Abstract
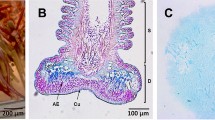
Based on carbohydrate histochemistry, including the use of lectins, and TEM, the study describes the distribution of terminal sugars in different structures of the demosponge Chondrilla nucula. The results of the general and specific carbohydrate histochemical approaches confirmed the presence of acidic and neutral glycoconjugates in the cells, and, with declining amounts from the ectosome to the mesohyl, in the extracellular matrix (ECM). AB-PAS staining indicated acidic complex carbohydrates particularly in the exopinacoderm, and more neutral ones in the cells and the ECM of the mesohyl. The PO-lectins applied demonstrated a general spectrum of free saccharide residues (α-d-mannose, α-/β-d-N-acetylglucosamine, α-d-N-acetylgalactosamine, α-d-galactose, β-d-galactose) in both sponge parts; α-l-fucose was only distinct in the ectosome. Sialic acids [siaα(2,3)-galactose, siaα(2,6)-N-acetylgalactosamine] were dominant in the very thin exopinacoderm, indicating O-linked high molecular weight glycoproteins. In this way a glycophysiologically ‘rigid’ outer mucus cover is developed as protection against mechanical hazards. Some of the free sugars (α-d-mannose, N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine β-d-galactose, α-l-fucose) are known to prevent the adherence of different bacteria and fungi to cellular surfaces. Thus a high concentration of such sugars, may impede massive attacks of micro-inhabitants on mobile sponge cells, pinacocytes, and the exopinacoderm layer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison RT (1987) The effects of various fixatives on subsequent lectin binding to tissue sections. Histochem J 19:65–74
Alroy J, Ucci AA, Pereira MEA (1988) Lectin histochemistry: an update. In: DeLellis RA (ed) Advances in immunohistochemistry (neoplasms diagnosis). Raven Press, New York, pp 93–131
Austin B (2002) The bacterial flora of fish. Sci World J 2:558–572
Baum C, Meyer W, Stelzer R, Fleischer L-G, Siebers D (2002) Average nanorough skin surface of the pilot whale (Globicephala melas, Delphinidae): considerations on the self-cleaning abilities based on nanoroughness. Mar Biol 140:653–657
Bond C, Harris A (1988) Locomotion of sponges and its physical mechanism. J Exp Zool 246:271–284
Boury-Esnault N (2002) Order Chondrosida Boury-Esnault & Lopés, 1985. Family Chondrillidae Gray, 1872. In: Hooper JNA, Van Soest RWM (eds) Systema Porifera: a guide to the classification of sponges. Kulwer/Plenum, New York, pp 291–297
Bretting H, Königsmann K (1979) Investigations on the lectin-producing cells in the sponge Axinella polypoides (Schmidt). Cell Tiss Res 201:487–497
Brümmer F, Calcinai B, Götz M, Leitermann F, Nickel M, Sidri M, Zucht W (2004) Overview on the sponge fauna of the Limski kanal, Croatia, Northern Adriatic Sea. Boll Mus Ist Biol Univ Genova 68:219–227
Campbell BJ (1999) Biochemical and functional aspects of mucus and mucin-type glycoproteins. In: Mathiowitz E, Chickering DE, Lehr CM (eds) Bioadhesive drug delivery systems, drugs and the pharmaceutical sciences, vol 98. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 85–130
Carballo JL, Gómez P, Cruz-Barraza JA, Flores-Sánchez DM (2003) Sponges of the family Chondrillidae (Porifera: Demospongiae) from the Pacific coast of Mexico, with the description of three new species. Proc Biol Soc Wash 116:515–527
Critchley IA, Douglas LJ (1987) Role of glycosides as epithelial cell receptors for Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol 133:637–643
Danguy A, Decaestecker C, Genten F, Salmon I, Kiss R (1998) Application of lectins and neoglycoconjugates in histology and pathology. Acta Anat 161:206–218
Daunter B, Forbes KL, Sanderson BM, Morrison J, Wright G (1992) Inhibition of binding of bacteria to amniochorionic membranes by amniotic fluid. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 47:95–102
De Vos L, Rützler K, Boury-Esnault N, Donadey C, Vacelet J (1991) Atlas de morphologie des eponges—Atlas of sponge morphology, vol 117. Smithsonian Inst Press, Washington
Fairchild CD, Jones IK, Glazer AN (1991) Absence of glycosylation on cyanobacterial phycobilisome linker polypeptides and rhodophytan phycoerythrins. J Bacteriol 173:2985–2992
