Abstract
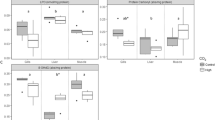
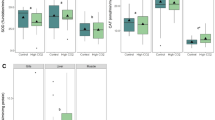
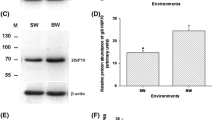
The jumbo squid, Dosidicus gigas, is an oceanic top predator in the eastern tropical Pacific that undergoes diel vertical migrations into mesopelagic oxygen minimum zones (OMZs). Besides glycogen breakdown, the pathways of the squid’s metabolic (suppression) strategy are poorly understood. Here, juvenile D. gigas were exposed to oxygen levels found in the OMZ off Gulf of California (1 % O2, 1 kPa at 10 °C) with the aim to identify, via proteomic tools, eventual anaerobic protein degradation as potential energy source at such depths. Under hypoxia, total protein concentration decreased nonsignificantly from 79.2 ± 12.4 mg g−1 wet mass to 74.7 ± 11.7 mg g−1 wet mass (p > 0.05). Yet, there was a significant decrease in heat-shock protein (Hsp) 90 and α-actinin contents (p < 0.05). The lower α-actinin concentration at late hypoxia was probably related to decreased protection of the Hsp90 chaperon machinery resulting in increased ubiquitination (p < 0.05) and subsequent degradation. Thus, the present findings indicate that D. gigas might degrade, at least under progressing hypoxia, specific mantle proteins anaerobically to increase/maintain anaerobic ATP production and extend hypoxia exposure time. Moreover, the ubiquitin–proteasome system seems to play an important role in hypoxia tolerance, but further investigations are necessary to discover its full potential and pathways.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almgren CM, Olson LE (1999) Moderate hypoxia increases heat shock protein 90 expression in excised rat aorta. J Vasc Res 36:363–371
Antonopoulou E, Kentepozicou E, Feidantsis K, Roufidou C, Despoti S, Chatzifotis S (2013) Starvation and re-feeding affect Hsp expression, MAPK activation and antioxidant enzymes activity of European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Comp Biochem Physiol A 165:79–88
Antonsson C, Whitelaw ML, McGuire J, Gustafsson J-A, Poellinger L (1995) Distinct roles of the molecular chaperone Hsp90 in modulating dioxin receptor function via the basic helix-loop-helix and PAS domains. Mol Cell Biol 15:756–765
Attaix D, Taillandier D (1998) The critical role of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in muscle wasting in comparison to lysosomal and Ca2+-dependent systems. Adv Mol Cell Biol 27:235–266
Attaix D, Combaret L, Pouch M-N, Taillandier D (2001) Regulation of proteolysis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 4:45–49
Bailey JR, Driedzic WR (1996) Decreased total ventricular and mitochondrial protein synthesis during extended anoxia in turtle heart. Am J Physiol 271:R1660–R1667
Bailey JL, Wang X, England BK, Price SR, Ding X, Mitch WE (1996) The acidosis of chronic renal failure activates muscle proteolysis in rats by augmenting transcription of genes encoding proteins of the ATP-dependent ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. J Clin Invest 97:1447–1453
Bickler PE, Buck LT (2007) Hypoxia tolerance in reptiles, amphibians, and fishes: life with variable oxygen availability. Annu Rev Physiol 69:145–170
Boone AN, Vijayan MM (2002) Constitutive heat shock protein 70 (HSC70) expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes: effect of heat shock and heavy metal exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol C: Toxicol Pharmacol 132:223–233
Boucher-Rodoni R, Mangold K (1985) Ammonia excretion during feeding and starvation in Octopus vulgaris. Mar Biol 86:193–197
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bruick RK (2013) Oxygen sensing in the hypoxic response pathway: regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor. Genes Devel 17:2614–2623
Buchner J (1999) Hsp90 & Co—a holding for folding. Trends Biochem Sci 24:136–141
Caplan AJ (1999) Hsp 90’s unfold: new insights from structural and functional studies. Trends Cell Biol 9:262–268
Cheng SH, So CH, Chan PK, Cheng CW, Wu RS (2003) Cloning of the HSP70 gene in barnacle larvae and its expression under hypoxic conditions. Mar Pollut Bull 46:665–671
Childress JJ, Mickel TJ (1980) A motion compensated shipboard precision balance system. Deep Sea Res 27:965–970
Chuang K-H, Ho S-H, Song Y-L (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of heat shock cognate 70 gene promoter in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Gene 405:10–18
Currie S, Moyes CD, Tufts B (2000) The effects of heat shock and acclimation temperature on Hsp 70 and Hsp30 mRNA expression in rainbow trout: in vivo and in vitro comparisons. J Fish Biol 56:398–408
