Abstract
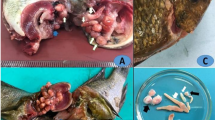
Cymothoa borbonica prevalence in the buccal cavity of Trachinotus botla was high, with 45 % of all fish sampled being infected. Smaller fish were more susceptible to infection with no parasites found in fish over 400 mm FL. The detrimental effects of parasite infection on their hosts include basihyal (the bone commonly known as the “tongue”) damage, a loss in buccal cavity volume as a result of female parasite attachment, and a severe impact on host growth. By combining short-term dietary analysis and medium-term stable isotope analysis, there was little evidence to suggest a modification in either the diet or feeding habits of infected fish where infected and uninfected fish occupied the same trophic niche. Inhibited growth in infected fish is hypothesized to be from respiratory distress from long-term oxygen deficiency through buccal obstruction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakenhaster MD, McBride RS, Price WW (2006) Life history of Glossobius hemiramphi (Isopoda: Cymothoidae): development, reproduction, and symbiosis with its host Hemiramphus brasiliensis (Pisces: Hemiramphidae). J Crustac Biol. doi:10.1651/c-2573.1
Brusca RC (1981) A monograph on the isopod Cymothoidae (Crustacea) of the eastern Pacific. Zool J Linn Soc. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1981.tb01592.x
Brusca RC, Gilligan MR (1983) Tongue replacement in a marine fish (Lutjanus guttatus) by a parasitic isopod (Crustacea: Isopoda). Copeia 3:813–816
Buchmann K, Lindenstrøm T (2002) Interactions between monogenean parasites and their fish hosts. Int J Parasitol 32:309–319
Bunkley-Williams L, Williams EH Jr (1998) Isopods associated with fishes: a synopsis and corrections. J Parasitol 84:893–896
Chavez-Lopez R, Rocha-Ramirez A, Alvarez F, Wetzer R (2005) Isopoda (Cymothoidae) parasitizing the inshore lizardfish, Synodus foetens (linnaeus, 1766) on the continental shelf off central Veracruz, Mexico. Crustac Int J Crustac Res 78:865–872
Colorni A, Trilles JP, Golani D (1997) Livoneca sp. (Flabellifera: Cymothoidae), an isopod parasite in the oral and branchial cavities of the Red Sea silverside Atherinomorus lacunosus (Perciformes, Atherinidae). Dis Aquat Org 31:65–71
Efron B (1979) Bootstrap methods: another look at the jackknife. Ann Stat 7:1–26
Fogelman R, Kuris AM, Grutter AS (2009) Parasitic castration of a vertebrate: effect of the cymothoid isopod, Anilocra apogonae, on the five-lined cardinalfish, Cheilodipterus quinquelineatus. Int J Parasit 39:577–583
Froese R (2006) Cube law, condition factor and weight–length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J Appl Ichthyol. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0426.2006.00805.x
Hadfield KA, Bruce NL, Smit NJ (2011) Cymothoa hermani spp. (Isopoda, Cymothoidae, Crustacea), a parasitic isopod, collected off the Zanzibar coast, Tanzania from the mouth of a parrotfish (Scaridae). Zootaxa 2876:57–68
Horton T, Okamura B (2001) Cymothoid isopod parasites in aquaculture: a review and case study of a Turkish sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and sea bream (Sparus auratus) farm. Dis Aquat Org 46:181–188
Hyslop EJ (1980) Stomach contents analysis: a review of methods and their application. J Fish Biol 17:411–429
Jackson AL, Inger R, Parnell AC, Bearhop S (2011) Comparing isotopic niche widths among and within communities: SIBER—Stable Isotope Bayesian Ellipses in R. J Anim Ecol 80:595–602
Layman CA, Arrington DA, Montana CG, Post DM (2007) Can stable isotope ratios provide for community-wide measures of trophic structure? Ecology 88:42–48
Leonardos I, Trilles JP (2003) Host-parasite relationships: occurrence and effect of the parasitic isopod Mothocya epimerica on sand smelt Atherina boyeri in the Mesolongi and Etolikon Lagoons (W. Greece). Dis Aquat Org 54:243–251
Man HSH, Hodgkiss IJ (1977) Studies on the ichthyo-fauna in Plover Cove Reservoir, Hong Kong: feeding and food relations. J Fish Biol 11:1–13
Marcogliese DJ (2005) Parasites of the superorganism: are they indicators of ecosystem health? Int J Parasitol 35:705–716
Marcogliese DJ, Cone DK (1997) Parasite communities as indicators of ecosystem stress. Parassitologia 39:227–232
Marks RE, Juanes F, Hare JA, Conover DO (1996) Occurrence and effect of the parasitic isopod, Lironeca ovalis (Isopoda: Cymothoidae), on young-of-the-year bluefish, Pomatomus saltatrix (Pisces: Pomatomidae). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:2052–2057
Parker D (2012) The life history and fishery assessment of largespot pompano, Trachinotus botla, in northern KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Masters thesis, Rhodes University, Grahamstown, South Africa
Scholz T (1999) Parasites in cultured and feral fish. Vet Parasitol 84:317–335
Sievers G, Lobos C, Inostroza R, Ernst S (1996) The effect of the isopod parasite Ceratothoa gaudichaudii on the body weight of farmed Salmo salar in southern Chile. Aquaculture 143:1–6
Turner TF, Collyer ML, Krabbenhoft TJ (2010) A general hypothesis-testing framework for stable isotope ratios in ecological studies. Ecology 91:2227–2233
Williams EH Jr, Bunkley-Williams L (2000) On the generic placement of ‘Livoneca sp’. a critique of Colorni et al. (1997). Dis Aquat Org 40:233–234
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of South Africa’s African Coelacanth Ecosystem Programme and Rhodes University. The iSimangaliso Wetland Park is thanked for allowing access for this study. Matt Parkinson and Reece Wartenberg are thanked for assisting with the research. Bruce Mann is thanked for his advice and guidance in data collection. All anglers are thanked for assisting with the collection of fish for research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Reusch.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parker, D., Booth, A.J. The tongue-replacing isopod Cymothoa borbonica reduces the growth of largespot pompano Trachinotus botla . Mar Biol 160, 2943–2950 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2284-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2284-7