Abstract
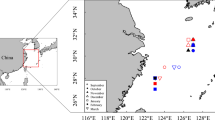
We applied the solution-based inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry to quantify trace elements in statoliths of Humboldt squid, Dosidicus gigas, collected from the high seas off Chile, Peru, and Costa Rica by Chinese squid jigging vessels during 2007–2009. All squid samples were aged and their spawning dates were back-calculated based on daily increments in statoliths. The most abundant trace elements in the whole statolith were Ca and Sr followed by other elements in the order of Fe, Mg, Zn, Ba, Cu, Mn, Ni, Al, Cr, Co, and U. Significant differences in Mn and Sr were found among samples from the three regions. Sr, Ni, Mn, and Co contributed significantly to the discrimination among the regions, with Co responsible for explaining most of the variation, followed by Ni, Mn, and Sr. Squid from the high seas off Costa Rica could be separated from those off Peru and Chile mostly due to the differences in Ni, Sr, and Co, while samples off Peru and Chile could be distinguished mainly because of differences in Mn and Co. Discriminant function analysis suggested that the overall cross-validated classification rate was 85.6 % with samples off Chile having the highest correct identification rates and samples off Costa Rica having the highest false classification rates. Significant positive relationships were found between sea surface temperature (SST) and Cr/Ca, Mn/Ca, and U/Ca, and there was a negative relationship between SST and Cu/Ca, Sr/Ca. This study suggests that the spatial difference in trace elements of statolith can be used to separate geographic populations of D. gigas and that elements having significant relationships with SST can be considered as natural indicators of ambient temperature.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arkhipkin AI (2005) Statolith as ‘black boxes’(life recorders) in squid. Mar Freshw Res 56:573–583
Arkhipkin AI, Campana SE, FitzGerald J, Thorrold SR (2004) Spatial and temporal variation in elemental signatures of statoliths from the Patagonian longfin squid (Loligo gahi). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 61:1212–1224
Ashford JR, Jones CM, Hofman E, Everson I, Moreno C, Duhamel G, Villiams R (2005) Can otolith elemental signature record the capture site of Patagonian toothfish Dissostichus eleginoides, a fully marine fish in the southern ocean? Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:2832–2840
Bath GE, Thorrold SR, Jones CM, Campana SE, McLaren JW, Lam JWH (2000) Sr and Ba uptake in aragonitic otolith of marine fish. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1705–1714
Beck JW, Edwards RL, Ito E, Frederick W, Jacques R, Francis R, Pascale J, Christian H (1992) Sea-surface temperature from coral skeletal strontium/calcium ratios. Science 257:644–647
Becker BJ, Fodrie FJ, McMillan PA, Levin LA (2005) Spatial and temporal variation in trace elemental fingerprints of mytilid mussel shells: a precursor to invertebrate larval tracking. Limnol Oceanogr 50:48–61
Begg GA, Cappo M, Cameron DS, Boyle S, Sellin MJ (1998) Stock discrimination of school mackerel, Scomberomorus queenslandicus, and spotted mackerel, Scomberomorus munroi, in coastal waters of eastern Australia by analysis of minor and trace elements in whole otoliths. Fish Bull 96:653–666
Benites C, Valdivieso V (1986) Resultados de la pesca exploratoria de 1979/80 y desembarque de cefalópodos pelágicos en el litoral Peruano. Bol Inst Mar del Perú 10:107–139
Bettencourt V, Guerra A (1999) Carbon- and oxygen-isotope composition of the cuttlebone of Sepia officinalis: a tool for predicting ecological information? Mar Biol 133:651–657
Bruland KW, Donat JR, Hutchins DA (1991) Interactive influences of bioactive trace metals on biological production in oceanic waters. Limnol Oceanogr 36:1555–1577
Campana SE (1999) Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: pathways, mechanisms and applications. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 188:263–297
Campana SE, Gagne JA, McLaren JW (1995) Elemental fingerprinting of fish otoliths using ID-ICPMS. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 122:115–120
Campana SE, Chouinard GA, Hanson JM, Fréchet A, Brattey J (2000) Otolith elemental fingerprints as biological tracers of fish stocks. Fish Res 46:343–357
Chen XJ, Zhao XH (2005) Catch distribution of jumbo flying squid and its relationship with SST in the offshore waters of Chile. Mar Fish 27:173–176 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Chen XJ, Li JH, Liu BL, Chen Y, Li G, Fang Z, Tian SQ (2013) Age, growth and population structure of Jumbo flying squid, Dosidicus gigas, off the Costa Rica Dome. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 93:567–573
Cherel Y, Hobson K (2005) Stable isotopes, beaks and predators: a new tool to study the trophic ecology of cephalopods, including giant and colossal squids. Proc R Soc Lond B 272:1601–1607
Clarke R, Paliza O (2000) The Humboldt current squid Dosidicus gigas (Orbigny, 1835). Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 35:1–38
