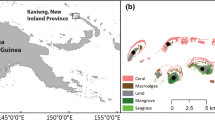
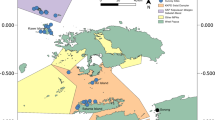
Abstract
Within the tropics, mangroves and coral reefs represent highly productive biomes. Although these habitats are often within close proximity, the role and importance of mangrove habitats for reef fish species remains unclear. Throughout the Indo-Pacific, reef fish species appear to have few links with estuarine mangrove habitats. In contrast, clear-water non-estuarine mangrove habitats throughout the Caribbean support many reef fish species and may be fundamental for sustaining reef fish populations. But how important are clear-water non-estuarine mangroves for reef fishes within the Indo-Pacific? Using visual surveys during diurnal high tide, the fish assemblages inhabiting clear-water mangrove and adjacent reef habitats of Orpheus Island, Great Barrier Reef, were recorded. Of the 188 species of fishes that were recorded, only 38 were observed to inhabit both habitats. Of these, only eight were observed more than five times within each habitat. These observations provide little indication that the clear-water mangroves are an important habitat for reef fish species. In addition, although based on just a 3-month survey period, we found little evidence to suggest that these areas are important nurseries for reef fish species. The clear-water mangroves of Orpheus Island may, however, provide an additional foraging area for the few reef fish species that were observed to utilize these habitats during high tide. The difference in the importance of clear-water mangroves for reef fishes within this study compared with clear-water mangrove counterparts within the Caribbean is surprising. Although only preliminary, our observations would support suggestions that the patterns reflect the different hydrological characteristics and evolutionary histories of these two biogeographic regions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman JL, Bellwood DR (2000) Reef fish assemblages: a re-evaluation using enclosed rotenone stations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 206:227–237. doi:10.3354/meps206227
Baker R, Sheaves M (2007) Shallow-water refuge paradigm: conflicting evidence from tethering experiments in a tropical estuary. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 349:13–22. doi:10.3354/meps07102
Bellwood DR (1997) Reef fish biogeography: habitat associations, fossils and phylogenies. Proc 8th Int Coral Reef Symp 1:379–384
Bellwood DR, Wainwright PC (2002) The history and biogeography of fishes on coral reefs. In: Sale PF (ed) Coral reef fishes. Dynamics and diversity in a complex ecosystem. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 5–32
Birkeland C (1985) Ecological interactions between mangroves, seagrass beds, and coral reefs. UNEP Reg Seas Rep Stud 73:1–26
Birkeland C, Amesbury SS (1987) Fish-transect surveys to determine the influence of neighbouring habitats on fish community structure in the tropical Pacific. UNEP Reg Seas Rep Stud 97:195–202
Blaber SJM (1980) Fish of the Trinity Inlet system of North Queensland with notes on the ecology of fish faunas of tropical Indo-Pacific estuaries. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 31:137–146
Blaber SJM, Milton DA (1990) Species composition, community structure and zoogeography of fishes of mangrove estuaries in the Solomon Islands. Mar Biol 105:259–267. doi:10.1007/BF01344295
Blaber SJM, Young JW, Dunning MC (1985) Community structure and zoogeographic affinities of the coastal fishes of the Dampier region of north-western Australia. Aust J Mar Freshw Res 36:247–266
Chittaro PM, Usseglio P, Sale P (2005) Variation in fish density, assemblage composition and relative rates of predation among mangrove, seagrass and coral reef habitats. Environ Biol Fish 72:175–187. doi:10.1007/s10641-004-9077-2
Clarke KR (1993) Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.1993.tb00438.x
Dahlgren CP, Eggleston DB (2000) Ecological processes underlying ontogenetic habitat shifts in a coral reef fish. Ecology 81:2227–2240. doi:10.1890/0012-9658(2000)081[2227:EPUOHS]2.0.CO;2
Dickens LC, Goatley CHR, Tanner JK, Bellwood DR (2011) Quantifying relative diver effects in underwater visual censuses. PLoS ONE 6:e18965. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018965
Doherty PJ, Williams DMcB (1988) The replenishment of coral reef populations. Oceanogr Mar Biol A Rev 26:487–551
