Abstract
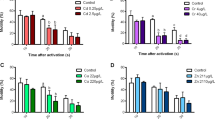
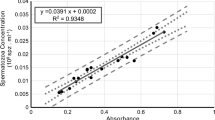
Blooms of the toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama cause massive bivalve kills in Japan. Mariculture of the Japanese pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata martensii, is the industry most affected by these blooms, especially in Ago Bay, Mie Prefecture, where they are frequent, cause mass mortality of oysters, and overlap with their spawning season. The goal of this August 2009 study was to assess the effects of a toxic strain of H. circularisquama isolated from Ago Bay on gametes, fertilization, and embryo development of pearl oysters. Spermatozoa, eggs, spermatozoa and eggs, and fertilized eggs of pearl oysters from Ago Bay were exposed to H. circularisquama at cell densities reported during the bloom (10–104 cells mL−1) for different periods of time. The concentration of H. circularisquama, exposure duration, and their interactions all had significant effects on gamete quality, fertilization, and embryo development. The motility and swimming velocity of spermatozoa, egg viability, fertilization, and embryo development rate were significantly reduced in all concentrations, with a cell density of 10 cells mL−1 determined to be the critical density of H. circularisquama for deleterious effects. This is the first evidence of inimical effects of an HAB species on bivalve spermatozoa upon direct exposure. Further field and laboratory studies are required to investigate the potential effects of H. circularisquama blooms on the reproduction and recruitment of Japanese pearl oysters and other bivalves.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basti L, Segawa S (2010) Mortality of the short-neck clam Ruditapes philippinarum induced by the toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. Fish Sci 76:625–631. doi:10.1007/s12562-010-0252-4
Basti L, Nagai K, Shimasaki Y, Oshima Y, Honjo T, Segawa S (2009) Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on the valve movement behavior of the Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Aquaculture 291:41–47. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.02.029
Basti L, Endo M, Segawa S (2011a) Physiological, pathological, and defense alterations in Manila clams (short-neck clams), Ruditapes philippinarum, induced by Heterocapsa circularisquama. J Shellfish Res 30:829–844. doi:10.2983/035.030.0324
Basti L, Go J, Higuchi K, Nagai K, Segawa S (2011b) Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on larvae of the pearl oyster Pinctada fucata martensii (Dunker, 1873). J Shellfish Res 30:177–186. doi:10.2983/035.030.0125
Berman FW, LePage KT, Murray TF (2002) Domoic acid and neurotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule neurons is controlled preferentially by the NMDA receptor Ca2+ influx pathway. Brain Res 924:20–29. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(01)03221-8
Bozzo MG, Ribes E, Sagrista E, Poquet M, Durfort M (1993) Fine structure of the spermatozoa of Crassostrea gigas (Mollusca, Bivalvia). Mol Reprod Dev 34:206–211. doi:10.1002/mdr.1080340213
Caldwell GS (2009) The influence of bioactive oxylipins from marine diatoms on invertebrate reproduction and development. Mar Drug 7:367–400. doi:10.3390/mrd7030367
Caldwell GS, Bentley MG, Olive PJW (2004) First evidence of sperm motility inhibition by the diatom aldehyde 2E,4E-decadienal. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 273:97–108. doi:10.3354/meps273097
Deguchi R, Morisawa M (2002) External Ca2+ is predominantly used for cytoplasmic and nuclear Ca2+ increases in fertilized oocytes of the marine bivalve Mactra chinensis. J Cell Sci 116:367–376. doi:10.1242/jcs.00221
Galimany E, Sulina I, Hégaret H, Ramón M, Wikfors GH (2008a) Experimental exposure of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis, L.) to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense: histology, immune responses, and recovery. Harmful Algae 7:702–711. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2008.02.006
