Abstract
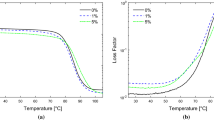
To overcome the ecological concern and fiber orientation problem, lignocellulosic wood filler reinforced epoxy composite is developed using ‘micro-size’ particle reinforcement in view of its promising applicability as automobile parts and consumer goods. To identify the phase and functional groups present, the wood microfiller is characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis. The properties of the developed ‘specific grade’ epoxy composite are investigated in uniaxial tension mode with variable strain rate and in three-point bending mode. The linear elastic fracture mechanics is adopted to find fracture toughness and strain energy release rate at fracture initiation. The dynamic mechanical properties of the produced viscoelastic material are determined over a range of temperature. The investigations demonstrated a noticeable improvement in static and dynamic mechanical properties with the addition of micron size fillers, and properties of this developed material are comparable (or even better) with existing different wood-based composites.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bledzki AK, Faruk O (2003) Wood fibre reinforced polypropylene composites: effect of fibre geometry and coupling agent on physico-mechanical properties. Appl Compos Mater 10(6):365–379
Cavdar AD, Mengeloğlu F, Karakus K (2015) Effect of boric acid and borax on mechanical, fire and thermal properties of wood flour filled high density polyethylene composites. Measurement 60:6–12
Cho J, Joshi MS, Sun CT (2006) Effect of inclusion size on mechanical properties of polymeric composites with micro and nano particles. Compos Sci Technol 66:1941–1952
Davi SDV, Fabienne T, Laurence CA (2014) Tension–tension fatigue behaviour of woven hemp fibre reinforced epoxy composite: a multi-instrumented damage analysis. Int J Fatigue 59:159–169
Doan TTL, Brodowsky H, Mäder E (2012) Jute fibre/epoxy composites: surface properties and interfacial adhesion. Compos Sci Technol 72:1160–1166
Dunne R, Desai D, Sadiku R (2016) A review of natural fibres, their sustainability and automotive applications. J Reinf Plast Compos 35:1041–1050
Fiore V, Scalici T, Vitale G, Valenza A (2014) Static and dynamic mechanical properties of Arundo Donax fillers-epoxy composites. Mater Des 57:456–464
Fiore V, Di BG, Valenza A (2015) The effect of alkaline treatment on mechanical properties of kenaf fibers and their epoxy composites. Compos B Eng 68:14–21
Goyat MS, Suresh S, Bahl S, Halder S, Ghosh PK (2015) Thermo mechanical response and toughening mechanisms of a carbon nano bead reinforced epoxy composite. Mater Chem Phys 166:144–152
Gurunathan T, Mohanty S, Nayak SK (2015) A review of the recent developments in biocomposites based on natural fibres and their application perspectives. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 77:1–25
Ikada Y, Tsuji H (2000) Biodegradable polyesters for medical and ecological applications. Macromol Rapid Commun 21:117–132
Karmarkar A, Chauhan SS, Modak JM, Chanda M (2007) Mechanical properties of wood–fiber reinforced polypropylene composites: effect of a novel compatibilizer with isocyanate functional group. Compos A Appl Sci Manuf 38:227–233
Kinloch AJ, Taylor AC, Techapaitoon M, Teo WS, Sprenger S (2015) Tough, natural-fibre composites based upon epoxy matrices. J Mater Sci 50:6947–6960
Kitey R, Tippur HV (2005) Role of particle size and filler–matrix adhesion on dynamic fracture of glass-filled epoxy. II. Linkage between macro- and micro-measurements. Acta Mater 53:1167–1178
Koronis G, Silva A, Fontul M (2013) Green composites: a review of adequate materials for automotive applications. Compos B Eng 44:120–127
Kranthi G, Satapathy A (2010) Evaluation and prediction of wear response of pine wood dust filled epoxy composites using neural computation. Comput Mater Sci 49:609–614
Kumar R, Kumar K, Sahoo P, Bhowmik S (2014) Study of mechanical properties of wood dust reinforced epoxy composite. Proced Mater Sci 6:551–556
Kumar R, Kumar K, Bhowmik S (2017a) Establishment and effect of constraint on different mechanical properties of bamboo filler reinforced epoxy composite. Int Polym Process 32(3):308–315
Kumar R, Kumar K, Bhowmik S (2017b) Assessment and response of treated Cocos nucifera reinforced toughened epoxy composite towards fracture and viscoelastic properties. J Polym Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1150-y
Madsen B, Lilholt H (2003) Physical and mechanical properties of unidirectional plant fibre composites-an evaluation of the influence of porosity. Compos Sci Technol 63:1265–1272
Milanese AC, Cioffi MOH, Voorwald HJC (2012) Thermal and mechanical behaviour of sisal/phenolic composites. Compos B Eng 43:2843–2850
Mirmehdi SM, Zeinaly F, Dabbagh F (2014) Date palm wood flour as filler of linear low-density polyethylene. Compos B Eng 56:137–141
