Abstract
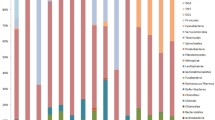
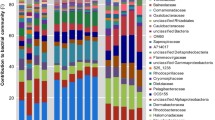
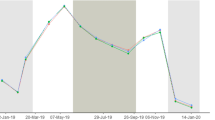
The mucus of scleractinian corals harbors a variety of prokaryotic and eukaryotic microorganisms, but little is known about the eukaryotic fraction of this microbiota. In this study, a quantitative and qualitative description of microalgae assemblages associated with the mucus of two species of massive corals is presented. During the first half of 2004, in “Los Frailes” Archipelago (Southern Caribbean), samples of mucus were randomly taken from healthy colonies of Diploria sp. and Colpophyllia sp. Also, samples of water surrounding each colony were taken monthly for six months. Multivariate analysis showed that microalgae assemblages from the mucus were significantly different from those found in the water column, and that variation of microalgae assemblage composition in time was dependent on the coral species. The results indicate that most of the microalgae assemblage associated with the mucus did not originate from a passive trapping of species commonly found in the phytoplankton. Nevertheless, temporal variations of both assemblages (i.e., phytoplankton and mucus) were very dynamic but closely associated.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson M (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Aust Ecol 26:32–46
Anthony K, Fabricius K (2000) Shifting roles of heterotrophy and autotrophy in coral energetics under varying turbidity. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 252:221–253
Avedaño-Herrera R, Riquelme C (2007) Production of a diatom-bacteria biofilm in a photobioreactor for aquaculture applications. Aquac Eng 36(2):97–104
Baker A (2004) Symbiont diversity on coral reefs and its relationship to bleaching resistance and resilience. In: Rosenberg E, Loya Y (eds) Coral health and disease. Springer, Berlin, pp 177–194
Banin E, Ben-Haim Y, Israely T, Loya Y, Rosenberg E (2000a) Effect of the environment on the bacterial bleaching of corals. Water Air Soil Poll 123:337–352
Banin E, Israely T, Kushmaro A, Loya Y, Orr E, Rosenberg E (2000b) Penetration of the coral-bleaching bacterium Vibrio shiloi into Oculina patagonica. Appl Environ Biol Ecol 66(7):3031–3036
Banin E, Israely T, Fine M, Loya Y, Rosenberg E (2001) Role of endosymbiotic zooxanthellae and coral mucus in the adhesion of the coral-bleaching pathogen Vibrio shiloi to its host. FEMS Microbiol Lett 199:33–37
Ben-Haim Y, Rosenberg E (2002) A novel Vibrio sp. pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Biol 141:47–55
Ben-Haim Y, Banin E, Kushmaro A, Loya Y, Rosenberg E (1999) Inhibition of photosynthesis and bleaching of zooxanthellae by the coral pathogen Vibrio shiloi. Environ Microbiol 1:223–229
Ben-Haim Y, Zicherman M, Rosenberg E (2003) Temperature-regulated bleaching and lysis of the coral Pocillopora damicornis by the novel pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(7):4236–4242
Bianchi F, Acri F, Bernardi Aubry F, Berton A, Boldrin A, Camatti E, Cassin D, Comaschi A (2003) Can plankton communities be considered as bio-indicators of water quality in the Lagoon of Venice? Mar Poll Bull 46:964–971
Bode A, Gonzalez N, Rodriguez C, Varela M, Varela M (2005) Seasonal variability of plankton blooms in the Ria de Ferrol (NW Spain): I. Nutrient concentrations and nitrogen uptake rates. Est Coast and Shelf Sci 63:269–284
Bourne D, Munn C (2005) Diversity of bacteria associated with the coral Pocillopora damicornis from the Great Barrier Reef. Environ Microbiol 7(8):1162–1174
Brouwer J, Stahl L (2001) Short term dynamics on microphytobenthos distribution and associated extracellular carbohydrates in surface sediments of an intertidal mudflat. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 218:33–44
Castellanos P, Varela R, Muller-Kager F (2002) Descripción de las áreas de surgencia al sur del mar Caribe examinadas con el sensor infrarrojo AVHRR. Mem FLASA Ciens Nat 154:55–76
Clark K, Warwick R (2001) Changes in marine Community: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E Ltd., Plymouth
Clavier J, Chauvaud L, Fichez R, Chifflet S (2005) Benthic response to ammonium pulses in a tropical lagoon: implications for coastal environmental processes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 316:231–241
Danger M, Lefleive J, Oumarou C, Ten-hage L, Lacroix G (2007) Control of phytoplankton bacteria interaction by stoichiometric constrains. Oikos 116(7):1079–1086
Descy J, Coste M (1990) Utilisation des diatome′ es benthiques pour l’ evaluation de la qualite′ des aux courantes, Contrat CEE B-71-23, Rapport final, Cemagref
Dodds W, Biggs B, Lowe R (1999) Photosynthesis-irradiance patterns in benthic microalgae: variations as a function of assemblages thickness and community structure. J Phycol 35:42–53
