Abstract
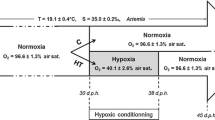
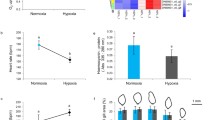
Hypoxia episodes have been generally studied over the last decade for their lethal consequences in coastal areas, which are nurseries for several fish species. The possible long-lasting effects of non-lethal hypoxia exposures at larval stage are, however, poorly documented. We investigated the long-lasting phenotypic impact of an experimental exposure to moderate hypoxia (40 % air saturation) between 30 and 38 days post-hatching in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). At the juvenile stage, our data indicate that this early hypoxia exposure impacted on juvenile growth rate but not on hypoxia tolerance. Growth depression was associated with a regulation of metabolism as suggested by a decrease in blood glycaemia, a decreased hepatic expression of the glucose transporter glut2 and of acaca involved in fatty acid synthesis as well as an increased hepatic expression of glycolytic ldh-a, which is a target gene of hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs). Interestingly, while fish were not exposed to hypoxia, the cellular oxygen sensor egln3 gene, which is also a target of HIFs, exhibited higher expression level in the hepatic tissue of juveniles that have experienced hypoxia at larval stage. Even if further studies are needed to evaluate the functional significance of such effects and to decipher the underlying molecular mechanisms, the present data evidence that early life exposure to a hypoxia event has long-lasting impact on sea bass juvenile physiology.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- acaca :
-
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Alpha
- C:
-
Control group
- Ct:
-
Cycle threshold
- dph:
-
Days post-hatching
- E:
-
Primer efficiency
- ef1α :
-
Elongation factor-1, isoform alpha
- Egln3 :
-
Egg-laying defective nine 3
- ELHT:
-
Early life hypoxia treatment group
- glut2 :
-
Glucose transporter 2
- HCT:
-
Hypoxic challenge Test
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia inducible factor
- igf-1 :
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1
- Ldh-a :
-
Lactate dehydrogenase-a
- NI:
-
Not investigated
- pH:
-
Power of hydrogen
- PIT:
-
Passive integrated transponder
- qPCR:
-
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- s.d.:
-
Standard deviation
References
Breitburg DL (1992) Episodic hypoxia in Chesapeake Bay: interacting effects of recruitment, behavior, and physical disturbance. Ecol Monogr 62:525–546. doi:10.2307/2937315
Burton T, Killen SS, Armstrong JD, Metcalfe NB (2011) What causes intraspecific variation in resting metabolic rate and what are its ecological consequences? Proc R Soc B 278:3465–3473. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.1778
Conceicao LEC, Morais S, Ronnestad I (2007) Tracers in fish larvae nutrition: a review of methods and applications. Aquaculture 267:62–75. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.02.035
Cook DG, Iftikar FI, Baker DW, Hickey AJR, Herbert NA (2013) Low-O-2 acclimation shifts the hypoxia avoidance behaviour of snapper (Pagrus auratus) with only subtle changes in aerobic and anaerobic function. J Exp Biol 216:369–378. doi:10.1242/jeb.073023
Craig JK, Rice JA, Crowder LB, Nadeau DA (2007) Density-dependent growth and mortality in an estuary-dependent fish: an experimental approach with juvenile spot Leiostomus xanthurus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 343:251–262. doi:10.3354/meps06864
Desai M, Hales CN (1997) Role of fetal and infant growth in programming metabolism in later life. Biol Rev 72:329–348. doi:10.1017/s0006323196005026
Diaz RJ (2001) Overview of hypoxia around the world. J Env Qual 30:275–281. doi:10.2134/jeq2001.302275x
Diaz RJ, Rosenberg R (1995) Marine benthic hypoxia: a review of its ecological effects and the behavioural responses of benthic macrofauna. Oceanogr Mar Biol 33:245–303
Dufour V, Cantou M, Lecomte F (2009) Identification of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) nursery areas in the north-western Mediterranean Sea. JMBA 89:1367–1374. doi:10.1017/s0025315409000368
Eby LA, Crowder LB, McClellan CM, Peterson CH, Powers MJ (2005) Habitat degradation from intermittent hypoxia: impacts on demersal fishes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 291:249–261. doi:10.3354/meps291249
Engstrom-Ost J, Isaksson I (2006) Effects of macroalgal exudates and oxygen deficiency on survival and behaviour of fish larvae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 335:227–234. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2006.03.007
Ferraresso S, Milan M, Pellizzari C, Vitulo N, Reinhardt R, Canario AVM, Patarnello T, Bargelloni L (2010) Development of an oligo DNA microarray for the European sea bass and its application to expression profiling of jaw deformity. BMC Genom 11:17. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-354
