Abstract
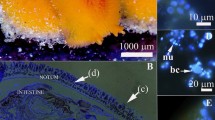
In the present study, the hypothesis that marine nudibranch mollusks harbor symbiotic bacteria was tested using analyses of fatty acids as biochemical markers and transmission electron microscopy of the tissues of Dendrodoris nigra (Gastropoda/Opisthobranchia/Nudibranchia). An aberrant level of the odd-numbered carbon chain and branched fatty acids, iso- and anteiso- that are specific for bacteria, was detected in the nudibranch tissues. Their amounts in the notum exceeded significantly that in the viscera. Rod-shaped gram-negative bacteria were revealed in the epithelial cells of the notum and the mantle edge as well as in the adjoining glycocalix. These bacteria were enclosed in secondary vacuoles in the epithelial cells. The consequent stages of inoculation of the bacteria into the cytoplasm of epithelial cells, from adhesion to the apical surface to invagination of the cell membrane and formation of the vacuole with an enclosed bacterium, were observed. The presence of dividing bacteria suggests that the epithelium includes a renewable, dividing population of symbiotic bacteria. No bacteria were detected in the gonads and the digestive system. Probable functions of these symbiotic bacteria such as involvement in protection or defense from predators and environmental impacts as well as their nutritional role in the nudibranch are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen CE, Tyler PA, Van Dover CL (2001) Lipid composition of the hydrothermal vent clam Calyptogena pacifica (Mollusca: Bivalvia) as a trophic indicator. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 81:817–821. doi:10.1017/S0025315401004647
Avila C, Durfort M (1996) Histology of epithelia and mantle glands of selected species of doridacean mollusks with chemical defensive strategies. Veliger 39:148–163
Bachok Z, Mfilinge PL, Tsuchiya M (2003) The diet of the mud clam Geloina coaxans (Mollusca, Bivalvia) as indicated by fatty acid markers in a subtropical mangrove forest of Okinawa, Japan. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 292:187–197. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(03)00160-6
Bates AE (2007) Persistence, morphology, and nutritional state of a gastropod hosted bacterial symbiosis in different levels of hydrothermal vent flux. Mar Biol 152:557–568. doi:10.1007/s00227-007-0709-x
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Brodie GD, Willan RC, Collins JD (1997) Taxonomy and occurrence of Dendrodoris nigra and Dendrodoris fumata (Nudibranchia: Dendrodorididae) in the Indo-West Pacific region. J Mollus Stud 63:407–423. doi:10.1093/mollus/63.3.407
Campoy E, Colombo MI (2009) Autophagy in intracellular bacterial infection. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:1465–1477. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.03.003
Canuel EA, Martens CS (1993) Seasonal variations in the sources and alteration of organic matter associated with recently-deposited sediments. Org Geochem 20:563–577. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(93)90024-6
Carreau JP, Dubacq JP (1978) Adaptation of macro-scale method to the micro-scale for fatty acid methyl transesterification of biological lipid extracts. J Chromatogr 151:384–390
Chaston J, Goodrich-Blair H (2010) Common trends in mutualism revealed by model associations between invertebrates and bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:41–58. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00193.x
Clegg S, Gerlach GF (1987) Enterobacterial fimbriae. J Bacteriol 169:934–938
Colaco A, Desbruyeres D, Guezennec J (2007) Polar lipid fatty acids as indicators of trophic associations in a deep-sea vent system community. Mar Ecol Evol Pers 28:15–24. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.2006.00123.x
Conway N, Cappuzzo JM (1991) Incorporation and utilization of bacterial lipids in the Solemya velum symbiosis. Mar Biol 108:277–291. doi:10.1007/BF01344343
Dalsgaard J, John MS, Kattner G, Muller-Navarra D, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment. Adv Mar Biol 46:241–251. doi:10.1016/S0065-2881(03)46005-7
Dembitsky VM, Rezanka T, Srebnik M (2003) Lipid compounds of freshwater sponges: family Spongillidae class Demospongiae. Chem Phys Lipids 123:117–155. doi:10.1016/S0009-3084(03)00020-3
Dubilier N, Bergin C, Lott C (2008) Symbiotic diversity in marine animals: the art of harnessing chemosynthesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:725–740. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1992
Duguid JP, Darekar MR, Wheater DWF (1976) Fimbriae and infectivity in Salmonella typhimurium. J Med Microbiol 9:459–473
Dunlap PV, Kojima Y, Nakamura S, Nakamura M (2009) Inception of formation and early morphogenesis of the bacterial light organ of the sea urchin cardinalfish, Siphamia versicolor. Mar Biol 156:2011–2020. doi:10.1007/s00227-009-1232-z