Correia AT, Pipa T, Gonçalves JMS, Erzini K, Hamer PA (2011) Insights into population structure of Diplodus vulgaris along the SW Portuguese coast from otolith elemental signatures. Fish Res 111:82–91
Dawe EG, Natsukari Y (1991) Light microscopy. In: Jereb P, Ragonese S, Boletzky SV (eds) Squid age determination using statoliths. Proceedings of the international workshop held in the Istituto di Tecnologia della Pesca e del Pescato, Special publication, pp 83–95
Doubleday ZA, Pecl GT, Semmens JM, Danyushevsky L (2008a) Stylet elemental signatures indicate population structure in a holobenthic octopus species, Octopus pallidus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 371:1–10
Doubleday ZA, Pecl GT, Semmens JM, Danyushevsky L (2008b) Using stylet elemental signatures to determine the population structure of Octopus maorum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 360:125–133
Hanlon RT, Bidwell JP, Tait R (1989) Strontium is required for statolith development and thus normal swimming behavior of hatching cephalopods. J Exp Biol 141:187–195
Ichii T, Mahapatra K, Watanabe T, Yatsu A, Inagake D, Okada Y (2002) Occurrence of jumbo fying squid Dosidicus gigas aggregations associated with the countercurrent ridge off the Costa Rica Dome during 1997 El Niño and 1999 La Niña. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 231:151–166
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W (1995) Preliminary report on the PIXE analysis of the squid statoliths. Int J PIXE 5:159–162
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W, Kidokoro H, Yoshida K (1996a) Relationship between statoliths and environmental variables in cephalopods. Int J PIXE 6:339–345
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W, Nateewathana A, Murayama T, Yatsu A, Yoshida K (1996b) PIXE analysis of trace elements in squid statoliths: compositon between Ommastrephidae and Loliginidae. Int J PIXE 6:537–542
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W, Kidokoro H, Yatsu A, Nateewathana A, Yoshida K (1997) Comparison on trace elements in squid statoliths of different species origin as available key for taxonomic and phylogenetic study. Int J PIXE 7:141–146
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W, Kidokoro H, Yoshida K (1998) Microchemistry of the statoliths of the Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus with special reference to it relation to the vertical temperature profiles of squid habitat. Fish Sci 64(2):179–184
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Sakamoto W, Kidokoro H, Mitsuhashi M, Yoshida K (1999) Preliminary report on PIXE analysis for trace elements of Octopus dofleini statoliths. Fish Sci 65:161–162
Ikeda Y, Yatsu A, Arai N, Sakamoto W (2002) Concentration of statolith trace elements in the jumbo flying squid during El Niño and non-El Niño years in the eastern Pacific. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 82:863–866
Ikeda Y, Arai N, Kidokoro H, Sakamoto W (2003) Strontium:calcium ratios in statoliths of Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) as indicators of migratory behaviour. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 251:169–179
Lea DW, Shen GT, Boly EA (1989) Coralline barium records temporal variability in equatorial Pacific upwelling. Nat 340:373–376
Lipinski MR, Underhill LG (1995) Sexual maturation in squid: quantum or continuum. S Afr J Mar Sci 15:207–223
Liu BL, Chen XJ, Ma J, Qian WG (2010) Review of studies of the microchemical structure of cephalopod statoliths. J Fish China 34:316–321 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Liu BL, Chen XJ, Lu HJ, Qian WG (2011) Trace elements in the statoliths of jumbo flying squid off the exclusive economic zones of Chile and Peru. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 420:93–101
Lukeneder A, Harzhauser M, Müllegger S, Piller WE (2008) Stable isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) in Spirula shells from three major oceans indicate developmental changes paralleling depth distributions. Mar Biol 154:175–182
Ma J (2010) Statolith microstructure and microchemistry of the neon flying squid, Ommastrephes bartramii, in the Northwest Pacific Ocean. MS Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, China, p 82 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Morris CC (1991) Statocyst fluid composition and its effects on calcium carbonate precipitation in the squid Alloteuthis subulata (Lamarck, 1798): towards a model for biomineralization. Bull Mar Sci 49:379–388
Nevárez-Martínez MO, Hernández-Herrera A, Morales-Bojórquez E, Balmori-Ramírez A, Cisneros-Mata MA, Morales-Azpeitia R (2000) Biomass and distribution of the jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas; d’Orbigny, 1835) in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Fish Res 49:129–140
Nigmatullin C, Nesis KN, Arkhipkin AI (2001) A review of the biology of the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae). Fish Res 54:9–19
Nishimoto MM, Washburn L, Warner RR, Love MS, Paradis GL (2010) Otolith elemental signatures reflect residency in coastal water masses. Environ Biol Fish 89:341–356
Rocha F, Vega M (2003) Overview of cephalopod fisheries in Chilean waters. Fish Res 60:151–159
