica. Ramoge Publication, Monaco
Bussers JC, Poulicek M, Diepvints J (1983) Description d’une suceuse à air comprimé économique et utilisable par un seul plongeur. Cah Biol Mar 24:215–217
Caine EA (1989) Caprellid amphipod behavior and predatory strikes by fish. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 126:173–180
Caine EA (1991) Caprellid amphipods: fast food for the reproductively active. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 148:27–33
Clements WH, Livingston RJ (1984) Prey selectivity of the fringed filefish, Monacanthus ciliatus (Pisces: Monacanthidae): role of prey accessibility. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 16:291–295
Connell SD (1997) Exclusion of predatory fish on a coral reef: The anticipation, pre-emption and evaluation of some caging artefacts. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 213:181–198
Di Franco A, Bussotti S, Navone A, Panzalis P, Guidetti P (2009) Evaluating effects of total and partial restrictions to fishing on Mediterranean rocky-reef fish assemblages. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 387:275–285
Duffy JE, Hay ME (2001) Ecology and evolution of marine consumer-prey interactions. In: Bertness M, Hay ME, Gaines SD (eds) Marine community ecology. Sinauer Press, Sunderland, pp 131–157
Edgar GJ (1990) Predator-prey interactions in seagrass beds. III. Impacts of the western rock lobster Panulirus Cygnus George on epifaunal gastropod populations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 139:33–42
Edgar GJ, Aoki M (1993) Resource limitation and fish predation: their importance to mobile epifauna associated with Japanese Sargassum. Oecologia 95:122–133
Englund G (1997) Importance of spatial scale and prey movements in predator caging experiments. Ecology 78:2316–2325
Englund G, Olsson T (1996) Treatment effects in a stream fish enclosure experiment: influence of predation rate and prey movements. Oikos 77:519–528
Francour P (1994) Pluriannual analysis of the reserve effect on ichthyofauna in the Scandola natural reserve (Corsica, Northwestern Mediterranean). Oceanol Acta 17:309–317
Francour P (2000) Evolution spatio-temporelle à long terme des peuplements de poissons des herbiers à Posidonia oceanica de la réserve naturelle de Scandola (Corse, Méditerranée Nord-Occidentale). Cybium 24:85–95
Gambi MC, Buia MC, Casola E, Scardi M (1989) Estimates of water movement in Posidonia oceanica beds: a first approach. In: Boudouresque CF, Meinesz CF, Fresi E, Gravez V (eds) International workshop on Posidonia beds. GIS Posidonie, France, pp 101–112
Gambi MC, Lorenti M, Russo GF, Scipione MB, Zupo V (1992) Depth and seasonal distribution of some groups of the vagile fauna of the Posidonia oceanica leaf stratum: structural and trophic analyses. Mar Ecol 13:17–39
García-Rubies A, Zabala M (1990) Effects of total fishing prohibition on the rocky fish assemblages of Medes Islands marine reserve (NW Mediterranean). Sci Mar 54:317–328
Giraud G (1979) Sur une méthode de mesure et de comptage des structures foliaires de Posidonia oceanica (Linnaeus) Delile. Bull Mus Hist Nat Marseille 39:33–39
Gobert S, Kyramarios M, Lepoint G, Pergent-Martini C, Bouquegneau JM (2003) Variations at different spatial scales of Posidonia oceanica (L) Delile beds; effects on the physico-chemical parameters of the sediment. Oceanol Acta 26:199–207
Gobert S, Cambridge ML, Velimirov B, Pergent G, Lepoint G, Bouquegneau JM, Dauby P, Pergent-Martini C, Walker DI (2006) Biology of Posidonia. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 387–408
González AR, Guerra-García JM, Maestre MJ, Ruiz-Tabares A, Espinosa F, Gordillo I, Sánchez-Moyano JE, García-Gómez JC (2008) Community structure of caprellids (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Caprellidae) on seagrasses from southern Spain. Helgol Mar Res 62:189–199
Guerra-García JM, Corzo J, García-Gómez JC (2002) Clinging behaviour of the Caprellidea (Amphipoda) from the Strait of Gibraltar. Crustaceana 75:41–50
Hairston NG, Smith FE, Slobodkin LB (1960) Community structure, population control and competition. Am Nat 94:421–425
Harmelin-Vivien ML, Harmelin JG, Chauvet C, Duval C, Galzin R, Lejeune P, Barnabe G, Blanc F, Chevalier R, Duclerc J, Lasserre G (1985) Evaluation visuelle des peuplements et populations de poissons: problèmes et méthodes. Rev Ecol (Terre Vie) 40:467–539
Heck KL Jr, Orth RJ (2006) Predation in seagrass beds. In: Larkum AWD, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 537–550
