Abstract
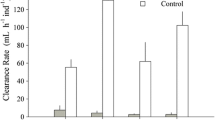
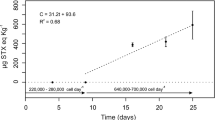
Physiological responses of Mytilus chilensis exposed to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella were measured over 21 days in the laboratory and were compared with control mussels not exposed to the dinoflagellate. Mussels were collected from culturing ropes at Yaldad Bay, southern Chile (43º08′S 73º44′W), in August 2004 and acclimated to laboratory conditions for one week prior to the experiment. After 8 days, the paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins (i.e. saxitoxin) in the tissues of exposed mussels exceeded safe levels for human consumption. Clearance rates, ingestion of organic matter, and absorption efficiency of exposed mussels were significantly lower than those of controls on day 0, but this was followed by an increase on day 3. The exposed mussels also increased their excretion rate over time, and this increase was significantly correlated with the accumulation of PSP toxins in their tissues. Oxygen consumption was not affected by the PSP toxins. The scope for growth (SFG) on day 0 was negative in exposed mussels, but it increased during the experiment. Although feeding activity and absorption efficiency were adversely affected during the first few days of exposure to PSP toxins from A. catenella in the laboratory, the M. chilensis cultured in Yaldad Bay may have evolved mechanisms that allow them to exploit the toxic dinoflagellate as a food source.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardouil M, Bohec M, Cormerais M, Bougrier S, Lassus P (1993) Experimental study of the effects of a toxic microalgae diet on feeding of the oyster Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg). J Shellfish Res 12:417–422
Bardouil M, Bohec M, Bougrier S, Lassus P, Truquet P (1996) Feeding responses of Crassostrea gigas (Thunberg) to inclusion of different proportions of toxic dinoflagellates in their diet. Oceanol Acta 19:177–182
Blasco D, Levasseur M, Bonneau E, Gelinas R, Packard TT (2003) Patterns of paralytic shellfish toxicity in the St. Lawrence region in relationship with the abundance and distribution of Alexandrium tamarense. Sci Mar (Barc.) 67:261–278
Bricelj VM, Shumway SE (1998) Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: occurrence, transfer kinetics, and biotransformation. Rev Fish Sci 6:315–383
Bricelj VM, Lee JH, Cembella AD, Anderson DM (1990) Uptake kinetics of paralytic shellfish toxins from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 63:117–188
Bricelj VM, Greene M, Cembella AD (1993) Growth of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis on toxic Alexandrium fundyense and effects of gut passage on dinoflagellate cells. In: Smayda TJ, Shimizu YE (eds) Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Elsevier, New York, pp 371–376
Bricelj VM, Connell L, Konoki K, MacQuarrie SP, Scheuer T, Catterall WA, Trainer VL (2005) Sodium channel mutation leading to saxitoxin resistance in clams increases risk of PSP. Nature 434:763–767
Clement A, Aguilera A, Fuentes C (2002) Análisis de marea roja en Archipiélago de Chiloé, contingencia verano 2002. XXII Congreso de Ciencias del Mar, 28–30 de mayo de 2002, Valdivia, Chile
Conover RJ (1966) Assimilation of organic matter by zooplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 11:338–345
Coughlan J (1969) The estimation of filtering rate from the clearance of suspensions. Mar Biol 2:356–358
Cucci TL, Shumway SE, Newell RC, Yentc CM (1985) A preliminary study of the effects of Gonyaulax tamarensis on feeding in bivalve molluscs. In: Anderson DM, White AW, Baden DG (eds) Toxic dinoflagellates. Elsevier, New York, pp 395–400
Dupuy JL, Sparks AK (1968) Gonyaulax washingtonensis, its relationship to Mytilus californianus and Crassostrea gigas as a source of paralytic shellfish toxin in Sequin Bay, Washington. In: Proceedings of the National Shellfish Association, 58 pp
Elliott JM, Davison W (1975) Energy equivalents of oxygen consumption in animal energetics. Oecologia 19:195–201
Fernández-Reiriz MJ, Navarro JM, Contreras AM, Labarta U (2008) Trophic interactions between the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and Mytilus chilensis: feeding and digestive behaviour to long-term exposure. Aquat Toxicol 87:245–251
Gainey LF, Shumway SE (1988) A compendium of the responses of bivalve mollusc to toxic dinoflagellates. J Shellfish Res 7:626–628