Faulkner DJ (2002) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 19:1–48
Faulkner DJ, Unson MD, Bewley CA (1994) The chemistry of some sponges and their symbionts. Pure Appl Chem 66:1983–1990
Fernandez-Busquets X, Burger MM (2003) Circular proteoglycans from sponges: first members of the spongican family. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:88–112
Gaino E, Pronzato R (1983) Étude en microscopie électronique du filament des formes étirées chez Chondrilla nucula (Porifera, Demospongiae). Ann Sci Nat Zool 5:221–234
Geyer G (1973) Ultrahistochemie. Histochemische Arbeitsvorschriften für die Elektronenmikroskopie, 2nd edn. G Fischer, Stuttgart
Hanstede JG, Gerrits PO (1983) The effects of embedding in water-soluble plastics on the final dimensions of liver sections. J Microsc 131:79–90
Hayat MA (1993) Stains and cytochemical methods. Plenum, New York
Hentschel U, Fieseler L, Wehrl M, Gernert C, Steinert M, Hacker J, Horn M (2003) Microbial diversity of marine sponges. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 37:59–88
Hoiczyk E (1998) Structural and biochemical analysis of the sheath of Phormidium uncinatum. J Bacteriol 180:3923–3932
Hoiczyk E, Baumeister W (1997) Oscillin, an extracellular, Ca2+-binding glycoprotein essential for the gliding motility of cyanobacteria. Mol Microbiol 26:699–708
Imhoff JF, Stöhr R (2003) Sponge-associated bacteria: a general overview and special aspects of bacteria associated with Halochondria panicea. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 37:35–57
Izhar M, Nuchamowitz Y, Mirelman D (1982) Adherence of Shigella flexneri to guinea pig intestinal cells is mediated by a mucosal adhesion. Infect Immun 35:1110–1118
James J, Tas J (1984) Histochemical protein staining methods (Microscopy handbooks 04). Oxford University Press, Royal Microsc Soc, Oxford
Jarchow J, Fritz J, Anselmetti D, Calabro A, Hascall VC, Gerosa D, Burger MM, Fernandez-Busquets X (2000) Supramolecular structure of a new family of circular proteoglycans mediating cell adhesion in sponges. J Struct Biol 132:95–105
Keyzers RA, Davies-Coleman MT (2005) Anti-inflammatory metabolites from marine sponges. Chem Soc Rev 34:355–365
Klautau M, Russo CAM, Lazoski C, Boury-Esnault N, Torpe J, Solé-Cava A (1999) Does cosmopolitanism result from overconservative systematics? A case study using the marine sponge Chondrilla nucula. Evolution 53:1414–1422
Lamblin G, Degroote S, Perini JM, Delmotte P, Scharfman A, Davril M, Lo-Guidice JM, Houdret N, Dumur V, Klein A, Roussel P (2001) Human airway mucin glycosylation: a combinatory of carbohydrate determinants which vary in cystic fibrosis. Glycoconj J 18:661–684
Luft JH (1961) Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:409–414
Maldonado M, Cortadellas N, Trillas MI, Rützler K (2005) Endosymbiontic yeast maternally transmitted in a marine sponge. Biol Bull 209:94–106
McGavin MH, Krajewska-Pietrasik D, Ryden C, Hook M (1993) Identification of a Staphylococcus aureus extracellular matrix-binding protein with broad specificity. Infect Immun 61:2479–2485
Mercurio M, Scalera-Liaci L, Corriero G (2001) La fauna a poriferi del bacino della strea di Porto Cesareo (Le). Biol Mar Medit 8:403–412
Meyer W, Seegers U (2004) A preliminary approach to epidermal antimicrobial defense in the Delphinidae. Mar Biol 244:841–844
Meyer W, Bollhorn M, Stede M (2000) Aspects of antimicrobial properties of skin secretions in the Common seal (Phoca vitulina). Dis Aquat Org 41:77–79
Meyer W, Neurand K, Tanyolac A (2001) General antimicrobial properties of the integument in fleece producing sheep and goats. Small Rumin Res 41:181–190
Meyer W, Seegers U, Schnapper A (2003a) Free sugars as antimicrobial agents on the epidermal surface of aquatic vertebrates. 96 Jahresvers Dtsch Zool Ges (Berlin), Abstracts, 135
Meyer W, Seegers U, Herrmann J, Schnapper A (2003b) Further aspects of general antimicrobial properties of skin secretions of pinnipeds. Dis Aquat Org 44:177–179
Millonig G (1981) Advantages of a phosphate buffer for OsO4 solutions in fixation. J Appl Phys 32:1637
Müller WE, Müller IM (2003) Analysis of the sponge (Porifera) gene repertoire: implications for the evolution of the metazoan body plan. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 37:1–33
