Abstract
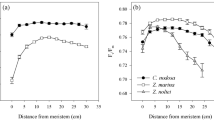
The photoacclimation capacity of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa was evaluated considering temporal (i.e. seasonal) and spatial (i.e. depth and within-leaf position) factors of variation. Changes along the leaf were measured in a population growing along a depth gradient (from intertidal to subtidal) in Cadiz Bay (Southern Spain) from 2004 to 2005. Photoacclimation was evaluated by photosynthesis (P–E curves), pigment content and leaf morphology. Plants of Cymodocea nodosa showed large physiological and morphological plasticity (mean %CV = 35.8 ± 3.4) according to the three factors considered. Seasonal patterns appeared for photosynthesis, respiration, pigment content and morphology. Nevertheless, seasonal patterns were not consistent with depth or leaf portions. The resulting data set offered different information depending on the analysis conducted; when only one factor (season, depth or leaf portion) was considered, some tendencies observed in the 3-way full design were masked. Accordingly, considering spatio–temporal variability is crucial when describing photoacclimation and estimating productivity in seagrass meadows.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberto F, Gouveia L, Arnaud-Haond S, Pérez-Lloréns JL, Duarte CM, Serrão EA (2005) Within-population spatial genetic structure, neighbourhood size and clonal subrange in seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Mol Ecol 14:2669–2681
Alcoverro T, Manzanera M, Romero J (1998) Seasonal and age-dependent variability of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile photosynthetic parameters. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 230:1–13
Alvarez O, Izquierdo A, Tejedor B, Mañanes R, Tejedor L, Kagan BA (1999) The influence of sediment load on tidal dynamics, a case study: Cadiz Bay. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 48:439–450
Bay D (1984) A field study of the growth dynamics and productivity of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in Calvi bay, Corsica. Aquat Bot 20:43–64
Björkman O (1981) Responses to different quantum flux densities. In: Pirson A, Zimmermann MH (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology, vol 12A. Springer, Berlin
Boese BL, Robbins BD, Thursby G (2005) Desiccation is a limiting factor for eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) distribution in the intertidal zone of a northeastern Pacific (USA) estuary. Bot Mar 48:274–283
Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85:1771–1789
Brun FG, Hernández I, Vergara JJ, Peralta G, Pérez-Lloréns JL (2002) Assessing the toxicity of ammonium pulses to the survival and growth of Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 225:177–187
Brun FG, Olivé I, Malta E-j, Vergara JJ, Hernández I, Pérez-Lloréns JL (2008) Increased vulnerability of Zostera noltii to stress caused by low light and elevated ammonium levels under phosphate deficiency. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 365:67–75. doi:10.3354/meps07512
Bulthuis DA (1983) Effects of insitu light reduction on density and growth of the seagrass Heterozostera tasmanica (Martens Ex Aschers) Den Hartog in Western Port, Victoria, Australia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 67:91–103
Bulthuis DA (1987) Effects of temperature on photosynthesis and growth of seagrasses. Aquat Bot 27:27–40
Cayabyab NM, Enríquez S (2007) Leaf photoacclimatory responses of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum under mesocosm conditions. A mechanistic scaling-up study. New Phytol 176:108–123
Collier CJ, Lavery PS, Masini RJ, Ralph PJ (2007) Morphological, growth and meadow characteristics of the seagrass Posidonia sinuosa along a depth-related gradient of light availability. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 337:103–115
Dennison WC (1990) Chlorophyll content. In: Phillips RC, McRoy CP (eds) Seagrass research methods. UNESCO, Paris, pp 83–85
Dennison WC, Alberte RS (1982) Photosynthetic responses of Zostera marina L. (eelgras) to in situ manipulations of light intensity. Oecologia 55:137–144
Dennison WC, Alberte RS (1986) Photoadaptation and growth of Zostera marina L. (eelgrass) transplants along a depth gradient. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 98:265–282
Drew EA (1978) Factors affecting photosynthesis and its seasonal variation in the seagrasses Cymodocea nodosa (Ucria) Aschers, and Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile in the Mediterranean. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 31:173–194
Drew EA (1979) Physiological aspects of primary production in seagrasses. Aquat Bot 7:139–150
Duarte CM (1989) Temporal biomass variability and production biomass relationships of seagrass communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 51:269–276
Duarte C, Dennison W, Orth R, Carruthers T (2008) The charisma of coastal ecosystems: addressing the imbalance. Estuaries Coasts 31:233–238
Enríquez S, Pantoja-Reyes NI (2005) Form-function analysis of the effect of canopy morphology on leaf self-shading in the seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Oecologia 145:235–243
Enríquez S, Duarte CM, Sand-Jensen K (1995) Patterns in the photosynthetic metabolism of Mediterranean macrophytes. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 119:243–252
Enríquez S, Merino M, Iglesias-Prieto R (2002) Variations in the photosynthetic performance along the leaves of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum. Mar Biol 140:891–900
Enríquez S, Marbà N, Cebrián J, Duarte CM (2004) Annual variation in leaf photosynthesis and leaf nutrient content of four Mediterranean seagrasses. Bot Mar 47:295–306
Geider RJ, Osborne BA (1992) Algal photosynthesis. Chapman and Hall, New York
Herzka SZ, Dunton KH (1997) Seasonal photosynthetic patterns of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum in the western Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 152:103–117