Dorenbosch M, van Riel MC, Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G (2004) The relationship of reef fish densities to the proximity of mangrove and seagrass nurseries. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:37–48. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2003.11.018
Dorenbosch M, Grol MGG, Christianen MJA, Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G (2005) Indo-Pacific seagrass beds and mangroves contribute to fish density and diversity on adjacent coral reefs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 302:63–76. doi:10.3354/meps302063
Dorenbosch M, Verberk W, Nagelkerken I, van der Veldel G (2007) Influence of habitat configuration on connectivity between fish assemblages of Caribbean seagrass beds, mangroves and coral reefs. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 334:103–116. doi:10.3354/meps334103
Dorenbosch M, Grol MGG, de Groene A, van der Velde G, Nagelkerken I (2009) Piscivore assemblages and predation pressure affect relative safety of some back-reef habitats for juvenile fish in a Caribbean bay. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 379:181–196. doi:10.3354/meps07896
Duke NC (1992) Mangrove floristics and biogeography. In: Robertson AI, Alongo DM (eds) Coastal and estuarine studies (tropical mangrove ecosystems). American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 63–101
Floeter SR, Rocha LA, Robertson DR, Joyeux JC, Smith-Vaniz WF, Wirtz P, Edwards AJ, Barreiros JP, Ferreira CEL, Gasparini JL, Brito A, Falcon JM, Bowen BW, Bernardi G (2008) Atlantic reef fish biogeography and evolution. J Biogeogr 35:22–47. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2007.01790.x
Fox RJ, Bellwood DR (2011) Unconstrained by the clock? Plasticity of diel avtivity rhythm in a tropical reef fish, Signaus lineatus. Funct Ecol. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2011.01874.x
Froese F, Pauly D (2011) Fishbase. www.fishbase.org
Gray CA, Chick RC, McElligott DJ (1998) Diel changes in assemblages of fishes associated with shallow seagrass and bare sand. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 46:849–859. doi:10.1006/ecss.1997.0321
Grol MGG, Dorenbosch M, Kokkelmans EMG, Nagelkerken I (2008) Mangroves and seagrass beds do not enhance growth of early juveniles of a coral reef fish. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 366:137–146. doi:10.3354/meps07509
Gullstrom M, Bodin M, Nilsson PG, Ohman MC (2008) Seagrass structural complexity and landscape configuration as determinants of tropical fish assemblage composition. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 363:241–255. doi:10.3354/meps07427
Halpern BS (2004) Are mangroves a limiting resource for two coral reef fishes? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 272:93–98. doi:10.3354/meps272093
Huxham M, Kimani E, Augley J (2004) Mangrove fish: a comparison of community structure between forested and cleared habitats. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:637–647. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2004.03.003
Krumme U (2009) Diel and tidal movements by fish and decapods linking tropical coastal ecosystems. In: Nagelkerken I (ed) Ecological connectivity among tropical coastal ecosystems. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 271–324
Laegdsgaard P, Johnson C (2001) Why do juvenile fish utilise mangrove habitats? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 257:229–253. doi:10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00331-2
Laroche J, Baran E, Rasoanandrasana NB (1997) Temporal patterns in a fish assemblage of a semiarid mangrove zone in Madagascar. J Fish Biol 51:3–20. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1997.tb02509.x
Layman CA (2000) Fish assemblage structure of the shallow ocean surf-zone on the eastern shore of Virginia Barrier Islands. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 51:201–213. doi:10.1006/ecss.2000.0636
Lindeman KC, Pugliese R, Waugh GT, Ault JS (2000) Developmental patterns within a multispecies reef fishery: management applications for essential fish habitats and protected areas. Bull Mar Sci 66:929–956
Little MC, Reay PJ, Grove SJ (1988) The fish community of an East African mangrove creek. J Fish Biol 32:729–747. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.1988.tb05413.x
Lugendo BR, de Groene A, Cornelissen I, Pronker A, Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G, Mgaya YD (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in fish community structure of a marine embayment in Zanzibar, Tanzania. Hydrobiologia 586:1–16. doi:10.1111/j.1444-2906.2007.01458.x