Hindell JS, Jenkins GP, Keough MJ (2000) Evaluating the impact of predation by fish on the assemblage structure of fishes associated with seagrass (Heterozostera tasmanica) (Martens ex Ascherson) den Hartog, and unvegetated sand habitats. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 255:153–174
Hindell JS, Jenkins GP, Keough MJ (2001) Spatial and temporal variability in the effects of fish predation on macrofauna in relation to habitat complexity and cage effects. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 224:231–250
Kabasakal H (2001) Description of the feeding morphology and the food habits of four sympatric labrids (Perciformes, Labridae) from South-Eastern Aegean Sea, Turkey. Neth J Zool 51:439–455
Kennelly SJ (1991) Caging experiments to examine the effects of fishes on understorey species in a sublittoral kelp community. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 147:207–230
Labropoulou M, Plaitis W (1995) Selective predation on small crustaceans by six demersal fish species in Iraklion Bay (Cretan Sea, North-eastern Mediterranean). In: Eleftheriou A, Ansell AD, Smith CJ (eds) Biology and ecology of shallow coastal waters: proceedings of the 28th European marine biology symposium. IMBC, Iraklio, pp 351–357
Langlois TJ, Anderson MJ, Babcock RC, Kato S (2006) Marine reserves demonstrate trophic interactions across habitats. Oecologia 147:134–140
Macpherson E, Gordoa A, Garcia-Rubies A (2002) Biomass size spectra in littoral fishes in protected and unprotected areas in the NW Mediterranean. Est Coast Shelf Sci 55:777–788
Main KL (1985) The influence of prey identity and size on selection of prey by two marine fishes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 88:145–152
Mazzella L, Scipione MB, Buia MC (1989) Spatio-temporal distribution of algal and animal communities in a Posidonia oceanica meadow. PSZN Mar Ecol 10:107–129
Michel L, Lepoint G, Dauby P, Sturaro N (2010) Sampling methods for amphipods of Posidonia oceanica meadows: a comparative study. Crustaceana 83:39–47
Michel LN, Dauby P, Gobert S, Graeve M, Nyssen F, Thelen N, Lepoint G (2015) Dominant amphipods of Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows display considerable trophic diversity. Mar Ecol 36:969–981
Moksnes P-O, Gullström M, Tryman K, Baden S (2008) Trophic cascades in a temperate seagrass community. Oikos 117:763–777
Morin PJ (2011) Predation and communities: empirical patterns. In: Morin PJ (ed) Community ecology, 2nd edn. Wiley Blackwell, Oxford, pp 90–119
Murdoch W, Briggs C, Nisbet R (2003) Consumer-resource dynamics. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Nelson WG (1979) Experimental studies of selective predation on amphipods: consequences for amphipod distribution and abundance. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 38:225–245
Nelson WG (1981) Experimental studies of decapod and fish predation on seagrass macrobenthos. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 5:141–149
Orth RJ, Heck KL, Van Montfrans J (1984) Faunal communities in seagrass beds: a review of the influence of plant structure and prey characteristics on predator-prey relationships. Estuaries 7:339–350
Paloheimo JE (1979) Indices of food type preference by a predator. J Fish Res Bd Can 36:470–473
Pergent G, Rico-Raimondino V, Pergent-Martini C (1997) Fate of primary production in Posidonia oceanica meadows of the Mediterranean. Aquat Bot 59:307–321
Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC (2000) Contributions of stable-isotope data to elucidating food webs of Mediterranean rocky littoral fishes. Oecologia 122:399–409
Pinnegar JK, Polunin NVC, Francour P, Badalamenti F, Chemello R, Harmelin-Vivien ML, Heureu B, Milazzo M, Zabala M, D’Anna G, Piptone C (2000) Trophic cascades in benthic marine ecosystems: lessons for fisheries and protected area management. Environ Conserv 27:179–200
Preisser EL, Bolnick DI, Benard MF (2005) Scared to death? The effect of intimidation and consumption in predator-prey interactions. Ecology 86:501–509
Sahyoun R, Bussotti S, Di Franco A, Navone A, Panzalis P, Guidetti P (2013) Protection effects on Mediterranean fish assemblages associated with different rocky habitats. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 93:425–435
Sala E (1997) The role of fishes in the organization of a Mediterranean sublittoral community. II: epifaunal communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 212:45–60
