Abstract
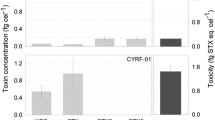
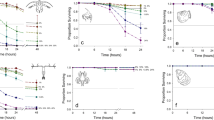
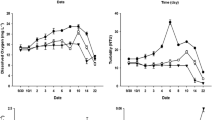
Cyanobacterial blooms are a common phenomenon in the Baltic Sea, and the hepatotoxin nodularin has been frequently detected in certain Baltic Sea fishes and mussels. However, there is no knowledge about the naturally occurring concentrations of nodularin in Baltic Sea zooplankton. The aim of this study was to survey the concentrations of nodularin in natural zooplankton assemblages, and to study the depuration of nodularin in one common copepod species, Eurytemora affinis, experimentally. The nodularin concentrations in common zooplankton species were determined from field-collected samples from the northern Baltic Proper in 2001 and 2002, during cyanobacterial blooms, and the samples were analysed by ELISA immunoassay. Nodularin could be detected from the field-collected zooplankton, suggesting that during a natural bloom event toxins accumulate in their tissues. The concentrations were relatively low (0.07±0.01 μg g−1 ww), ranging from below detection limit to 0.62 μg g−1 ww. Some variation occurred in the concentrations between species and years; generally concentrations were higher in 2001 than in 2002. In the depuration experiment E. affinis copepods were fed with toxic Nodularia spumigena for 24 h, and their toxin contents were monitored for 24 h after transferring them to filtered seawater. A rapid decrease in nodularin concentrations occurred during the first 0.5–3 h after the exposure. However, after a 24-h depuration period in filtered seawater, nodularin could be still detected in E. affinis tissues, indicating that part of the accumulated nodularin, or its derivatives, could be transferred to planktivores.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bury NR, Newlands AD, Eddy FB, Codd GA (1998) In vivo and in vitro intestinal transport of 3H-microcystin-LR, a cyanobacterial toxin, in rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 42:139–148
Burris JE (1980) Vertical migration of zooplankton in the Gulf of Finland. Am Midland Nat 103:316–322
Engström J, Koski M, Viitasalo M, Reinikainen M, Repka S, Sivonen K (2000) Feeding interactions of Eurytemora affinis and Acartia bifilosa with toxic and non-toxic Nodularia sp. J Plankton Res 22:1403–1409
Engström-Öst J, Lehtiniemi M, Green S, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B, Viitasalo M (2002) Does cyanobacterial toxin accumulate in mysid shrimps and fish via copepods? J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 276:95–107
Ferrao-Filho AS, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B, Azevedo SMFO (2002) Accumulation of microcystins by a tropical zooplankton community. Aquat Toxicol 59:201–208
Flinkman J, Are E, Vuorinen I, Viitasalo M (1998) Changes in northern Baltic zooplankton and herring nutrition from 1980s to 1990s: top-down and bottom-up processes at work. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 165:127–136
Gasparini S, Castel J (1997) Autotrophic and heterotrophic nanoplankton in the diet of the estuarine copepods Eurytemora affinis and Acartia bifilosa. J Plankton Res 19:877–890
Kahru M, Horstmann U, Rud O 1994: Satellite detection of increased cyanobacteria blooms in the Baltic Sea—natural fluctuation or ecosystem change. Ambio 23:469–472
Kankaanpää HT, Sipiä VO, Kuparinen JS, Ott JL, Carmichael WW (2001) Nodularin analyses and toxicity of a Nodularia spumigena (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) water-bloom in the western Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea, in August 1999. Phycologia 40:268–274
Kankaanpää H, Vuorinen PJ, Sipiä V, Keinänen M (2002) Acute effects of Nodularia spumigena and bioaccumulation of nodularin in sea trout (Salmo trutta m. trutta L.) under laboratory conditions. Aquat Toxicol 61:155–168
Kankaanpää HT, Holliday J, Schröder H, Goddard TJ, von Fister R, Carmichael WW (2005) Cyanobacteria and prawn farming in northern New South Wales, Australia—a case study on cyanobacteria diversity and hepatotoxin bioaccumulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:243–256