Müller WEG, Zahn RK, Kurelec B, Müller I (1984) A catalogue of the sponges near Rovinj. Thalassia Jugoslavica 20:13–23
Novosel M, Bakran-Petricioli T, Požar-Domac A, Kružic P, Radic I (2002) The benthos of the Northern part of the Velebit channel (Adriatic Sea, Croatia). Nat Croat 11:387–409
Ollert MW, Söhnchen R, Korting HC, Ollert U, Bräutigam S, Bräutigam W (1993) Mechanisms of adherence of Candida albicans to cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. Infect Immun 61:4560–4568
Passow U (2000) Formation of transparent exopolymer particles, TEP, from dissolved precursor material. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 192:1–11
Pearse AGE (1968) Histochemistry. Theoretical and applied, 3rd edn, vol 1. Preparative and optical technology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Pearse AGE (1980) Histochemistry. Theoretical and applied, 4th edn, vol 1. Preparative and optical technology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Pearse AGE (1985) Histochemistry. Theoretical and applied, 4th edn, vol 2. Analytical technology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Proksch P, Ebel R, Edrada RA, Wray V, Steube K (2003) Bioactive natural products from marine invertebrates and associated fungi. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 37:117–142
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate of high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–212
Richardson KC, Jarett L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–323
Rittman BR, Mackenzie IC (1983) Effects of histological processing on lectin binding patterns in oral mucosa and skin. Histochem J 15:467–474
Romero-Steiner S, Witek T, Balish E (1990) Adherence of skin bacteria to human epithelial cells. J Clin Microbiol 28:27–31
Rützler K (1965) Systematik und Ökologie der Poriferen aus Littoral-schattengebieten der Nordadria. Z Morph Ökol Tiere 55:1–82
Schauer R (2004) Sialic acids: fascinating sugars in higher animals and man. Zoology 107:49–64
Schmitz FJ, McDonald FJ (1974) Isolation and identification of cerebrosides from the marine sponge Chondrilla nucula. J Lipid Res 15:158–164
Sciscioli M, Feri D, Liquori GE, Lepore E, Santarelli G (2000) Lectin histochemistry and ultrastructure of microgranular cells in Cinachyra tarentina (Porifera, Demospongiae). Acta Histochem 102:219–230
Sharon N, Eshdat Y, Silverblatt FJ, Ofek I (1981) Bacterial adherence to cell surface sugars. CIBA Found Symp 80:119–141
Sidri M (2004) Chondrilla nucula (Porifera, Demospongie): an example of successful plasticity. Ecological and morphological aspects. Dissertation Thesis, University of Stuttgart, Germany, 226 pp
Sionov E, Roth D, Sandovsky-Losica H, Kashman Y, Rudi A, Chill L, Berdicevsky I, Segal E (2005) Antifungal effect and possible mode of activity of a compound from the marine sponge Dysidea herbacea. J Infect 50:453–460
Sobel JD, Myers PG, Kaye D, Levison ME (1981) Adherence of Candida albicans to human vaginal and buccal epithelial cells. J infect Dis 143:1, 76–82
Spicer SS, Schulte BA (1992) Diversity of cell glycoconjugates shown histochemically: a perspective. J Histochem Cytochem 40:1–38
Stempak JG, Ward RT (1964) An improved staining method for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 22:697–701
Usher KM, Toze S, Fromont J, Kuo J, Sutton DC (2004) A new species of cyanobacterial symbiont from the marine sponge Chondrilla nucula. Symbiosis 36:183–192
Acknowledgements
The skillfull technical assistance of M. Gähle and K. Rohn, and the help of Dr. A. Schnapper is gratefully acknowledged. Part of this work (MS, FB) was supported by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the University of Stuttgart and the Ministry of Science, Research and Arts of the State of Baden-Württemberg through the excellence center BIOTECmarin (03F0345D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, W., Sidri, M. & Brümmer, F. Glycohistochemistry of a marine sponge, Chondrilla nucula (Porifera, Desmospongiae), with remarks on a possibly related antimicrobial defense strategy and a note on exopinacoderm function. Mar Biol 150, 313–319 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0353-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-006-0353-x