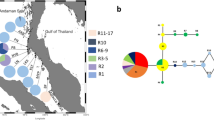
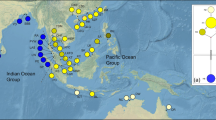
Abstract
Phylogeographical study of the brown macroalga, Sargassum aquifolium using nuclear internal transcribed spacer 2, plastidal RuBisCo spacer, and mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit-III revealed the populations in Southeast Asia to be homogeneous. On the other hand, genetic differences were detected between populations from Southeast Asia and western Pacific Islands/Guam, suggesting the presence of genetic break between these regions. This further suggests that populations of S. aquifolium may have survived east of Sunda Shelf during the Last Glacial Maximum and recent recolonization led to homogeneity of the populations in the Sunda Shelf region. Recolonization could be facilitated by year-round reproduction of the populations and dispersal of germlings on floating thalli by coastal currents. Restricted current flow across Maluku Sea and directional equatorial current flows could have isolated the Pacific Island and Guam populations from those of Southeast Asia. Our results support the presence of multiple refugia as the source of different lineages of S. aquifolium populations with a lack of secondary contact in the post-glacial dispersal between Southeast Asia and western Pacific as the mechanisms behind the phylogeographical patterns observed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreakis N, Procaccini G, Maggs C, Kooistra WHCF (2007) Phylogeography of the invasive seaweed Asparagopsis (Bonnemaisoniales, Rhodophyta) reveals cryptic diversity. Mol Ecol 16:2285–2299
Andreakis N, Kooistra WHCF, Procaccini G (2009) High genetic diversity and connectivity in the polyploid invasive seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis (Bonnemaisoniales) in the Mediterranean, explored with microsatellite alleles and multilocus genotypes. Mol Ecol 18:212–226
Ang PO (2006) Phenology of Sargassum spp. in Tung Ping Chau Marine Park, Hong Kong SAR, China. J Appl Phycol 18:629–636
Ang PO, Leung SM, Choi MM, Cheang CC (2008) The genus Sargassum in the South China Sea region: a compilation list and preliminary biogeographical analysis. In: Phang SM, Lewmanomont K, Lim PE (eds) Taxonomy of Southeast Asia Seaweeds. Institute of Ocean and Earth Sciences, University of Malaya Monograph Series 2, pp 147–158
Bae DY, Ang PO, Boo SM (2013) Mitochondrial cox3 and trnW-I sequence diversity of Sargassum muticum. Aquat Bot 104:220–223
Barber PH (2000) A marine Wallace’s line? Nature 406:692–693
Barber PH, Erdmann MV, Palumbi SR (2006) Comparative phylogeography of three codistributed stomatopods: origins and timing of regional lineage diversification in the coral triangle. Evolution 60:1825–1839
Benzie JAH, Williams ST (1997) Genetic structure of giant clam (Tridacna maxima) populations in the West Pacific is not consistent with dispersal by present-day ocean currents. Evolution 51:768–783
Carpenter KE, Barber PH, Crandall ED et al (2011) Comparative phylogeography of the coral triangle and implications for marine management. J Mar Biol 2011:1–14
Chan SW, Cheang CC, Chirapart A et al (2013) Homogeneous population of the brown alga Sargassum polycystum in Southeast Asia: possible role of recent expansion and asexual propagation. PLoS ONE 8:e77662
Cheang CC, Chu KH, Ang PO (2010a) Phylogeography of the marine macroalga Sargassum hemiphyllum (Phaeophyceae, Heterokontophyta) in northwestern Pacific. Mol Ecol 19:2933–2948
Cheang CC, Chu KH, Fujita D et al (2010b) Low genetic variability of Sargassum muticum (Phaeophyceae) revealed by a global analysis of native and introduced populations. J Phycol 46:1063–1074
Clement M, Posada D, Crandall KA (2000) TCS: a computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol Ecol 9:1657–1659
Coyer JA, Peters AF, Stam WT, Olsen JL (2003) Post-ice age recolonization and differentiation of Fucus serratus L. (Phaeophyceae; Fucaceae) populations in Northern Europe. Mol Ecol 12:1817–1829
Crandall ED, Jones ME, Muñoz MM et al (2008) Comparative phylogeography of two seastars and their ectosymbionts within the coral triangle. Mol Ecol 17:5276–5290
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A (2007) BEAST: bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evolut Biol 7:214
Drummond AJ, Rambaut A, Shapiro B, Pybus OG (2005) Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol Biol Evol 22:1185–1192
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Resour 10:564–567
Fu Y-X (1997) Statistical tests of neutrality against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 147:915–925
Gordon AL (2005) Oceanography of the Indonesian seas and their throughflow. Oceanography 18:14–27
Gordon AL, Fine RA (1996) Pathways of water between the Pacific and Indian oceans in the Indonesian seas. Nature 379:146–149
Grant WS, Liu M, Gao T, Yanagimoto T (2012) Limits of Bayesian skyline plot analysis of mtDNA sequences to infer historical demographies in Pacific herring (and other species). Mol Phylogenet Evol 65:203–212
Guindon S, Dufayard J-F, Lefort V et al (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Hu Z-M, Uwai S, Yu S-H et al (2011) Phylogeographic heterogeneity of the brown macroalga Sargassum horneri (Fucaceae) in the northwestern Pacific in relation to late Pleistocene glaciation and tectonic configurations. Mol Ecol 20:3894–3909
Hughes TP, Bellwood DR, Connolly SR (2002) Biodiversity hotspots, centres of endemicity, and the conservation of coral reefs. Ecol Lett 5:775–784
Kendrick GA, Walker DI (1995) Dispersal of propagules of Sargassum spp. (Sargassaceae: Phaeophyta): Observations of local patterns of dispersal and consequences for recruitment and population structure. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 192:273–288