De Zwaan A, Putzer V (1985) Metabolic adaptations of intertidal invertebrates to environmental hypoxia (a comparison of environmental anoxia to exercise anoxia). Symp Soc Exp Biol 39:33–62
Deane EE, Woo NYS (2003) Ontogeny of thyroid hormones, cortisol, Hsp70 and Hsp90 during silver sea bream larval development. Life Sci 72:805–818
Deng DF, Wang CF, Lee SH, Bai SC, Hung SSO (2009) Feeding rates affect heat shock protein levels in liver of larval white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Aquaculture 287:223–226
Dietz T (1994) Acclimation of the threshold induction temperatures for Hsp 70 and Hsp 90 in the fish Gyllicthys mirabilis. J Exp Biol 188:333–338
Douglas W, Friede A, Pickwell GV (1976) Fishes in oxygen minimum zones: blood oxygenation characteristics. Science 191:957–959
Falsone SF, Gesslbauer B, Tirk F, Piccinini A-M, Kungl AJ (2005) A proteomic snapshot of the human heat shock protein 90 interactome. FEBS Lett 579:6350–6354
Fang C-H, Wang JJ, Hobler S, Li BG, Fischer JE, Hasselgren P-O (1998) Proteasome blockers inhibit protein breakdown in skeletal muscle after burn injury in rats. Clin Sci 95:225–233
Feidantsis K, Pörtner HO, Lazou A, Kostoglou B, Michaelidis B (2009) Metabolic and molecular stress responses of the gilthead sea bream Sparus aurata during long term exposure to increasing temperatures. Mar Biol 156:797–809
Feidantsis K, Antonopoulou E, Lazou A, Pörtner HO, Michaelidis B (2012) Seasonal variations of cellular stress response of the gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). J Comp Physiol B doi:10.1007/s00360-012-0735-y
Francis T, Sukumaran N (1992) Influence of salinity on energy utilization of Etroplus suratensis (Bloch). J Aquacult Trop 7:21–26
Fraser KPP, Houlihan DF, Lutz PL, Leone-Kabler S, Manuel L, Brechin JG (2001) Complete suppression of protein synthesis during anoxia with no post-anoxia protein synthesis debt in the red-eared slider turtle Trachemys scripta elegans. J Exp Biol 204:4353–4360
Gerber HP, Condorelli F, Park J (1997) Differential transcriptional regulation of the two vascular endothelial growth factor receptor genes. Flt-1, but not Flk-1/KDR, is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 272:23659–23667
Gilly WF, Markaida U, Baxter CH, Block BA, Boustany A, Zeidberg L, Reisenbichler K, Robison B, Baxxino G, Salinas C (2006) Vertical and horizontal migrations by the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas revealed by electronic tagging. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 324:1–17
Grieshaber MK, Hardewig I, Kreutze U, Pörtner HO (1994) Physiological and metabolic responses to hypoxia in invertebrates. Rev Physiol Bioch P 125:43–147
Grigoriou P, Richardson CA (2009) Effect of body mass, temperature and food deprivation on oxygen consumption rate of common cuttlefish. Sepia officinalis Mar Biol 156:2437–2481
Guppy M, Withers P (1999) Metabolic depression in animals: physiological perspectives and biochemical generalizations. Biol Rev 74:1–40
Guppy M, Fuery CJ, Flanigan JE (1994) Biochemical principles of metabolic depression. Comp Biochem Physiol B 109:175–189
Han D, Huang SSY, Wang W-F, Deng D-F, Hung SSO (2012) Starvation reduces the heat shock protein responses in white sturgeon larvae. Environ Biol Fish 93:333–342
Hawkins AJS (1991) Protein turnover: a functional appraisal. Funct Ecol 5:222–233
Hendrick JP, Hartl FU (1993) Molecular chaperone functions of heat shock proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 62:349–384
Hochachka PW, Mommsen TP (1983) Protons and anaerobiosis. Science 219:1391–1397
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (1973) Strategies of biochemical adaptation. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, WB
Hochachka PW, Somero GN (2002) Biochemical adaptation: mechanisms and process in physiological evolution. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Höhfeld J, Cyr DM, Patterson C (2001) From cradle to the grave: molecular chaperones that may choose between folding and degradation. EMBO Rep 2:885–890
Houlihan DF, Kelly K, Boyle PR (1998) Correlates of growth and feeding in laboratory-maintained Eledone cirrhosa (Cepalopoda: Octopoda). J Mar Biol Assoc UK 78:919–932
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF (1998) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:7987–7992
Isaacs JS, Jung Y-J, Mimnaugh EG, Martinez A, Cuttitta F, Neckers LM (2002) Hsp90 regulates a von Hippel Lindau-independent hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-degradative pathway. J Biol Chem 277:29936–29944
Kallio PJ, Wilson WJ, O’Brien S, Makino Y, Tanaka H, Poellinger L (1998) Regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor 1α by the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. J Biol Chem 274:6519–6525