Galimany E, Sulina I, Hégaret H, Ramón M, Wikfors GH (2008b) Pathology and immune responses of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) after an exposure to the harmful dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Harmful Algae 7:630–638. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2008.01.001
Garrido O, Gallardo CS (1996) Ultrastructure of sperms in bivalve molluscs of the Mytilidae family. Invertebr Repr Dev 29:95–102. doi:10.1080/07924259.1996.9672501
Granmo A, Havenhand J, Magnusson K, Svane I (1988) Effects of the planktonic flagellate Chrysochromulina polylepis Manton et Park on fertilization and early development of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis (L.) and the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 124:65–71. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(88)90206-7
Haberkorn H, Lambert C, Le Goïc N, Moal J, Suquet M, Guéguen M, Sunila I, Soudant P (2010) Effects of Alexandrium minutum exposure on nutrition-related processes and reproductive output in oysters Crassostrea gigas. Harmful Algae 9:427–439. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2010.01.003
Hégaret H, Wikfors GH (2005a) Effects of natural and field simulated blooms of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum upon hemocytes of Eastern oysters, Crassostrea virginica, from two different populations. Harmful Algae 4:201–209. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2003.12.005
Hégaret H, Wikfors GH (2005b) Time-dependent changes in hemocytes of Eastern oysters, Crassostrea virginica, and northern bay scallops, Argopecten irradians irradians, exposed to a culture strain of Prorocentrum minimum. Harmful Algae 4:187–199. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2003.12.004
Hégaret H, Wikfors GH, Shumway SE (2007) Diverse feeding responses of five species of bivalve mollusc when exposed to three species of harmful algae. J Shellfish Res 26:549–559. doi:10.2983/0730-8000(2007)26[549:DFROFS]2.0.CO;2
Hégaret H, Shumway SE, Wikfors GH, Pate S, Burkholder JM (2008) Potential transfer of harmful algae through relocation of bivalve molluscs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 361:169–181. doi:10.3354/meps07375
Heisler J, Gilbert PM, Burkholder JM, Anderson DM, Cochlan W, Dennison WC, Dortch Q, Gobler CJ, Heil CA, Humphries E et al (2008) Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: a scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 8:3–13. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2008.08.006
Horiguchi T (1995) Heterocapsa circularisquama sp. nov. (Peridiniales, Dinophyceae): a new marine dinoflagellate causing mass mortality of bivalves in Japan. Phycol Res 43:129–136. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1835.1995.tb00016.x
Imai I, Yamaguchi M, Hori Y (2006) Eutrophication and occurrence of harmful algal blooms in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res 1:71–84. doi:10.3800/pbr.1.71
Kakizaki A, Takahashi M, Akagi H, Tachikawa E, Yamamoto T, Taira E, Yamakuni T, Ohizumi Y (2006) Ca2+ channel activating action of maitotoxin in cultured brainstem neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 536:223–231. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.02.052
Kamiyama T, Arima S (1997) Lethal effect of the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama upon the tintinnid ciliate Favella taraikaensis. Mar Eol Prog Ser 160:27–33. doi:10.3354/meps160027
Kim D, Myazaki Y, Nakashima T, Iwashita T, Fujita T, Yamaguchi K, Choi S, Oda T (2008) Cytotoxic action mode of a novel porphyrin derivative isolated from harmful red tide dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 22:158–165. doi:10.1002/jbt.20216
LePage KT, Baden DG, Murray TF (2003) Brevetoxin derivatives act as partial agonists at neurotoxin site 5 on the voltage-gated Na+ channel. Brain Res 959:120–127. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03737-X