Firth JD, Ebert BL, Ratcliffe PJ (1995) Hypoxic regulation of lactate-dehydrogenase. A interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and cAMP response elements. J Biol Chem 270:21021–21027
Fu SJ, Brauner CJ, Cao ZD, Richards JG, Peng JL, Dhillon R, Wang YX (2011) The effect of acclimation to hypoxia and sustained exercise on subsequent hypoxia tolerance and swimming performance in goldfish (Carassius auratus). J Exp Biol 214:2080–2088. doi:10.1242/jeb.053132
Geist SJ, Ekau W, Kunzmann A (2013) Energy demand of larval and juvenile Cape horse mackerels, Trachurus capensis, and indications of hypoxia tolerance as benefit in a changing environment. Mar Biol 160:3221–3232. doi:10.1007/s00227-013-2309-2
Hall JR, Short CE, Driedzic WR (2006) Sequence of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) GLUT4, GLUT2 and GPDH: developmental stage expression, tissue expression and relationship to starvation-induced changes in blood glucose. J Exp Biol 2006:4490–4502
Hamdoun A, Epel D (2007) Embryo stability and vulnerability in an always changing world. PNAS 104:1745–1750. doi:10.1073/pnas.0610108104
Ho DH, Burggren WW (2012) Parental hypoxic exposure confers offspring hypoxia resistance in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Exp Biol 215:4208–4216. doi:10.1242/jeb.074781
Ishibashi Y, Kotaki T, Yamada Y, Ohta H (2007) Ontogenic changes in tolerance to hypoxia and energy metabolism of larval and juvenile Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 352:42–49. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2007.06.036
Jennings S, Pawson MG (1992) The origin and recruitment of bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, larvae to nursery areas. J Mar Biol Ass 72:199–212. doi:10.1017/S0025315400048888
Johnston IA, Temple GK (2002) Thermal plasticity of skeletal muscle phenotype in ectothermic vertebrates and its significance for locomotory behaviour. J Exp Biol 205:2305–2322
Johnston IA, Vieira V, Hill J (1996) Temperature and ontogeny in ectotherms: muscle phenotype in fish. In: Johnston IA, Bennett AF (eds) Animals and temperature: Phenotypic and evolutionary adaptation . Society of experimental biology, Seminar Series. Cambridge University Press, pp 153–181
Johnston EF, Alderman SL, Gillis TE (2013) Chronic hypoxia exposure of trout embryos alters swimming performance and cardiac gene expression in larvae. PBZ 86:567–575. doi:10.1086/672012
Kohin S, Stary CM, Howlett RA, Hogan MC (2001) Preconditioning improves function and recovery of single muscle fibers during severe hypoxia and reoxygenation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C142–C146
Lakani FB, Sattari M, Falahatkar B (2013) Effect of different oxygen levels on growth performance, stress response and oxygen consumption in two weight groups of great sturgeon Huso huso. Iran J Fish Sci 12:533–549
Lindström J (1999) Early development and fitness in birds and mammals. Trends Ecol Evol 14:343–348. doi:10.1016/s0169-5347(99)01639-0
Lu GW, Yu S, Li RH, Cui XY, Gao CY (2005) Hypoxic preconditioning—a novel intrinsic cytoprotective strategy. Mol Neurobiol 31:255–271. doi:10.1385/mn:31:1-3:255
McClain DA, Abuelgasim KA, Nouraie M, Salomon-Andonie J, Niu XM, Miasnikova G, Polyakova LA, Sergueeva A, Okhotin DJ, Cherqaoui R, Okhotin D, Cox JE, Swierczek S, Song J, Simon MC, Huang JY, Simcox JA, Yoon D, Prchal JT, Gordeuk VR (2013) Decreased serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels in patients with Chuvash polycythemia: a role for HIF in glucose metabolism. J Mol Med-Jmm 91:59–67. doi:10.1007/s00109-012-0961-5
McKenzie DJ, Lund I, Pedersen PB (2008) Essential fatty acids influence metabolic rate and tolerance of hypoxia in Dover sole (Solea solea) larvae and juveniles. Mar Biol 154:1041–1051. doi:10.1007/s00227-008-0998-8
McNatt RA, Rice JA (2004) Hypoxia-induced growth rate reduction in two juvenile estuary-dependent fishes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 311:147–156. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2004.05.006
Metcalfe NB, Monaghan P (2001) Compensation for a bad start: grow now, pay later? Trends Ecol Evol 16:254–260. doi:10.1016/s0169-5347(01)02124-3
Metcalfe NB, Monaghan P (2003) Growth versus lifespan: perspectives from evolutionary ecology. Exp Gerontol 38:935–940. doi:10.1016/s0531-5565(03)00159-1
Monaghan P (2008) Early growth conditions, phenotypic development and environmental change. Phil Trans B 363:1635–1645. doi:10.1098/rstb.2007.0011
Mulvey JM, Renshaw GMC (2000) Neuronal oxidative hypometabolism in the brainstem of the epaulette shark (Hemiscyllium ocellatum) in response to hypoxic pre-conditioning. Neurosci Lett 290:1–4. doi:10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01321-5