Kee AJ, Combaret L, Tilignac T, Souweine B, Aurousseau E, Dalle M, Taillandier D, Attaix D (2003) Ubiquitin–proteasome-dependent muscle proteolysis responds slowly to insulin release and refeeding in starved rats. J Physiol 546:765–776
Lamarre SG, Ditlecadet D, McKenzie DJ, Bonnaud L, Driedzic WR (2012) Mechanisms of protein degradation in mantle muscle and proposed gill remodeling in starved Sepia officinalis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303:R427–R437
Land SC, Buck LT, Hochachka PW (1993) Response of protein synthesis to anoxia and recovery in anoxia-tolerant hepatocytes. Am J Physiol 265:R41–R48
McGuire J, Whitelaw ML, Pongratz I, Gustafsson J-A, Poellinger L (1994) A cellular factor stimulates ligand-dependent release of Hsp90 from the basic helix-loop-helix dioxin receptor. Mol Cell Biol 14:2438–2446
Medina R, Wing SS, Goldberg AL (1995) Increase in levels of polyubiquitin and proteasome mRNA in skeletal muscle during starvation and denervation atrophy. Biochem J 307:631–637
Melzner F, Mark FC, Pörtner HO (2007) Role of blood-oxygen transport in thermal tolerance of the cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. Integr Comp Biol 47:645–655
Minet E, Mottet D, Michel G, Roland I, Raes M, Remacle J, Michiels C (1999) Hypoxia-induced activation of HIF-1: role of HIF-1α-Hsp90 interaction. FEBS Lett 460:251–256
Mitch WE, Goldberg AL (1996) Mechanisms of muscle wasting—the role of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. N Engl J Med 335:1897–1905
Mosser DD, Theodorakis NG, Morimoto RI (1988) Coordinate changes in heat shock element-binding activity and HSP70 gene transcription rates in human cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:4736–4744
O’Dor RK, Webber DM (1986) The constraints on cephalopods: why squid aren’t fish. Can J Zool 64:1591–1605
O’Dor RK, Mangold K, Wells MJ, Wells J, Boucher-Rodon R (1984) Nutrient absorption, storage and remobilization in Octopus vulgaris. Mar Behav Physiol 11:239–258
Otey CA, Carpen O (2004) Alpha-actinin revisited: a fresh look at an old player. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 58:104–111
Pickart CM (2001) Mechanisms underlying ubiquitination. Annu Rev Biochem 70:503–533
Pörtner HO (1994) Coordination of metabolism, acid-base regulation and haemocyanin function in cephalopods. Mar Fresh Behav Physiol 25:131–148
Pörtner HO (2002) Environmental and functional limits to muscular exercise and body size in marine invertebrates athletes. Comp Biochem Physiol A 133:303–321
Pörtner HO, Finke E, Lee PG (1996) Metabolic and energy correlates of intracellular pH in progressive fatigue of squid (L. brevis) mantle muscle. Am J Physiol 271:R1403–R1414
Pratt WB, Toft DO (2003) Regulation of signaling protein function and trafficking by the Hsp90/Hsp70-based chaperone machinery. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 217:420–434
Pratt WB, Morishima Y, Peng H-M, Osawa Y (2010) Proposal for a role of the Hsp90/Hsp70-based chaperon machinery in making triage decisions when proteins undergo oxidative and toxic damage. Exp Biol Med 235:278–289
Price SR, Bailey JL, Wang X, Jurkovitz C, England BK, Ding X, Phillips LS, Mitch WE (1996) Muscle wasting in insulinopenic rats, results from activation of the ATP-dependent, ubiquitin–proteasome proteolytic pathway by a mechanism including gene transcription. J Clin Invest 98:1703–1708
Pruski AM, Fiala-Medioni A, Fisher CR, Colomines JC (2000) Composition of free amino acids and related compounds in invertebrates with symbiotic bacteria at hydrocarbon seeps in the Gulf of Mexico. Mar Biol 136:411–420
Randall DJ, Wright PA (1987) Ammonia distribution and excretion in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 3:107–120
Rosa R, Seibel BA (2008) Synergistic effects of climate-related variables suggests future physiological impairment in a top oceanic predator. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:20776–20780. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806886105
Rosa R, Seibel BA (2010) Metabolic physiology of the Humboldt squid, Dosidicus gigas: implications for vertical migration in a pronounced oxygen minimum zone. Prog Oceanogr 86:72–80
Rosa R, Costa PR, Nunes ML (2004) Effect of sexual maturation in the tissue biochemical composition of Octopus vulgaris and O. defilippi (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Mar Biol 145(3):563–574
Rosa R, Costa PR, Bandarra N, Nunes ML (2005a) Changes in tissue biochemical composition and energy reserves associated with sexual maturation in the ommastrephid squids Illex coindetii and Todaropsis eblanae. Biol Bull 208(2):100–113