Karjalainen M, Reinikainen M, Lindvall F, Spoof L, Meriluoto JAO (2003) Uptake and accumulation of dissolved, radiolabeled nodularin in Baltic Sea zooplankton. Environ Toxicol 18:52–60
Karjalainen M, Reinikainen M, Spoof L, Meriluoto JAO, Sivonen K, Viitasalo M (2005) Trophic transfer of cyanobacterial toxins from zooplankton to planktivores: consequences for pike larvae and mysid shrimps. Environ Toxicol 20:354–362
Karlsson KM, Kankaanpää H, Huttunen M, Meriluoto J (2005) First observation of microcystin-LR in pelagic cyanobacterial blooms in the northern Baltic Sea. Harmful Algae 4:163–166
Kim SW, Onbé T, Yoon YH (1989) Feeding habits of marine cladocerans in the Inland Sea of Japan. Mar Biol 100:313–318
Kononen K, Sivonen K, Lehtimäki J (1993) Toxicity of phytoplankton blooms in the Gulf of Finland and Gulf of Bothnia, Baltic Sea. In: Smayda TJ, Shimizu Y (eds) Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 269–273
Kononen K, Kuparinen J, Mäkelä K, Laanemets J, Pavelson J, Nõmmann S (1996) Initiation of cyanobacterial blooms in a frontal region at the entrance to the Gulf of Finland, Baltic Sea. Limnol Oceanogr 41:98–112
Koski M, Engström J, Viitasalo M (1999) Reproduction and survival of the calanoid copepod Eurytemora affinis fed with toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 186:187–197
Koski M, Schmidt K, Engström-Öst J, Viitasalo M, Jónasdóttir S, Repka S, Sivonen K (2002) Calanoid copepods feed and produce eggs in the presence of toxic cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena. Limnol Oceanogr 47:878–885
Kotak BG, Zurawell RW, Prepas EE, Holmes CFB (1996) Microcystin-LR concentration in aquatic food web compartments from lakes of varying trophic status. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 53:1974–1985
Kozlowsky-Suzuki B, Karjalainen M, Lehtiniemi M, Engström-Öst J, Koski M, Carlsson P (2003) Feeding, reproduction and toxin accumulation by the copepods Acartia bifilosa and Eurytemora affinis in the presence of the toxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 249:237–249
Kozlowsky-Suzuki B (2004): Effects of toxin-producing phytoplankton on copepods: feeding, reproduction and implications to the fate of toxins. PhD Thesis, Lund University, 118 p
Magalhães VF, Moraes Soares R, Azevedo SMFO (2001) Microcystin contamination in fish from the Jacarepaguá Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil): ecological implication and human health risk. Toxicon 39:1077–1085
Metcalf JS, Beattie KA, Pflughmacher S, Codd GA (2000) Immuno-crossreactivity and toxicity assessment of conjugation products of the cyanobacterial toxin, microcystin-LR. FEMS Microbiol Lett 189:155–158
Meyer-Harms B, Reckermann M, Voβ M, Siegmund H, von Bodungen B (1999) Food selection by calanoid copepods in the euphotic layer of the Gotland Sea (Baltic Proper) during mass-occurrences of N2-fixing cyanobacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 191:243–250
Nishiwaki-Matsushima R, Ohta T, Nishiwaki S, Suganuma M, Kohyama K, Ishikawa T, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (1992) Liver tumour promotion by the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin-LR. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 118:420–424
Lehtiniemi M, Engström-Öst J, Karjalainen M, Kozlowsky-Suzuki B, Viitasalo M (2002) Fate of cyanobacterial toxins in the pelagic food web: transfer to copepods or to faecal pellets? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 241:13–21
Ojaveer H, Kuhns LA, Barbiero RP, Tuchman ML (2001) Distribution and population characteristics of Cercopagis pengoi in Lake Ontario. J Great Lakes Res 27:10–18
Raid T, Lankov A (1995) Recent changes in the growth and feeding of Baltic herring and sprat in the northeastern Baltic Sea. Proc Est Acad Sci Ecol 5:38–55
Reinikainen M, Lindvall F, Meriluoto JAO, Repka S, Sivonen K (2002) Effects of cyanobacterial toxins on the survival and egg hatching of estuarine calanoid copepods. Mar Biol 140:577–583
Rudstam LG, Hansson S, Johansson S, Larsson U (1992) Dynamics of planktivory in a coastal area of the northern Baltic Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 80:159–173