Fader CM, Colombo MI (2009) Autophagy and multivesicular bodies: two closely related partners. Cell Death Differ 16:70–78. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.168
Fdhila F, Vazquez V, Sanchez JL, Riguera R (2003) DD-diketopiperazines: antibiotics active against Vibrio anguillarum isolated from marine bacteria associated with cultures of Pecten maximus. J Nat Prod 66:1299–1301. doi:10.1021/np068026c
Fujiwara Y, Kawato M, Noda C, Kinoshita G, Yamanaka T, Fujita Y, Uematsu K, Miyazaki J (2010) Extracellular and mixotrophic symbiosis in the whale-fall mussel Adipicola pacifica: a trend in evolution from extra- to intracellular symbiosis. PLOS One 5(N7), Article No e11808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011808
Galap C, Netchitailo P, Leboulenger F, Grillot JP (1999) Variations of fatty acid contents in selected tissues of the female dog cockle (Glycymeris glycymeris L., Mollusca, Bivalvia) during the annual cycle. Comp Biochem Physiol 122A:241–254. doi:10.1016/S1095-6433(99)00006-9
Gillan FT, Johns RB (1986) Chemical markers for marine bacteria: fatty acids and pigments. In: Johns RB (ed) Biological markers in the sedimentary environment. Elsevier Science Publisher, Amsterdam, pp 291–309
Goffredi SK, Orphan VJ, Rouse GW, Jahnke L, Embaye T, Turk K, Lee R, Vrijenhoek RC (2005) Evolutionary innovation: a bone-eating marine symbiosis. Environ Microbiol 7:1369–1378. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00824.x
Johnson MA, LePennec M (1995) Association between mollusk bivalve Loropes lucinalis and Chlamydia-like organism, with comments on its pathogenic impact, life cycle and possible mode of transmission. Mar Biol 123:523–530. doi:10.1007/BF00349231
Jones BW, Nishiguchi MK (2004) Counterillumination in the Hawaiian bobtail squid, Euprymna scolopes Berry (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Mar Biol 144:1151–1155. doi:10.1007/s00227-003-1285-3
Kadar E, Bettencourt R, Costa V, Santos RS, Lobo-Da-Cunha A, Dando P (2005) Experimentally induced endosymbiont loss and re-acquirement in the hydrothermal vent bivalve Bathymodiolus azoricus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 318:99–110. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2004.12.025
Kaneda T (1991) Iso-fatty and anteiso-fatty acids in bacteria—biosynthesis, function, and taxonomic significance. Microbiol Rev 55:288–302
Kattner G, Hagen W, Graeve M, Albers C (1998) Exceptional lipids and fatty acids in the pteropod Clione limacina (Gastropoda) from both polar oceans. Mar Chem 61:219–228. doi:10.1016/S0304-4203(98)00013-9
Kharlamenko VI, Zhukova NV, Khotimchenko SV, Svetashev VI, Kamenev GM (1995) Fatty-acids as markers of food sources in a shallow-water hydrothermal ecosystem (Kraternaya Bight, Yankich Island, Kurile Islands). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 120:231–241. doi:10.3354/meps120231
Klussmann-Kolb A, Brodie GD (1999) Internal storage and production of symbiotic bacteria in the reproductive system of a tropical marine gastropod. Mar Biol 133:443–447. doi:10.1007/s002270050483
Lindquist N (2002) Chemical defense of early life stages of benthic marine invertebrates. J Chem Ecol 28:1987–2000. doi:10.1023/A:1020745810968
Lindquist N, Barber PH, Weisz JB (2005) Episymbiotic microbes as food and defence for marine isopods: unique symbioses in a hostile environment. Proc R Soc Lond B 272:1209–1216. doi:10.1098/rspb.2005.3082
Lopanik NB, Targett NM, Lindquist N (2006) Ontogeny of a symbiont-produced chemical defense in Bugula neritina (Bryozoa). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 327:183–191. doi:10.3354/meps327183
Martinez-Pita I, Garcia F, Pita ML (2005) Fatty acid composition and utilization in developing eggs of some marine nudibranchs (Mollisca: Gastropoda: Opistobranchia) from southwest Spain. J Shell Res 24:1209–1216
McDonald GR, Nybakken JW (1999) A worldwide review of the food of nudibranch mollusks. II. The suborder Dendronotacea. Veliger 42:62–66
McKenzie JD, Kelly MS (1994) Comparative-study of sub-cuticular bacteria in brittlestars (Echinodermata, Ophiuroidea). Mar Biol 120:65–80
McKenzie JD, Black KD, Kelly MS, Newton LC, Handley LL, Scrimgeour CM, Raven JA, Henderson RJ (2000) Comparisons of fatty acids and stable isotope ratios in symbiotic and non-symbiotic brittlestars from Oban Bay, Scotland. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 80:311–320. doi:10.1017/S0025315499001885
Meziane T, Tsuchiya M (2000) Fatty acids as tracers of organic matter in the sediment and food web of a mangrove/intertidal flat ecosystem, Okinawa, Japan. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 200:49–57. doi:10.3354/meps200049
Nussbaumer AD, Fisher CR, Bright M (2006) Horizontal endosymbiont transmission in hydrothermal vent tubeworms. Nature 441:345–348. doi:10.1038/nature04793