Luo J, Serafy JE, Sponaugle S, Teare PB, Kieckbusch D (2009) Movement of gray snapper Lutjanus griseus among subtropical seagrass, mangrove, and coral reef habitats. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 380:255–269. doi:10.3354/meps07911
Methven DA, Haedrich RL, Rose GA (2001) The fish assemblage of a Newfoundland estuary: diel, monthly and annual variation. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:669–687. doi:10.1006/ecss.2001.0768
Milicich MJ, Doherty PJ (1994) Larval supply of coral reef fish populations: magnitude and synchrony of replenishment to Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 110:121–134. doi:10.3354/meps110121
Mumby PJ, Edwards AJ, Arias-Gonzalez JE, Lindeman KC, Blackwell PG, Gall A, Gorczynska MI, Harborne AR, Pescod CL, Renken H, Wabnitz CCC, Llewellyn G (2004) Mangroves enhance the biomass of coral reef fish communities in the Caribbean. Nature 427:533–536. doi:10.1038/nature02286
Mwandya AW, Gullstrom M, Ohman MC, Andersson MH, Mgaya YD (2009) Fish assemblages in Tanzanian mangrove creek systems influenced by solar salt farm constructions. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 82:193–200. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2008.12.010
Myers RF (1999) Micronesian reef fishes. Coral Graphics, Guam
Nagelkerken I, Faunce CH (2008) What makes mangroves attractive to fish? Use of artificial units to test the influence of water depth, cross-shelf location, and presence of root structure. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 79:559–565. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2008.04.011
Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G (2002) Do non-estuarine mangroves harbour higher densities of juvenile fish than adjacent shallow-water and coral reef habitats in Curacao (Netherlands Antilles)? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 245:191–204. doi:10.3354/meps245191
Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G (2004) Relative importance of interlinked mangroves and seagrass beds as feeding habitats for juvenile reef fish on a Caribbean island. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 274:153–159. doi:10.3354/meps274153
Nagelkerken I, Dorenbosch M, Verberk W, de la Moriniere EC, van der Velde G (2000a) Importance of shallow-water biotopes of a Caribbean bay for juvenile coral reef fishes: patterns in biotope association, community structure and spatial distribution. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 202:75–192. doi:10.3354/meps202175
Nagelkerken I, van der Velde G, Gorissen MW, Meijer GJ, van’t Hof T, den Hartog C (2000b) Importance of mangroves, seagrass beds and the shallow coral reef as a nursery for important coral reef fishes, using a visual census technique. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 5:31–44. doi:10.1006/ecss.2000.0617
Nagelkerken I, Kleijnen S, Klop T, van den Brand R, de la Moriniere EC, van der Velde G (2001) Dependence of Caribbean reef fishes on mangroves and seagrass beds as nursery habitats: a comparison of fish faunas between bays with and without mangroves/seagrass beds. Mar Ecol Pro Ser 214:225–235
Nagelkerken I, Roberts CM, van der Velde G, Dorenbosch M, van Riel MC, de la Morinere EC, Nienhuis PH (2002) How important are mangroves and seagrass beds for coral-reef fish? The nursery hypothesis tested on an island scale. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 244:299–305. doi:10.3354/meps244299
Nakamura Y, Horinouchi M, Shibuno T, Tanaka Y, Miyajima T, Koike I, Kurokura H, Sano M (2008) Evidence of ontogenetic migration from mangroves to coral reefs by black-tail snapper Lutjanus fulvus: stable isotope approach. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 355:257–266. doi:10.3354/meps07234
Paperno R, Mille KJ, Kadison E (2001) Patterns in species composition of fish and selected invertebrate assemblages in estuarine subregions near Ponce de Leon Inlet, Florida. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:117–130. doi:10.1006/ecss.2000.0732
Payne NL, Gillanders BM (2009) Assemblages of fish along a mangrove-mudflat gradient in temperate Australia. Mar Freshw Res 60:1–13. doi:10.1071/MF08124
Persson L, Eklov P (1995) Prey refuges affecting interactions between piscivorous perch and juvenile perch and roach. Ecology 76:70–81. doi:10.2307/1940632
Quinn NJ, Kojis BJ (1985) Does the presence of coral reefs in proximity to a tropical estuary affect the estuarine fish assemblage? Proc 5th Int Coral Reef Cong Tahiti 5:445–450
