Abstract
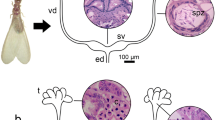
The morphological expressions of imposex in gastropods have been classified into seven stages (S0–S6) with three types (a, b and c). This typical imposex scheme, however, fails to cover some new findings such as specimens with the proximal vas deferens section passing by the vaginal opening (VDSP) and aborted egg capsules. In the present study, Cantharus cecillei was sampled from the coastal waters of China from May to November in 2003. This species showed all the morphological expressions in the typical imposex scheme with the exception of S1b and S2b. In addition, specimens with VDSP occurred in all stages other than stage 4, and were documented for the first time with scanning electron micrographs or in histological sections. Besides VDSP, which was observed exteriorly, excrescent tissue, e.g. the vas deferens, also originated in the ventral channel or the inner wall of the pallial oviduct was extruded. Based on these new findings, the typical imposex scheme was modified to obtain one valid for C. cecillei. Types a*, b* and c* were added as new types corresponding to types a, b and c, respectively. S4* was also rearranged to correspond to S4; S4*, thus, no longer represented the end of imposex development. The updated scheme was not only valid for describing diverse expressions of imposex development in C. cecillei and Nassarius reticulatus, but could also be generalized to define various forms of VDSP in other species. Histological observation indicated that egg capsules would be blocked by the tissues of the vas deferens section or the extrusion of the pallial oviduct wall. This new mechanism, leading to the sterilization of imposex-affected females, was first conclusively revealed and described in the present scheme.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axiak V, Vella AJ, Micallef D, Chircop P, Mintoff B (1995) Imposex in Hexaplex trunculus (Gastropoda: Muricidae): first results from biomonitoring of tributyltin contamination in the Mediterranean. Mar Biol 121:685–691
Barreiro R, González R, Quintela M, Ruiz J M (2001) Imposex, organotin bioaccumulation and sterility of female Nassarius reticulatus in polluted areas of NW Spain. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 218:203–212
Barroso CM, Moreira MH, Bebianno MJ (2002) Imposex, female sterility and organotin contamination of the prosobranch Nassarius reticulatus from the Portuguese coast. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 230:127–135
Bech M (2002) A survey of imposex in muricids from 1996 to 2000 and identification of optimal indicators of tributyltin contamination along the east coast of Phuket Island, Thailand. Mar Pollut Bull 44:887–896
Bettin C, Oehlmann J, Stroben E (1996) TBT-induced imposex in marine neogastropods is mediated by an increasing androgen level. Helgol Meeresunters 50:299–317
deFur PL (ed) (1999) Endocrine disruption in invertebrates: endocrinology, testing, and assessment. SETAC, USA
Fioroni P, Oehlmann J, Stroben E (1991) The pseudohermaphroditism of prosobranchs, morphological aspects. Zool Anz 226:1–26
Gibbs PE (1993) A male genital defect in the dog-whelk, Nucella lapillus (Neogastropoda), favoring the survival of a population in a TBT-polluted area. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 73:667–678
Gibbs PE, Bryan GW (1986) Reproductive failure in populations of the dog-whelk, Nucella lapillus, caused by imposex induced by tributyltin from antifouling paints. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 66:767–777
Gibbs PE, Bryan GW (1996) TBT-induced imposex in neogastropod snails: masculinization to mass extinction. In: de Mora SJ (ed) Tributyltin: case study of an environmental contaminant. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 212–236
Huet M, Fioroni P, Oehlmann J, Stroben E (1995) Comparison of imposex response in three prosobranch species. Hydrobiologia 309:29–35
Mensink BP, Everarts JM, Kralt H, Hallers CC, Boon JP (1996) Tributyltin exposure in early life stages induces the development of male sexual characteristics in the common whelk, Buccinum undatum. Mar Environ Res 42:151–154
Nias DJ, McKillup SC, Edyvane KS (1993) Imposex in Lepsiella vinosa from southern Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 26:380–384
Oehlmann J, Stroben E, Fioroni P (1991) The morphological expression of imposex in Nucella lapillus (Linnaeus) (Gastropoda: Muricidae). J Molluscan Stud 57:375–390
Oehlmann J, Stroben E, Fioroni P (1992) The rough tingle Ocenebra erinacea (Gastropoda: Muricidae): an exhibitor of imposex in comparison to Nucella lapillus. Helgol Meeresunters 46:311–328
Oehlmann J, Fioroni P, Stroben E, Markert B (1996) Tributyltin (TBT) effects on Ocenebrina aciculate (Gastropoda: Muricidae): imposex development, sterilization, sex change and population decline. Sci Total Environ 188:205–223
Power AJ, Keegan BF (2001) The significance of imposex levels and TBT contamination in the red whelk, Neptunea antiqua (L.), from the offshore Irish Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 42:761–772
Ramón M, Amor M J (2001) Increasing imposex in populations of Bolinus brandaris (Gastropoda: Muricidae) in the north-western Mediterranean. Mar Environ Res 52:463–475
Reitsema TJ, Spickett JT (1999) Imposex in Morula granulata as a bioindicator of tributyltin (TBT) contamination in the Dampier Archipelago, Western Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 39:280–284
Shi HH, Huang CJ (2001) Morphological characters of imposex in marine gastropod. J Oceanogr Taiwan Strait 20:552–555
Stroben E, Oehlmann J, Fioroni P (1992) The morphological expression of imposex in Hinia reticulata (Gastropoda: Buccinidae): a potential biological indicator of tributyltin pollution. Mar Biol 113:625–636
Tan KS (1999) Imposex in Thais gradata and Chicoreus capucinus (Mollusca, Neogastropoda, Muricidae) from the Straits of Johor: a case study using penis length, area and weight as measures of imposex severity. Mar Pollut Bull 39:295–303
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Oehlmann for comments and J.H. Sheng for histological sections. This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid from the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (40176029), Developing Marine Economy Project of Guangdong (A200005F02) and Natural Science Fund of Guangdong (000792). The experiments comply with the current laws of China where the experiments were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Ikeda, Hakodate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Huang, C., Yu, X. et al. An updated scheme of imposex for Cantharus cecillei (Gastropoda: Buccinidae) and a new mechanism leading to the sterilization of imposex-affected females. Marine Biology 146, 717–723 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-004-1475-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-004-1475-7