Rosa R, Costa PR, Bandarra N, Nunes ML (2005b) Changes in tissue biochemical composition and energy reserves associated with sexual maturation in the ommastrephid squids Illex coindetii and Todaropsis eblanae. Biol Bull 208(2):100–113
Schmidt-Nielsen K (1975) Animal physiology: adaptation and the environment. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Seibel BA (2011) Critical oxygen levels and metabolic suppression in oceanic oxygen minimum zones. J Exp Biol 214:326–336
Seibel BA (2013) The jumbo squid, Dosidicus gigas (Ommastrephidae), living in oxygen minimum zones II: blood-oxygen binding. Deep Sea Res Part II. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.10.003
Shulman GE, Abolmasova GI, Muravskaya ZA (1993) Protein utilization in energy metabolism of hydrobionts. Usp Sovrem Biol 113:576–586
Shulman GE, Chesalin MV, Abolmasova GI, Yuneva TV, Kideys A (2002) Metabolic strategy in pelagic squid of genus Sthenoteuthis (Ommastrephidae) as the basis of high abundance and productivity: an overview of the Soviet investigations. Bull Mar Sci 71:815–836
Sjöblom B, Salmazo A, Djinovic-Carugo K (2008) α-Actinin structure and regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2688–2701
Smith DF (1993) Dynamics of heat shock protein 90-progesterone receptor binding and the disactivation loop model for steroid receptor complexes. Mol Endocrinol 7:1418–1429
Smith RW, Houlihan DF, Nilsson GE, Brechin JG (1996) Tissue-specific changes in protein synthesis rates in vivo during anoxia in crucian carp. Am J Physiol 271:R897–R904
Spees JL, Chang SA, Snyder MJ, Chang ES (2002) Osmotic induction of stress-responsive gene expression in the lobster Homarus americanus. Biol Bull 203:331–337
Squire JM (1997) Architecture and function in the muscle sarcomere. Curr Opin Struct Biol 7:247–257
Storey KB, Storey JM (1983) Carbohydrate metabolism in cephalopod molluscs. In: Hochachka PW (ed) The mollusca. Academic Press, London, pp 92–137
Stramma L, Johnson GC, Sprintall J, Mohrholz V (2008) Expanding oxygen-minimum zones in the tropical oceans. Science 320:655–658
Sukumaran N, Kutty MN (1977) Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion in the catfish Mystus armatus, with special reference to swimming speed and ambient oxygen. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad B 86:195–206
Svetlichny LS, Gubareva ES, Arashkevich EG (1998) Physiological and behavioural response to hypoxia in active and diapausing stage V copepodites of Calanus euxinus. Adv Limnol Arch Hydrobiol Spec Issue 52:507–519
Trübenbach K, Teixeira T, Diniz M, Rosa R (2012) Hypoxia tolerance and antioxidant defense system of jumbo squids in oxygen minimum zones. Deep-Sea Res Part II. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2012.10.001
Trübenbach K, Pegado RM, Seibel BA, Rosa R (2013) Ventilation rates and activity levels of jumbo squids under metabolic suppression in the oxygen minimum zones. J Exp Biol 216:359–368
Vijayan MM, Aluru N, Maule AG, Jørgensen EV (2006) Fasting augments PCB impact on liver metabolism in anadromous arctic char. Toxicol Sci 91:431–439
Whitelaw M, Gottlicher M, Gustafsson J-A, Poellinger L (1993) Definition of a novel ligand binding domain of a nuclear bHLH receptor: co-localization of ligand and Hsp90 binding activities within the regulable inactivation domain of the dioxin receptor. EMBO J 12:4169–4179
Wing SS, Haas AL, Goldberg AL (1995) Increase in ubiquitin–protein conjugates concomitant with the increase in proteolysis in rat skeletal muscle during starvation and atrophy denervation. Biochem J 307:639–645
Yamuna A, Kabila V, Geraldine P (2000) Expression of heat shock protein 70 in freshwater prawn Macrobrachium malcolmsonii (H. Milne Edwards) following exposure to Hg and Cu. Indian J Exp Biol 38:921–925
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Brad Seibel for making the participation in the research cruise aboard RV New Horizon possible, and Unai Markaida for his assistance in collecting the specimens. We also thank IPATIMUP (Porto, Portugal) for help processing our samples. This work was supported by research grants to R.R. from the Portugal–US Research Networks Program (FLAD/US National Science Foundation Research Grant) and The Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT, Ciência 2007 Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.-O. Pörtner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trübenbach, K., da Costa, G., Ribeiro-Silva, C. et al. Hypoxia-driven selective degradation of cellular proteins in jumbo squids during diel migration to the oxygen minimum zones. Mar Biol 161, 575–584 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2360-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2360-z