Sellner KG, Olson MM, Kononen K (1994) Copepod grazing in a summer cyanobactreia bloom in the Gulf of Finland. Hydrobiologia 292/293:249–254
Sipiä VO, Kankaanpää H, Flinkman J, Lahti K, Meriluoto JAO (2001a) Time-dependent accumulation of cyanobacterial hepatotoxins in flounders (Platichtys flesus) and mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the northern Baltic Sea. Environ Toxicol 16:330–336
Sipiä V, Kankaanpää H, Lahti K, Carmichael WW, Meriluoto J (2001b) Detection of nodularin in flounders and cod from the Baltic Sea. Environ Toxicol 16:121–126
Sipiä VO, Kankaanpää HT, Pflugmacher S, Flinkman J, Furey A, James KJ (2002a) Bioaccumulation and detoxication of nodularin in tissues of flounder (Platichthys flesus), mussels (Mytilus edulis, Dreissena polymorpha), and clams (Macoma balthica) from the northern Baltic Sea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 53:305–311
Sipiä VO, Lahti K, Kankaanpää HT, Vuorinen PJ, Meriluoto JAO (2002b) Screening for cyanobacterial hepatotoxins in herring and salmon from the Baltic Sea. Aquatic Ecosyst Health Manage 5:451–456
Sipiä VO, Karlsson KM, Meriluoto JAO, Kankaanpää H (2003) Eiders (Somateria mollissima) obtain nodularin, a cyanobacterial hepatotoxin, in Baltic Sea food web. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1256–1260
Sivonen K, Jones G (1999) Cyanobacterial toxins. In: Chorus I, Bartram J (eds) Toxic cyanobacteria in the water. E & FN Spon, London, pp 41–111
Sivonen K, Kononen K, Carmichael WW, Dahlem AM, Rinehart K, Kiviranta J, Niemelä SI (1989) Occurrence of the hepatotoxic cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea and the structure of the toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1990–1995
Thostrup L, Christoffersen K (1999) Accumulation of microcystin in Daphnia magna feeding on toxic Microcystis. Arch Hydrobiol 145:447–467
Uitto A, Gorokhova E, Välipakka P (1999) Distribution of the non-indigenous Cercopagis pengoi in the coastal waters of the eastern Gulf of Finland. ICES J Mar Sci 56(Suppl):49–57
Vanderploeg HA, Cavaletto JF, Liebig JR, Gardner WS (1998) Limnocalanus macrurus (Copepoda:Calanoida) retains a marine arctic lipid and life cycle strategy in Lake Michigan. J Plankton Res 20:1581–1597
Vihervuori A, Ahvonen A (1997) Miten kalankulutusta arvioidaan? Kalavirrat - tietoa kalan tarjonnasta ja käytöstä. Riista- ja kalatalouden tutkimuslaitos (in Finnish). SVT-Ympäristö 1997:13. pp 34–39
Ward CJ, Lee EYC, Beattie KA, Codd GA (1998) Colorimetric protein phosphatase inhibition assay for microcystins and nodularin in laboratory cultures and natural blooms of cyanobacteria. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Proceedings of VIII international conference harmful algae. Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, pp 541–544
Watanabe MM, Kaya K, Takamura N (1992) Fate of the toxic cyclic heptapeptides, the microcystins, from blooms of Microcystis (Cyanobacteria) in a hypertrophic lake. J Phycol 28:761–767
Acknowledgements
Prof. Kaarina Sivonen (University of Helsinki) is acknowledged for providing the Nodularia spumigena strain AV1; Eveliina Lindén, Sanna Rönkkönen and Hermanni Backer for help with collecting the zooplankton samples during summer 2002; Maija Huttunen and Emil Vahtera for counting the phytoplankton samples; and Jari-Pekka Pääkkönen for help in calculations. Marko Reinikainen and Marja Koski gave valuable comments on the manuscript. This study was financed by Walter and Andrée de Nottbeck Foundation, Maj and Tor Nessling Foundation, Finnish Cultural Foundation, the Academy of Finland (grant number 50679) and the Brazilian National Council for Research (CNPq). Two anonymous referees are acknowledged for constructive criticism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Kühl, Helsingør
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karjalainen, M., Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B., Lehtiniemi, M. et al. Nodularin accumulation during cyanobacterial blooms and experimental depuration in zooplankton. Marine Biology 148, 683–691 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0126-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0126-y