Rodhouse PG, Robinson K, Gajdatsy SB, Daly HI, Ashmore MJS (1994) Growth, age structure and environmental history in the cephalopod Martialia hyadei (Teuthoidea: Ommastrephidae) at the Atlantic Polar Frontal Zone and on the Patagonian Shelf Edge. Antarct Sci 6:259–267
Rooker JR, Secor DH, Zdanowicz VS, Itoh T (2001) Discrimination of northern bluefin tuna from nursery areas in the Pacific Ocean using otolith chemistry. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 218:275–282
Sandoval-Castellanos E, Uribe-Alcocer M, Díaz-Jaimes P (2007) Population genetic structure of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) evaluated by RAPD analysis. Fish Res 83:113–118
Shen GT, Dunbar RB (1995) Environmental controls on uranium in reef corals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:2009–2024
Silva N, Rojas N, Fedele A (2009) Water masses in the Humboldt Current System: properties, distribution, and the nitrate deficit as a chemical water mass tracer for equatorial subsurface water off Chile. Deep-sea Res PT II 56:1004–1020
Staaf DJ, Ruiz-Cooley RI, Elliger C, Lebaric Z, Campos B, Markaida U, Gilly WF (2010) Ommastrephid squids Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis and Dosidicus gigas in the eastern Pacific show convergent biogeographic breaks but contrasting population structures. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 418:165–178
Swart PK, Elderfield H, Greaves MJ (2002) A high-resolution calibration of Sr/Ca thermometry using the Caribbean coral Montastraea annularis. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 3:1–11
Taipe A, Yamashiro C, Mariategui L, Rojas P, Roque C (2001) Distribution and concentrations of jumbo flying squid (Dosidicus gigas) off the Peruvian coast between 1991 and 1999. Fish Res 54:21–32
Waluda CM, Yamashiro C, Elvidge CD, Hobson VR, Rodhouse PG (2004) Quantifying light-fishing for Dosidicus gigas in the eastern Pacific using satellite remote sensing. Remote Sens Environ 91:129–133
Warner RR, Hamilton SL, Sheehy MS, Zeidberg LD, Brady BC, Caselle JE (2009) Geographic variation in natal and early larval trace-elemental signatures in the statoliths of the market squid Doryteuthis (formerly Loligo) opalescens. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 379:109–121
Yamane K, Shirai K, Nagakura Y, Yamaguchi M, Takiya A, Horii T, Tanaka N, Yamane S, Arai T, Otake T (2010) Spatial variation of otolith elemental compositions in Pacific herring Clupea pallasii. Aquat Biol 10:293–300
Yatsu A, Midorikawa S, Shimada T, Uozumi Y (1997) Age and growth of the neon flying squid, Ommastrephes bartramii, in the North Pacific Ocean. Fish Res 29:257–270
Yatsu A, Mochioka N, Morishita K, Toh H (1998) Strontium/calcium ratios in statoliths of the neon flying squid, Ommastrephes bartrami (Cephalopoda), in the North Pacific Ocean. Mar Biol 131:275–282
Ye XC, Chen XJ (2007) Study of mantle length composition and maturity of jumbo flying squid (Dosidicus gigas) in fishing ground off Peru. J Shanghai Fish Univ 16(4):347–350 (In Chinese with English Abstract)
Zacherl DC (2005) Spatial and temporal variation in statolith and protoconch trace elements as natural tags to track larval dispersal. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 290:145–163
Zacherl DC, Paradis GD, Lea DW (2003) Barium and strontium uptake into larval protoconchs and statoliths of the marine neogastropod Kelletia kelletii. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:4091–4099
Zumholz K, Hansteen TH, Klügel A, Piatkowski U (2006) Food effects on statolith compositon of the common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Mar Biol 150:237–244
Zumholz K, Hansteen TH, Piatkowski U, Croot PL (2007a) Influence of temperature and salinity on the trace element incorporation into statoliths of the common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis). Mar Biol 151:1321–1330
Zumholz K, Klügel A, Hansteen TH, Piatkowski U (2007b) Statolith microchemistry traces environmental history of the boreoatlantic armhook squid Gonatus fabricii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 333:195–204
Zúñiga MJ, Cubillos LA, Ibáñez C (2008) A regular pattern of periodicity in the monthly catch of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) along the Chilean coast (2002–2005). Cien Mar 34:91–99
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences for element analyses. This work was funded by National Science Foundation of China (NSFC41276156), State 863 projects (2012AA092303), the innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (13YE091), and Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (Fisheries Discipline, Code A). Y. Chen was supported by Shanghai Oversea Teaching Scholar Program and SHOU International Center for Marine Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by U. Sommer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Chen, X., Chen, Y. et al. Geographic variation in statolith trace elements of the Humboldt squid, Dosidicus gigas, in high seas of Eastern Pacific Ocean. Mar Biol 160, 2853–2862 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2276-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-013-2276-7