Sala E, Boudouresque CF (1997) The role of fishes in the organization of a Mediterranean sublittoral community. I: algal assemblages. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 212:25–44
Sánchez-Jerez P, Ramos-Esplá AA (1996) Detection of environmental impacts by bottom trawling on Posidonia oceanica (L) Delile meadows: sensitivity of fish and macroinvertebrate communities. J Aquat Ecosyst Health 5:239–253
Sánchez-Jerez P, Barberá-Cebrian C, Ramos-Esplá AA (2000) Influence of the structure of Posidonia oceanica meadows modified by bottom trawling on crustacean assemblages: comparison of amphipods and decapods. Sci Mar 64:319–326
Scipione MB, Gambi MC, Lorenti M, Russo GF, Zupo V (1996) Vagile fauna of the leaf stratum of Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa in the Mediterranean Sea. In: Kuo J, Phillips RC, Walker DI, Kirkman H (eds) Seagrass biology: proceedings on an international workshop. Rottnest Island, Western Australia, pp 249–260
Shurin JB, Borer ET, Seabloom EW, Anderson K, Blanchette CA, Broitman BR, Cooper SD, Halpern BS (2002) A cross-ecosystem comparison of the strength of trophic cascades. Ecol Lett 5:785–791
Sih A, Crowley P, McPeek M, Petranka J, Strohmeier (1985) Predation, competition and prey communities: a review of field experiments. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 16:269–311
Steele MA (1996) Effects of predators on reef fishes: separating cage artefacts from effects of predation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 198:249–267
Stein RA (1977) Selective predation, optimal foraging, and the predator-prey interaction between fish and crayfish. Ecology 58:1237–1253
Sturaro N, Guerra-García JM (2012) A new species of Caprella (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from the Mediterranean Sea. Helgol Mar Res 66:33–42
Sturaro N, Lepoint G, Pérez-Perera A, Vermeulen A, Panzalis P, Navone A, Gobert S (2014) Seagrass amphipod assemblages in a Mediterranean marine protected area: a multiscale approach. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 506:175–192
Sturaro N, Lepoint G, Vermeulen S, Gobert S (2015) Multiscale variability of amphipod assemblages in Posidonia oceanica meadows. J Sea Res 95:258–271
Valentine JF, Duffy JE (2006) The central role of grazing in seagrass ecology. In: Larkum AW, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Netherlands, pp 463–501
Valle C, Bayle-Sempere JT (2009) Effects of a marine protected area on fish assemblages associated with Posidonia oceanica seagrass beds: temporal and depth variations. J Appl Ichthyol 25:537–544
Vázquez-Luis M, Sanchez-Jerez P, Bayle-Sempere JT (2010) Effects of Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea on prey availability: an experimental approach to predation of amphipods by Thalassoma pavo (Labridae). Hydrobiologia 654:147–154
Virnstein R, Nelson W, Lewis F, Howard R (1984) Latitudinal patterns in seagrass epifauna: do patterns exist, and can they be explained? Estuaries 7:310–330
Woods C (2009) Caprellid amphipods: an overlooked marine finfish aquaculture resource? Aquac 289:199–211
Zupo V, Stübing D (2010) Diet of fish populations in Posidonia oceanica meadows off the Island of Ischia (Gulf of Naples, Italy): assessment of spatial and seasonal variability. Nat Sci 2:1274–1286
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank R. Biondo for technical assistance in the development of the caging devices (Laboratoire d’Océanologie, Université de Liège, Belgium), S. Vitale for technical assistance during field work (Consorzio di Gestione Area Marina Protetta Tavolara-Punta Coda Cavallo, Olbia, Italy) and all volunteers for field and laboratory assistance. We would like to thank P. Guidetti, S. Vermeulen and anonymous referees for their critical comments which greatly improved the manuscript. This study was supported by the Belgian Fund for Research for the Industry and Agriculture (FRIA, grant nr. FC77010), by a Special Research Fund of the University of Liege (FSR) and by the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research (FNRS). This paper is MARE publication number 321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: F. Bulleri.
Reviewed by undisclosed experts.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sturaro, N., Gobert, S., Pérez-Perera, A. et al. Effects of fish predation on Posidonia oceanica amphipod assemblages. Mar Biol 163, 58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2830-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-2830-1