Matsuyama Y (2003a) Physiological and ecological studies on harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. II. Clarification on the toxicity of H. circularisquama and its mechanisms causing shellfish kills. Bull Fish Res Agen 9:13–117 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Matsuyama Y (2003b) Physiological and ecological studies on harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama. I. Elucidation of environmental factors underlying the occurrence and development of H. circularisquama red tide. Bull Fish Res Agen 7:24–105 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Matsuyama Y (2012) Impacts of the harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama bloom on shellfish aquaculture in Japan and some experimental studies on invertebrates. Harmful Algae 14:144–155. doi:10.1016/j.hal.201.10.019
Matsuyama Y, Nagai K, Mizuguchi T, Fujiwaram M, Ishimura M, Yamaguchi M, Uchida T, Honjo T (1995) Ecological features and mass mortality of pearl oysters during the red tide of Heterocapsa sp. in Ago Bay in 1992. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 61:35–41. doi:10.2331/suisan.61.35 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Matsuyama Y, Uchida T, Nagai K, Ishimura M, Nishimura A, Yamaguchi M, Honjo T (1996) Biological and environmental aspects of noxious dinoflagellate red tides by Heterocapsa circularisquama in the west Japan. In: Yasumoto T, Oshima Y, Fukuyo Y (eds) Harmful and toxic algal blooms. IOC of UNESCO, Paris, pp 247–250
Matsuyama Y, Uchida T, Honjo T (1997) Toxic effects of the dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on clearance rate of the blue mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 146:73–80. doi:10.3354/meps146073
Matsuyama Y, Usuki H, Uchida T, Kotani Y (2001) Effects of harmful algae on the early planktonic larvae of the oyster, Crassostrea gigas. In: Hallegraeff G, Blackburn S, Bolch C, Lewis R (eds) Harmful algal blooms. IOC, UNESCO, Paris, pp 411–414
Moore SK, Trainer VL, Mantua NJ, Parker MS, Laws EA, Backer LC, Fleming LE (2008) Impacts of climate variability and future climate change on harmful algal blooms and human health. Environ Health 7(Suppl 2):S4. doi:10.1186/1476-069X-7-S2-S4
Morisawa M, Yoshida M (2005) Activation of motility and chemotaxis in the spermatozoa: from invertebrates to humans. Reprod Med Biol 4:101–114. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0578.2005.00099.x
Nagai K, Matsuyama Y, Uchida T, Yamaguchi M, Ishimaru M, Nishimaru A, Akamatsu S, Honjo T (1996) Toxicity and LD50 levels of the red tide dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama on juvenile pearl oysters. Aquaculture 144:149–154. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01307-5
Nagai K, Honjo T, Go J, Yamashita H, Oh SJ (2006) Detecting the shellfish killer Heterocapsa circularisquama (Dinophyceae) by measuring bivalve valve activity with a Hall element sensor. Aquaculture 255:395–401. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.12.018
Padilla DK, Miner BG (2006) Legacies in complex life histories of marine invertebrates: a tribute to Larry McEdward. Integr Comp Biol 46:217–223. doi:10.1093/icb/icj029
Pearce I, Handlinger J, Hallegraeff GM (2005) Histopathology in Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) spat caused by the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymum. Harmful Algae 4:61–74. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2003.11.002
Pechenik JA (1987) Environmental influences on larval survival and development. In: Giese AC, Pearse JS, Pearse VB (eds) Reproduction of marine invertebrates, vol 9. Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Cambridge, pp 551–608
Pérez-Gómez A, Ferrero-Gutierrez A, Novelli A, Franco JM, Paz B, Fernández-Sánchez MT (2006) Potent neurotoxic action of the shellfish biotoxin yessotoxin on cultured cerebellar neurons. Toxicol Sci 90:168–177. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfj064
Przeslawski R, Bourdeau PE, Doall MH, Pan J, Perino L, Padilla DK (2008) The effects of a harmful alga on bivalve larval lipid storage. Harmful Algae 7:802–807. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2008.04.003
Roger AD, Laffoley D d’A (2011) International Earth system expert workshop on ocean stresses and impacts. Summary report. IPSO, Oxford, p 18
Rurangwa E, Kime DE, Ollevier F, Nash JP (2004) The measurement of sperm motility and factors affecting sperm quality in cultured fish. Aquaculture 234:1–28. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2003.12.006