Facca C, Sfrisso A (2007) Epipelic diatom spatial and temporal distribution and relationship with the main environmental parameters in coastal water. Est Coast and Shelf Sci 75:35–49
Facca C, Sfrisso A, Soca G (2002) Changes in abundance and composition of phytoplankton and microphytobenthos due to increased sediment fluxes in the Venice Lagoon, Italy. Est Coast Shelf Sci 54:773–792
Falkowski P, Raven J (2007) Aquatic photosynthesis. Princeton, New Jersey
Fine M, Loya Y (2002) Endolithic algae: an alternative source of photoassimilates during coral bleaching. Proc R Soc Lond 269:1205–1210
Frías-López J, Zerkle A, Bonheyo G, Fouke B (2002) Partitioning of bacterial communities between seawater and healthy, black band diseased, and dead coral surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(5):2214–2228
García A, Cróquer A, Malaver N (2004) Algunas características funcionales de las comunidades bacterianas del mucus asociado a tejidos sanos y con síndrome de banda amarilla en Montastraea annularis. Interciencia 29(1):39–45
Gil S, Rosenberg E (2008) Bacterial growth on coral mucus. Curr Microbiol 56:481–488
Hasle G (1978) The inverted microscope method. In: Sournia L (ed) Phytoplankton manual. SCOR-UNESCO, Paris, pp 250–337
Huang B, Hong H, Wang H (1999) Size-fractionated primary productivity and the phytoplankton-bacteria relationship in the Taiwan Strait. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 183:29–38
Kellogg C (2004) Tropical archaea: diversity associated with the surface microlayer of corals. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 273:81–88
Klaus J, Janse I, Heikoop J, Sanfors R, Fouke B (2007) Coral microbial communities, zooxanthellae and mucus along gradients of seawater depth and coastal pollution. Environ Microbiol 9(5):1291–1305
Knowlton N, Rohwer F (2003) Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: the host as an habitat. Am Nat 162(Scs Mod):50–62
Koren O, Rosenberg E (2006) Bacteria associated with mucus and tissues of the coral Oculina patagonica in summer and winter. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(8):5254–5259
Larkum A, Koch E, Kuhl M (2003) Diffusive boundary layers and photosynthesis of the epilithic algal community of coral reefs. Mar Biol 142:1073–1082
Lesser M, Mazel C, Gorbunov M, Falkowski P (2004) Discovery of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in corals. Science 305:997–1000
Licursi M, Gomez N (2009) Effects of dredging on benthic diatom assemblages in lowland stream. J Environ Manag 90:973–982
Marshall J, Ross T, Pyecroft S, Hallegraeff G (2005) Superoxide production by marine microalgae II. Towards understanding ecological consequences and possible functions. Mar Biol 147:541–549
Mindl B, Sonntag B, Pernthaler J, Vrba J, Psenner R, Posch T (2005) Effects of phosphorus loading on interactions of algae and bacteria: reinvestigation of the ‘phytoplankton–bacteria paradox’ in a continuous cultivation system. Aquat Microb Ecol 38:203–213
Miyajima T, Umezawa M, Koike I (2001) Microbiological nitrogen transformation in carbonate sediments of coral-reef lagoon and associated seagrass beds. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 271:273–286
Nagai H, Masayuki S, Yasumoto T (1990) Antimicrobial activities of polyether compounds of dinoflagellate origins. J Appl Phycol 2:305–308
Naumann R, Richter C, el-Zibdah M, Wild C (2009) Coral mucus as an efficient trap for picoplanktonic cyanobacteria: implications for pelagic-benthic coupling in the reef ecosystem. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 385:65–76
Paul J, DeFlaunn M, Jeffrey W (1986) Elevated levels of microbial activities in the coral surface microlayer. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 33:29–40
Piontek J, Handel N, Langer G, Wohlers J, Riebesell U, Engel A (2009) Effects of rising temperature on the formation and microbial degradation of marine diatom aggregates. Aquat Microbiol Ecol 54:305–318
Pismam T, Galayda Y, Loginova N (2005) Population dynamics of an algal–bacterial cenosis in closed ecological system. Adv Space Res 35(9):1579–1583
Ralph P, Larkum A, Kuhl A (2007) Photobiology of endolithic microorganisms in living coral skeletons: 1. Pigmentation, spectral reflectance and variable chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of endoliths in the massive corals Cyphastrea serailia, Porites lutea and Goniastrea australensis. Mar Biol 152:395–404
Reis A, Araújo S, Moura R, Francini-Filho R, Pappas G, Coelho A, Krüger R, Thompson F (2009) Bacterial diversity associated with the Brazilian endemic reef coral Mussismilia braziliensis. J Appl Microbiol 106:1378–1387
Reshef L, Koren O, Loya Y, Zilber-Rosenberg I, Rosenberg E (2006) The coral probiotic hypothesis. Environ Microbiol 8(12):2068–2073
Richardson L (1997) Occurrence of the black band disease cyanobacterium on healthy corals of the Florida keys. Bull Mar Sci 61(2):485–490