Randall JE, Allen GR, Steene RC (1997) Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Crawford House Publishing Pty Ltd, Bathurst
Renema W, Bellwood DR, Braga JC, Bromfield K, Hall R, Johnson KG, Lunt P, Meyer CP, McMonagle L, Morley RJ, O’dea A, Todd JA, Wesselingh FP, Wilson MEJ, Pandolfi JM (2008) Hopping hotspots: global shifts in marine biodiversity. Science 321:654–657. doi:10.1126/science.1155674
Robertson AI, Duke NC (1987) Mangroves as nursery sites: comparisons of the abundance and species composition of fish and crustaceans in mangroves and other nearshore habitats in tropical Australia. Mar Biol 96:193–205. doi:10.1007/BF00427019
Schaffelke B (2001) Surface alkaline phosphatase activities of macroalgae on coral reefs of the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 19:310–317. doi:10.1007/s003380000128
Sheaves M (1996a) Do spatial differences in the abundance of two serranid fishes in estuaries of tropical Australia reflect long-term salinity patterns? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 137:39–49. doi:10.3354/meps137039
Sheaves M (1996b) Habitat specific distributions of some fishes in a tropical estuary. Mar Freshw Res 47:827–830. doi:10.1071/MF9960827
Sheaves M (2005) Nature and consequences of biological connectivity in mangrove systems. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 302:293–305. doi:10.3354/meps302293
Sheaves M (2009) Consequences of ecological connectivity: the coastal ecosystem mosaic. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 391:107–115. doi:10.3354/meps08121
Sheaves M, Molony B (2000) Short-circuit in the mangrove food chain. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 199:97–109. doi:10.3354/meps199097
Shibuno T, Nakamura Y, Horinouchi M, Sano M (2008) Habitat use patterns of fishes across the mangrove-seagrass-coral reef seascape as Ishigaki Island, southern Japan. Ichthyol Res 55:218–237. doi:10.1007/s10228-007-0022-1
Thollot P (1992) Importance of mangroves for pacific reef fish species, myth or reality? Proc 7th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:934–941
Thollot P, Kulbicki M (1988) Overlap between the fish fauna inventories of coral reefs, soft bottoms and mangroves in Saint-Vincent Bay (New Caledonia). Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:613–618
Unsworth RKF, Bell JJ, Smith DJ (2007) Tidal fish connectivity of reef and sea grass habitats in the Indo-Pacific. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 87:1287–1296. doi:10.1017/S002531540705638X
Unsworth RKF, Salinas De Leon P, Garrard SL, Jompa J, Smith DJ, Bell JJ (2008) High connectivity of Indo-Pacific seagrass fish assemblages with mangrove and coral reef habitats. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 353:213–224. doi:10.3354/meps07199
Unsworth RKF, Garrard SL, Salinas De Leon P, Cullen LC, Smith DJ, Sloman KA, Bell JJ (2009) Structuring of Indo-Pacific fish assemblages along the mangrove-seagrass continuum. Aquat Biol 5:85–95. doi:10.3354/ab00139
Valiela I, Bowen JL, York JK (2001) Mangrove forests: one of the world’s threatened major tropical environments. Bioscience 51:807–815. doi:10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0807:MFOOTW]2.0.CO;2
van der Velde G, Gorissen MW, den Hartog C, van’t Hoff T, Meijer GJ (1992) Importance of the Lac-Lagoon (Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles) for a selected number of reef fish species. Hydrobiologia 247:139–140
Verweij MC, Nagelkerken I, de Graaff D, Peeters M, Bakker EJ, van der Velde G (2006) Structure, food and shade attract juvenile coral reef fish to mangrove and seagrass habitats: a field experiment. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 306:257–268. doi:10.3354/meps306257
Williamson I, King C, Mather PB (1994) A comparison of fish communities in unmodified and modified inshore habitats of Raby Bay, Queensland. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 39:401–411. doi:10.1006/ecss.1994.1072
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the staff of Orpheus Island Research Station for field support, C. Chustz, C. Clarke, S. Ditthavong, E. Game and J. Pitt for field assistance and T. Harvey, A. Hoey, C. Fulton and two anonymous reviewers for helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. David.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, L., Bellwood, D.R., Sheaves, M. et al. The use of clear-water non-estuarine mangroves by reef fishes on the Great Barrier Reef. Mar Biol 159, 211–220 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1801-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1801-9