Kochzius M, Nuryanto A (2008) Strong genetic population structure in the boring giant clam, Tridacna crocea, across the Indo-Malay Archipelago: implications related to evolutionary processes and connectivity. Mol Ecol 17:3775–3787
Komatsu T, Tatsukawa K, Filippi JB et al (2007) Distribution of drifting seaweeds in eastern East China Sea. J Mar Syst 67:245–252
Lee KM, Yang EC, Coyer JA et al (2012) Phylogeography of the seaweed Ishige okamurae (Phaeophyceae): evidence for glacial refugia in the northwest Pacific region. Mar Biol 159:1021–1028
Lourie SA, Green DM, Vincent ACJ (2005) Dispersal, habitat differences, and comparative phylogeography of Southeast Asian seahorses (Syngnathidae: Hippocampus). Mol Ecol 14:1073–1094
Maggs CA, Castilho R, Foltz D et al (2008) Evaluating signatures of glacial refugia for North Atlantic benthic marine taxa. Ecology 89:S108–S122
Mattio L, Payri CE, Stiger-Pouvreau V (2008) Taxonomic revision of Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) from French Polynesia based on morphological and molecular analyses. J Phycol 44:1541–1555
Mattio L, Payri CE, Verlaque M (2009) Taxonomic revision and geographic distribution of the subgenus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) in the Western and central Pacific Islands based on morphological and molecular analyses. J Phycol 45:1213–1227
McGregor HV, Gagan MK, McCulloch MT et al (2008) Mid-Holocene variability in the marine 14C reservoir age for northern coastal Papua New Guinea. Quat Geochronol 3:213–225
McManus JW (1985) Marine speciation, tectonics, and sea level changes in Southeast Asia. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Coral Reef Congress, Tahiti 4: 133–138
Miller KG (2009) Sea level change, last 250 million years. http://www.springerreference.com/docs/html/chapterdbid/77470.html. Accessed 19 July 2007
Nei M (1987) Molecular evolutionary genetics. Columbia University Press, New York
Nei M, Li J (1989) Variances of the average numbers of nucleotide substitutions within and between populations. Mol Biol Evol 6:290–300
Ohno M (1984) Observation on the floating seaweed on the near-shore waters of the southern Japan. Hydrobiologia 116⁄117: 408–412
Olsen JL, Zechman FW, Hoarau G et al (2010) The phylogeographic architecture of the fucoid seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum: an intertidal “marine tree” and survivor of more than one glacial-interglacial cycle. J Biogeogr 37:842–856
Phillips N (1995) Biogeography of Sargassum (Phaeophyta) in the Pacific basin. In: Abbott IA (ed) Taxonomy of economic seaweeds with reference to some Pacific Species, vol 5. California Sea Grant College Program, La Jolla, pp 107–145
Phillips NE, Smith CM, Morden CW (2005) Testing systematic concepts of Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) using portions of the rbcLS operon. Phycoll Res 53:1–10
Provan J, Wattier RA, Maggs CA (2005) Phylogeographic analysis of the red seaweed Palmaria palmata reveals a Pleistocene marine glacial refugium in the English Channel. Mol Ecol 14:793–803
Rogers AR, Harpending H (1992) Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol Biol Evol 9:552–569
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P et al (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542
Rousset F (1997) Genetic differentiation and estimation of gene flow from F-statistics under isolation by distance. Genetics 145:1219–1228
Stiger V, Horiguchi T, Yoshida T et al (2000) Phylogenetic relationships of Sargassum (Sargassaceae, Phaeophyceae) with reference to a taxonomic revision of the section Phyllocystae based on ITS-2 nrDNA sequences. Phycol Res 48:251–260
Stiger V, Horiguchi T, Yoshida T et al (2003) Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Sargassum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae), inferred from ITS-2 nrDNA, with an emphasis on the taxonomic subdivision of the genus. Phycol Res 53:1–10
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evolut 28:2731–2739
Timm J, Kochzius M (2008) Geological history and oceanography of the Indo-Malay Archipelago shape the genetic population structure in the false clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris). Mol Ecol 17:3999–4014
Timm J, Planes S, Kochzius M (2012) High similarity of genetic population structure in the false clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris) found in microsatellite and mitochondrial control region analysis. Conserv Genet 13:693–706
Uwai S, Yotsukura N, Serisawa Y et al (2006) Intraspecific genetic diversity of Undaria pinnatifida in Japan, based on the mitochondrial cox3 Gene and the ITS1 of nrDNA. Hydrobiologia 553:345–356
Voris HK (2000) Maps of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time durations. J Biogeogr 27:1153–1167
Wyrtki K (1961) Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian waters. NAGA Report Vol. 2, The University of California, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California
Yeong M-LB, Wong C-L (2012) Seasonal growth rate of Sargassum species at Teluk Kemang, Port Dickson, Malaysia. J Appl Phycol 25:805–814
Acknowledgments
We thank Tharith C (Cambodia), Phang Siew Moi (Malaysia), Edna Ganzon-Fortes (Philippines), Jeff Low (Singapore), Jaruwan Mayakun, and Achana Prathep (Thailand), for their hospitality during our collecting trips and for help with the collection of samples. Tsang Ho Leung assisted in the collection in Guam. This study was supported by RGC-CRF Project 460108 to P Ang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Uthicke.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, S.W., Cheang, C.C., Yeung, C.W. et al. Recent expansion led to the lack of genetic structure of Sargassum aquifolium populations in Southeast Asia. Mar Biol 161, 785–795 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2377-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2377-3