Olsvik PA, Vikesa V, Lie KK, Hevroy EM (2013) Transcriptional responses to temperature and low oxygen stress in Atlantic salmon studied with next-generation sequencing technology. BMC Genom 14:817. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-817
Perera F, Herbstman J (2011) Prenatal environmental exposures, epigenetics, and disease. Reprod Toxicol 31:363–373. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2010.12.055
Perez-Dominguez R, Holt GJ (2006) Interrenal and thyroid development in red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus): effects of nursery environment on larval growth and cortisol concentration during settlement. Gen Comp Endocr 146:108–118. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2005.10.006
Pescador N, Cuevas Y, Naranjo S, Alcaide M, Villar D, Landazuri M, Del Peso L (2005) Identification of a functional hypoxia-responsive element that regulates the expression of the egl nine homologue 3 (egln3/phd3) gene. Biochem J 390:189–197. doi:10.1042/bj20042121
Pichavant K, Person-Le-Ruyet J, Le Bayon N, Sévère A, Le Roux A, Quéméner L, Maxime V, Nonnotte G, Bœuf G (2000) Effects of hypoxia on growth and metabolism of juvenile turbot. Aquaculture 188:103–114
Pihl L, Baden SP, Diaz RJ (1991) Effects of periodic hypoxia on distribution of demersal fish and crustaceans. Mar Biol 108:349–360. doi:10.1007/bf01313644
Pihl L, Baden SP, Diaz RJ, Schaffner LC (1992) Hypoxia-induced structural changes in the diet of bottom-feeding fish and crustacea. Mar Biol 112:349–361. doi:10.1007/bf00356279
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. http://www.R-project.org/, R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Richards JG (2009) Chapter 10: Metabolic and molecular responses of fish to hypoxia fish physiology, vol 27: Hypoxia. Academic Press, New York, pp 443–485
Roze T, Christen F, Amerand A, Claireaux G (2013) Trade-off between thermal sensitivity, hypoxia tolerance and growth in fish. J Therm Biol 38:98–106
Semenza GL (2011) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulator of mitochondrial metabolism and mediator of ischemic preconditioning. BBA Mol Cell Res 1813:1263–1268. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.08.006
Stierhoff KL, Targett TE, Miller K (2006) Ecophysiological responses of juvenile summer and winter flounder to hypoxia: experimental and modeling analyses of effects on estuarine nursery quality. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 325:255–266. doi:10.3354/meps325255
Thompson DB (1999) Genotype-environment interaction and the ontogeny of diet-induced phenotypic plasticity in size and shape of Melanoplus femurrubrum (Orthoptera:acrididae). J Evol Biol 12:38–48. doi:10.1046/j.1420-9101.1999.00005.x
Wexler JB, Margulies D, Scholey VP (2011) Temperature and dissolved oxygen requirements for survival of yellowfin tuna, Thunnus albacares, larvae. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 404:63–72. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2011.05.002
Yamanaka H, Takahara T, Kohmatsu Y, Yuma M (2013) Body size and temperature dependence of routine metabolic rate and critical oxygen concentration in larvae and juveniles of the round crucian carp Carassius auratus grandoculis Temminck and Schlegel 1846. J Appl Ichthyol 29:891–895. doi:10.1111/jai.12126
Yang H, Cao ZD, Fu SJ (2013) The effects of diel-cycling hypoxia acclimation on the hypoxia tolerance, swimming capacity and growth performance of southern catfish (Silurus meridionalis). Comp Biochem Phys A 165:131–138. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.02.028
Zambonino-Infante JL, Cahu CL, Peres A, Quazuguel P, Le Gall MM (1996) Sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae fed different Artemia rations: growth, pancreas enzymatic response and development of digestive functions. Aquaculture 139:129–138. doi:10.1016/0044-8486(95)01149-8
Zambonino-Infante JL, Claireaux G, Ernande B, Jolivet A, Quazuguel P, Severe A, Huelvan C, Mazurais D (2013) Hypoxia tolerance of common sole juveniles depends on dietary regime and temperature at the larval stage: evidence for environmental conditioning. Proc R Soc B 280:9. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.3022
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Helen McCombie for her help with editing the English language. The first author was supported by a joint Ifremer–Région Bretagne doctoral grant.
Conflict of interest
No Conflict of interests declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Pörtner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanderplancke, G., Claireaux, G., Quazuguel, P. et al. Hypoxic episode during the larval period has long-term effects on European sea bass juveniles (Dicentrarchus labrax). Mar Biol 162, 367–376 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2601-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2601-9