Holmer M, Bondgaard EJ (2001) Photosynthetic and growth response of eelgrass to low oxygen and high sulfide concentrations during hypoxic events. Aquat Bot 70:29–38
Horton P, Ruban AV, Walters RG (1996) Regulation of light harvesting in green plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:655–684
Langdon C, Gattuso J-P, Andersson AJ (2010) Measurements of calcification and dissolution of benthic organisms and communities. In: Riebesell U, Fabry VJ, Hansson L, Gattuso J-P (eds) Guide to best practices in ocean acidification research and data reporting. Office for official publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg, pp 155–174
Lee KS, Dunton KH (1997) Effects of in situ light reduction on the maintenance, growth and partitioning of carbon resources in Thalassia testudinum Banks ex Kijnig. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 210:53–73
Lichtenthaler H, Wellburn A (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophyll a and b of leaf extract in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 603:591–592
Markager S, Sand-Jensen K (1994) The physiology and ecology of light-growth relationship in macroalgae. In: Round FE, Chapman DJ (eds) Progress in phycological research, vol 10. Biopress Ltd., Bristol, pp 209–298
Marquardt R, Schubert H, Varela DA, Huovinen P, Henríquez L, Buschmann AH (2010) Light acclimation strategies of three commercially important red algal species. Aquaculture 299:140–148. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.11.004
Marsh JAJ, Dennison WC, Alberte RS (1986) Effects of temperature on photosynthesis and respiration in eelgrass (Zostera marina L.). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 101:257–267
Mazzella L, Alberte RS (1986) Light adaptation and the role of autotrophic epiphytes in primary production of the temperate seagrass Zostera marina L. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 100:165–180
McCree KJ, Troughton JH (1966) Prediction of growth rate at different light levels from measured photosynthesis and respiration rates. Plant Physiol 41:559–566. doi:10.1104/pp.41.4.559
Murray L, Wetzel RL (1987) Oxygen production and consumption associated with the major autotrophic components in two temperate seagrass communities. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 38:231–239
Nellemann C, Corcoran E, Duarte CM, Valdés L, DeYoung C, Fonseca L, Grimsditch G (2009) Blue Carbon. The role of healthy oceans in binding carbon. UNEP, FAO and IOC/UNESCO, Norway
Olesen B, Sand-Jensen K (1993) Seasonal acclimatization of eelgrass Zostera marina growth to light. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 94:91–99
Olesen B, Enríquez S, Duarte CM, Sand-Jensen K (2002) Depth-acclimation of photosynthesis, morphology and demography of Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa in the Spanish Mediterranean Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 236:89–97
Olivé I, García-Sánchez MP, Brun FG, Vergara JJ, Pérez-Lloréns JL (2009) Interactions of light and organic matter under contrasting resource simulated environments: the importance of clonal traits in the seagrass Zostera noltii. Hydrobiologia 629:199–208
Orth RJ, Carruthers TJB, Dennison WC, Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL, Hughes AR, Kendrick GA, Kenworthy WJ, Olyarnik S, Short FT, Waycott M, Williams SL (2006) A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. Bioscience 56:987–996
Ott JA (1980) Growth and production of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile, P.S.Z.N.I. Mar Ecol 1:47–64
Pérez M, Romero J (1992) Photosynthetic response to light and temperature of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa and the prediction of its seasonality. Aquat Bot 43:51–62
Pérez M, Romero J, Duarte CM, Sand-Jensen K (1991) Phosphorus limitation of Cymodocea nodosa growth. Mar Biol 109:129–133
Pirc H (1986) Seasonal aspects of photosynthesis in Posidonia oceanica: influence of depth, temperature and light intensity. Aquat Bot 26:203–212
Ruíz JM, Romero J (2001) Effects of in situ experimental shading on the Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 215:107–120
Sand-Jensen K (1975) Biomass, net production and growth dynamics in an eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) population im Vellerup Vig, Denmark. Ophelia 14:185–201
Short F (1980) A simulation model of the seagrass production system. In: Phillips R, McRoy C (eds) Handbook of seagrass biology. An ecosystem perspective. Garland Press, New York, p 353
Terrados J, Duarte CM, Kamp-Nielsen L, Agawin NSR, Gacia E, Lacap D, Fortes MD, Borum J, Lubanski M, Greve T (1999) Are seagrass growth and survival constrained by the reducing conditions of the sediment? Aquat Bot 65:175–197
West RJ (1990) Depth-related structural and morphological variations in an Australian Posidonia seagrass bed. Aquat Bot 36:153–166
Zimmerman RC (2003) A bio-optical model of irradiance distribution and photosynthesis in seagrass canopies. Limnol Oceanogr 48:568–585
Acknowledgments
The financial support through the research projects CTM2005-00395/MAR and CTM2008-0012/MAR from the Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain is thankful. Authors thank Dr. G. Peralta and Dr. E.P. Morris for their help with in situ data. I. Olivé holds a postdoctoral grant from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology. This is CEIMAR journal publication no. 16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Bischof.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olivé, I., Vergara, J.J. & Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Photosynthetic and morphological photoacclimation of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa to season, depth and leaf position. Mar Biol 160, 285–297 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2087-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2087-2