Perry GJ, Volkman JK, Johns RB, Bavor HJ (1979) Fatty acids of bacterial origin in contemporary marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43:1715–1725
Piel J (2004) Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat Prod Rep 21:519–538. doi:10.1039/b310175b
Pond DW, Segonzac M, Bell MV, Dixon DR, Fallick AE, Sargent JR (1997) Lipid and lipid carbon stable isotope composition of the hydrothermal vent shrimp Mirocaris fortunata: evidence for nutritional dependence on photosynthetically fixed carbon. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 157:221–231. doi:10.3354/meps157221
Pond DW, Allen CE, Bell MV, Van Dover CL, Fallick AE, Dixon DR, Sargent JR (2002) Origins of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in the hydrothermal vent worms Ridgea piscesae and Protis hydrothermica. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 225:219–226. doi:10.3354/meps225219
Pranal V, FialaMedioni A, Guezennec J (1996) Fatty acid characteristics in two symbiotic gastropods from a deep hydrothermal vent of the west Pacific. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 142:175–184. doi:10.3354/meps142175
Proksch P, Edrada RA, Ebel R (2002) Drugs from the seas—current status and microbiological implications. Appl Microbiol Biot 59:125–134. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1006-8
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Rezanka T, Sigler K (2009) Odd-numbered very-long-chain fatty acids from the microbial, animal and plant kingdoms. Prog Lipid Res 48:206–238. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2009.03.003
Rieley G, Van Dover CL, Hedrick DB, Eglinton G (1999) Trophic ecology of Rimicaris exoculata: a combined lipid abundance stable isotope approach. Mar Biol 133:495–499. doi:10.1007/s002270050489
Rodkina SA, Latyshev NA, Imbs AB (2003) Fatty acids from the Sea of Japan sponge Halichondria panacea. Russ J Bioorg Chem 29:382–386
Saffo MB (1992) Invertebrates in endosymbiotic associations. Amer Zool 32:557–565
Saito H, Hashimoto J (2010) Characteristics of the fatty acid composition of a deep-sea vent gastropod, Ifremeria nautilei. Lipids 45:537–548. doi:10.1007/s11745-010-3436-x
Schmidt EW, Donia MS (2010) Life in cellulose houses: symbiotic bacterial biosynthesis of ascidian drugs and drug leads. Curr Opin Biotech 21:827–833. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2010.10.006
Silina AV, Zhukova NV (2007) Growth variability and feeding of scallop Patinopecten yessoensis on different bottom sediments: evidence from fatty acid analysis. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 348:46–59. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2007.03.018
Stewart FJ, Cavanaugh CM (2006) Bacterial endosymbioses in Solemya (Mollusca: Bivalvia)—model systems for studies of symbiont-host adaptation. Anton Leeuw Int J G 90:343–360. doi:10.1007/s10482-006-9086-6
Stimpson W (1855) Descriptions of some of the new marine Invertebrata from the Japanese and Chinese Seas. Proc Acad Nat Sci Phila 7:375–384
Wägele H, Ballesteros M, Avila C (2006) Defensive glandular structures in Opisthobranch molluscs—from histology to ecology. Oceanogr Mar Biol 44:197–276
Wilkinson CR, Garrone R, Vacelet J (1984) Marine sponges discriminate between food bacteria and bacterial symbionts: electron microscope radioautography and in situ evidence. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 220:519–528
Xu PN, Distel DL (2004) Purification and characterization of an endo-1,4-beta-D glucanase from the cellulolytic system of the wood-boring marine mollusk Lyrodus pedicellatus (Bivalvia: Teredinidae). Mar Biol 144:947–953. doi:10.1007/s00227-003-1251-0
Zhukova NV (2007) Lipid classes and fatty acid composition of the tropical nudibranch mollusks Chromodoris sp. and Phyllidia coelestis. Lipids 42:1169–1175. doi:10.1007/s11745-007-3123-8
Zhukova NV, Kharlamenko VI, Svetashev VI, Rodionov IA (1992) Fatty-acids as markers of bacterial symbionts of marine bivalve mollusks. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 162:253–263. doi:10.1016/0022-0981(92)90205-O
Acknowledgments
The authors thank A.V. Chernyshev for the identification of the species and four anonymous reviewers for comments. This research was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (grant 11_04-98507-p_vostok_a) and the Government of the Russian Federation (grant 11.G34.31.0010) to N.V. Zhukova.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. P. Grassle.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhukova, N.V., Eliseikina, M.G. Symbiotic bacteria in the nudibranch mollusk Dendrodoris nigra: fatty acid composition and ultrastructure analysis. Mar Biol 159, 1783–1794 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1969-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-1969-7