Richardson L, Kuta K (2003) Ecological physiology of the black band disease cyanobacterium Phormidium corallyticum. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 43:287–298
Richardson L, Smith G, Ritchie K, Carlton R (2001) Integrating microbiological, microsensor, and physiologic techniques in the study of coral disease pathogenesis. Hydrobiologia 460:71–89
Ritchie K (2006) Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 322:3–14
Ritchie K, Smith G (1995) Carbon-source utilization patterns of coral-associated marine heterotrophs. J Mar Biotechnol 3:105–107
Ritchie K, Smith G (2004) Microbial communities of coral surface polysaccharide layers. In: Rosenberg E, Loya Y (eds) Coral health and disease. Springer, Berlin, pp 259–263
Rohwer F, Breitbar M, Jara J, Azam F, Knowlton N (2001) Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi. Coral Reefs 20:85–91
Rohwer F, Seguritan V, Azam F, Knowlton N (2002) Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 243:1–10
Rosenberg E, Koren O, Reshef L, Efrony R, Zilber-Rosenberg I (2007) The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nature Rev Microbiol 5:335–362
Santavy D, Peters E, Kozlowski J, Wilkinson S (1995) Characterization of the bacterium suspected in the incidence of white band disease. Abstr Gen Meet Am Soc Microbiol 95(N-1):332
Sommer U (1994) Are marine diatoms favoured by high Si:N ratios? Mar Ecol Progr Ser 115:309–315
Strickland J, Parsons T (1972) Manual of seawater analysis. Bull Fish Res Bd Canadá 125:310
Toller R, Rowan R, Knowlton N (2002) Genetic evidence for a protozoan (phylum Apicomplexa) associated with the corals of the Montastraea annularis species complex. Coral Reefs 21:143–146
Trench R (1987) Dinoflagellates in non-parasitic symbiosis. In: Taylor F (ed) Biology of dinoflagellates. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 530–570
Tuchman N, Schollett M, Rier S, Geddes P (2006) Differential heterotrophic utilization of organic compounds by diatoms and bacteria under light and dark conditions. Hydrobiologia 561:167–177
Ukeles R, Rose W (1976) Observations on organic carbon utilization by photosynthetic marine microalgae. Mar Biol 37:11–28
Urban-Malinga B, Wiktor J (2003) Microphytobenthic primary production along a non-tidal sandy beach gradient: an annual study from the Baltic Sea. Oceanologia 45(4):705–720
Valdor R, Aboal M (2007) Effects of living cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial extracts and pure microcystins on growth and ultrastructure of microalgae and bacteria. Toxicon 49(6):769–779
Van Oppen M, Palstra F, Piquet A, Miller D (2001) Patterns of coral-dinoflagellate associations in Acropora: significance of local availability and physiology of Symbiodinium strains and host-symbiont selectivity. Proc R Soc Lond 268:1759–1767
Vardi A, Schatz D, Beeri K, Motro U, Sukenik A, Levne A, Kaplan A (2002) Dinoflagellate-cyanobacterium communication may determine the composition of phytoplankton assemblage in a mesotrophic lake. Curr Biol 12:1767–1772
Warner M, Chilcoat G, McFarland F, Fitt W (2002) Seasonal fluctuations in the photosynthetic capacity of photosystem II in symbiotic dinoflagellates in the Caribbean reef building coral Montastraea. Mar Biol 141:31–38
Warner M, LaJeunesse T, Robison J, Thur R (2006) The ecological distribution and comparative photobiology of symbiotic dinoflagellates from reef corals in Belize: potential implications for coral bleaching. Limnol Oceanogr 51:1887–1897
Wassmund N, Voss M, Lochte K (2001) Evidence of nitrogen fixation by non-heterocystous cyanobacteria in the Baltic Sea and re-calculation of a budget of nitrogen fixation. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 214:1–14
Watermann F, Gerdes G, Krumbein W, Sommer U (1999) Competition between benthic cyanobacteria and diatoms as influenced by different grain sizes and temperatures. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 187:77–87
Wild C, Huettel M, Klueter A, Kremb S, Rasheed M, Jergensen B (2004) Coral mucus as an energy carrier and particle trap in the reef ecosystem. Nature 428:66–70
Acknowledgments
Sampling assistance was kindly provided by Mayne Cacique and Zhandra Marcano. We thank Aquanauts Diving Center for providing the diving equipment and boat transportation. We are especially grateful to Dr. Carolina Bastidas (Universidad Simón Bolívar) and three anonymous reviewers, who helped considerably to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. L. Goulet.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavada, F., Ayala, R., Troccoli, L. et al. Microalgae from the mucus layer of two massive corals: more than sunken plankton. Mar Biol 158, 2495–2504 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1750-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1750-3