Santella L, Lim D, Moccia F (2004) Calcium and fertilization: the beginning of life. Trends Biochem Sci 29:400–408. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2004.06.009
Shiraishi T, Hiroishi S, Nagai K, Go J, Yamamoto T, Imai I (2007) Seasonal distribution of the shellfish killing dinoflagellate in Ago Bay monitored by indirect fluorescent antibody technique using monoclonal antibodies. Plankton Benthos Res 2:49–62. doi:10.3800/pbr.2.49
Shumway SE (1990) A review of the effects of algal blooms on shellfish and aquaculture. J World Aquacult Soc 21:65–104. doi:10.1111/j.1749-7345.1990.tb00529.x
Shumway SE, Cucci TL, Gainey L, Yentsch CM (1985) A preliminary study of the behavioural and physiological effects of Gonyaulax tamarensis on bivalve molluscs. In: Anderson DM, White AM, Barden GG (eds) Toxic dinoflagellates. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 389–394
Stoecker DK, Adolf JA, Place AR, Glibert PM, Meritt DW (2008) Effects of the dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum and Prorocentrum minimum on the early life history stages of the eastern oyster (Crassostrea virginica). Mar Biol 154:81–90. doi:10.1007/s00227-007-0901-z
Stricker SA (1999) Comparative biology of calcium signaling during fertilization and egg activation in animals. Dev Biol 211:157–176. doi:10.1006/dbio.1999.9340
Tran D, Haberkorn H, Soudant P, Ciret P, Massabuau JC (2010) Behavioral responses of Crassostrea gigas exposed to the harmful algae Alexandrium minutum. Aquaculture 298:338–345. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2009.10.030
Uchida T (2001) The role of cell contact in the life cycle of some dinoflagellate species. J Plankton Res 23:889–891. doi:10.1093/plankt/23.8.889
Uchida T, Yamaguchi M, Matsuyama Y, Honjo T (1995) The bloom dinoflagellate Heterocapsa sp. kills Gyrodinium instriatum by cell contact. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 118:301–303. doi:10.335/meps118301
Wada KT (1984) Breeding of the pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata. Bull Natl Res Inst Aquacult (Fish Agency Jpn) 6:79–157 (in Japanese with English abstract)
Wang L, Yan T, Zhou M (2006) Impacts of HAB species Heterosigma akashiwo on early development of the scallop Argopecten irradians Lamarck. Aquaculture 255:347–383. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2005.11.057
Wikfors GH, Smolowitz RM (1995) Experimental and histological studies of 4 life-history stages of the Eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica, exposed to a cultured strain of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Biol Bull 188:313–328
Yamatogi T, Sakaguchi M, Matsuda M, Iwanaga S, Iwataki M, Matsuoka K (2005) Effect on bivalve molluscs of a harmful dinoflagellate Heterocapsa circularisquama isolated from Omura Bay, Japan and its growth characteristics. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 71:746–754. doi:10.2331/suisan.71.746 (in Japanese, with English abstract)
Yan T, Zhou M, Fu M, Wang Y, Yu R, Li J (2001) Inhibition of egg hatching and larvae survival of the scallop, Chlamys farreri, associated with exposure to cells and cell fragments of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Toxicon 39:1239–1244. doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(01)00080-0
Yan T, Zhou MJ, Fu M, Yu RC, Wang YF, Li J (2003) Effects of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on early development of the scallop Argopecten irradians concentricus. Aquaculture 217:167–178. doi:10.1016/S0044-8486(02)00117-5
Zingone A, Oksfeldt Enevoldsen H (2000) The diversity of harmful algal blooms: a challenge for science and management. Ocean Coast Manage 43:725–748. doi:10.1016/S0964-5691(00)00056-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. P. Grassle.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basti, L., Nagai, K., Tanaka, Y. et al. Sensitivity of gametes, fertilization, and embryo development of the Japanese pearl oyster, Pinctada fucata martensii, to the harmful dinoflagellate, Heterocapsa circularisquama . Mar Biol 160, 211–219 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2079-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2079-2