Mishra S, Misra M, Tripathy SS, Nayak SK, Mohanty AK (2001) Graft copolymerization of acrylonitrile on chemically modified sisal fibers. Macromol Mater Eng 286:107–113
Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT (2001) Surface modifications of natural fibers and performance of the resulting biocomposites: an overview. Compos Interfaces 8:313–343
Mylsamy K, Rajendran I (2011) The mechanical properties, deformation and thermomechanical properties of alkali treated and untreated agave continuous fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Mater Des 32:3076–3084
Nagarajan V, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2016) Biocomposites with size-fractionated biocarbon: influence of the microstructure on macroscopic properties. ACS Omega 1(4):636–647
Nayak R, Tarkes DP, Satapathy A (2010) A computational and experimental investigation on thermal conductivity of particle reinforced epoxy composites. Comput Mater Sci 48:576–581
Ndiaye D, Fanton E, Morlat-Therias S, Tidjani A, Gardette JL (2008) Durability of wood polymer composites: part 1. Influence of wood on the photochemical properties. Compos Sci Technol 68:2779–2784
Ndiaye D, Gueye M, Diop B (2013) Characterization, physical and mechanical properties of polypropylene/wood-flour composites. Arab J Sci Eng 38(1):59–68
Pérez E, Famá L, Pardo SG, Abad MJ, Bernal C (2012) Tensile and fracture behaviour of PP/wood flour composites. Compos B Eng 43:2795–2800
Poletto M, Júnior HLO, Zattera AJ (2014) Native cellulose: structure, characterization and thermal properties. Materials 7:6105–6119
Ray D, Sarkar BK, Rana AK, Bose NR (2001) Effect of alkali treated jute fibres on composite properties. Bull Mater Sci 24:129–135
Rong MZ, Zhang MQ, Liu Y, Yang GCZH (2001) The effect of fiber treatment on the mechanical properties of unidirectional sisal-reinforced epoxy composites. Compos Sci Technol 61:1437–1447
Roudsari GM, Mohanty AK, Misra M (2017) Exploring the effect of poly (propylene carbonate) polyol in a biobased epoxy interpenetrating network. ACS Omega 2(2):611–617
Sarki J, Hassan SB, Aigbodion VS, Oghenevweta JE (2011) Potential of using coconut shell particle fillers in eco-composite materials. J Alloys Compd 509:2381–2385
Sepet H, Tarakcioglu N, Misra RDK (2016) Investigation of mechanical, thermal and surface properties of nanoclay/HDPE nanocomposites produced industrially by melt mixing approach. J Compos Mater 50:3105–3116
Shakuntala O, Raghavendra G, Samir Kumar A (2014) Effect of filler loading on mechanical and tribological properties of wood apple shell reinforced epoxy composite. Adv Mater Sci Eng 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/538651
Singh NK, Lesser AJ (2010) Mechanical and thermo-mechanical studies of double networks based on thermoplastic elastomers. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 48:778–789
Sliwa F, Charrier F, Marin G, Malet F (2012) Mechanical and interfacial properties of wood and bio-based thermoplastic composite. Compos Sci Technol 72:1733–1740
Suhaily SS, Khalil HPSA, Nadirah WOW, Jawaid M (2013) Bamboo based biocomposites material, design and applications. Mater Sci 549:489–518
Szolnoki B, Bocz K, Soti PL (2015) Development of natural fibre reinforced flame retarded epoxy resin composites. Polym Degrad Stab 119:68–76
Thakur VK, Thakur MK (2014) Processing and characterization of natural cellulose fibers/thermoset polymer composites. Carbohydr Polym 109:102–117
Wong KJ, Yousif BF, Low KO, Ng Y, Tan SL (2010) Effects of fillers on the fracture behaviour of particulate polyester composites. J Strain Anal Eng Des 45:67–78
Yusuf IT, Jimoh YA, Salami WA (2016) An appropriate relationship between flexural strength and compressive strength of palm kernel shell concrete. Alex Eng J 55:1553–1562
Zhang H (2014) Effect of a novel coupling agent, alkyl ketene dimer, on the mechanical properties of wood–plastic composites. Mater Des 59:130–134
Zhou XX, Yu Y, Chen LH (2015) Effects of zirconaluminate coupling agent on mechanical properties, rheological behavior and thermal stability of bamboo powder/polypropylene foaming composites. Eur J Wood Prod 73:199–207
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the SAIF-IIT, Bombay, SAIF-Gauhati University, CIF-BIT, Mesra, and CIPET-LARPM, Bhubaneswar, for providing the test facilities. The authors also would like to acknowledge Machine element laboratory, NIT Silchar for giving necessary facilities to carry out the research work. The authors also would like to express gratitude toward Science, Technology and Innovation Scheme (STIS) Project, NIT Silchar for support to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Kumar, K. & Bhowmik, S. Mechanical characterization and quantification of tensile, fracture and viscoelastic characteristics of wood filler reinforced epoxy composite. Wood Sci Technol 52, 677–699 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-018-0995-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-018-0995-0