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum press, N.Y., USA, pp 29–60
Guillard RRL (1995) Culture methods. In: Hallegraeff GM, Anderson DM, Cembella AD (eds) Manual on harmful marine microalgae. IOC manuals and guides No. 33 UNESCO, Paris, pp 45–62
Leverone JR, Shumway SE, Blake NJ (2007) Comparative effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Karenia brevis on clearance rates in juveniles of four bivalve molluscs from Florida, USA. Toxicon 49:634–645
Li SC, Wang WX, Hsieh DPF (2001) Feeding and absorption of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense by two marine bivalves from the South China Sea. Mar Biol 139:617–624
Li SC, Wang WX, Hsieh DPF (2002) Effects of toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on the energy budgets and growth of two marine bivalves. Mar Environ Res 53:145–160
Marsden ID, Shumway SE (1992) Effects of dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense on the greenshell mussel Perna canaliculus. New Zeal J Mar Fresh 26:371–378
Marsden ID, Shumway SE (1993) The effect of a toxic dinoflagellate (Alexandrium tamarense) on the oxygen uptake of juvenile filter-feeding bivalve molluscs. Comp Biochem Phys A 106:769–773
McDonald P, Edwards RA, Greenhalgh JFD (1988) Animal Nutrition, 4th edn. Longman, Copublished in the U.S. with Wiley, New York. Chapter 10, Evaluation of foods (A) digestibility pp 200–217
McLusky DS (1981) The estuarine ecosystem, 2nd edn. Blackie, Glasgow, Chapter 2, Primary producers, pp 37–52
Molinet C, Lafon A, Lembeye G, Moreno CA (2003) Spatial and temporal distribution patterns of blooms of Alexandrium catenella (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech 1985, on inland seas of northwest Patagonia, Chile. Rev Chil Hist Nat 76:681–698
Navarro JM, Winter JE (1982) Ingestion rate, assimilation efficiency and energy balance in Mytilus chilensis in relation to body size and different algal concentration. Mar Biol 67:255–266
Navarro JM, Muñoz MG, Contreras AM (2006) Temperature as factor regulating growth and toxin content in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Harmful Algae 5:762–769
Navarro JM, Contreras AM, Chaparro OR (2008) Short-term feeding response of the mussel Mytilus chilensis exposed to diets containing the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Rev Chil Hist Nat 81:41–49
Pérez M (1998) Efecto de las distintas concentraciones y fuentes de nitrógeno sobre el crecimiento y toxicidad de Alexandrium catenella (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech 1985. Thesis Escuela de Biología Marina, Facultad de Ciencias, UACh
Shumway SE, Cucci TL (1987) The effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Protogonyaulax tamarensis on the feeding and behavior of bivalve molluscs. Aquat Toxicol 10:9–27
Smolowitz R, Shumway SE (1997) Possible cytotoxic effects of the dinoflagellate Gyrodinium aureolum, on juvenile bivalve mollusks. Aquacult Int 5:291–300
Solórzano L (1969) Determination ammonia in natural water by the phenolhypochlorite methods. Limnol Oceanogr 14:799–801
Vélez P, Sierralta J, Alcayaga C, Fonseca M, Loyola H, Johns DC, Tomaselli GF, Suárez-Isla BA (2001) A functional assay for paralytic shellfish toxins that uses recombinant sodium channels. Toxicon 39:929–935
Widdows J (1978) Physiological indices of stress in Mytilus edulis. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 58:125–142
Widdows J (1985) Physiological responses to pollution. Mar Pollut Bull 16:129–134
Widdows J, Moore MN, Lowe DM, Salkeld PN (1979) Some effects of the dinoflagellate bloom (Gyrodinium aureolum) on the mussel Mytilus edulis. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 59:522–524
Wildish D, Lassus P, Martin J, Saulnier A, Bardouil M (1998) Effect of the PSP-causing dinoflagellate, Alexandrium sp. on the initial feeding response of Crassostrea gigas. Aquat Living Resour 11:35–43
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank to G. Urrutia and V. Garrido for technical assistance during the experiments. This study was supported by a research grant to JMN (FONDECYT 1080127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. P. Grassle.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Navarro, J.M., Contreras, A.M. An integrative response by Mytilus chilensis to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella . Mar Biol 157, 1967–1974 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1465-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1465-x