Abstract
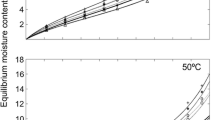
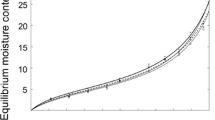
The hygroscopicity and thermodynamic properties of buried juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood with an age of 1,170 ± 40 BP were compared with the corresponding values of juvenile wood of the same species from recently cut trees. The 35 and 50°C isotherms were plotted following the saturated salts method and subsequently fitted in accordance with the GAB model. The isotherms were then compared by means of the hysteresis coefficients. X-ray diffractograms were used to analyse the crystal structure of the cellulose. The effect of time on the buried wood caused hemicelluloses degradation and a decrease in the crystallinity index and the crystallite length, resulting in an increase in the proportion of amorphous zones. Because of this, the equilibrium moisture contents of the buried wood are higher than of the recent wood, both in adsorption and desorption. In terms of the thermodynamic properties, the heat involved is greater in the buried wood than in the recent wood.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis S (1997) The basis of sorption. COST Action E8, Mechanical performance of wood and wood products. In: International conference on wood–water relations. Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–17 June, pp 1–16
BCR Community Bureau of Reference (1989) Certified Reference Material, Certificate of Measurement CRM 302, Water content of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) in equilibrium with the atmosphere above specified aqueous saturated SALT solutions at 25°C
Esteban LG, Guindeo A, de Palacios P, García Fernández F (2004) Satured salt method determination of hysteresis of Pinus sylvestris L. wood for 35°C isotherms. Mater Constr 276:51–64
Esteban LG, Gril J, de Palacios P, Guindeo A (2005) Reduction of wood hygroscopicity and associated dimensional response by repeated humidity cycles. Ann For Sci 62:275–284
Esteban LG, García Fernández F, Guindeo A, de Palacios P, Gril J (2006) Comparison of the hygroscopic behaviour of 205-year-old and recently cut juvenile wood from Pinus sylvestris L. Ann For Sci 63:309–317
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, García Fernandez F, Guindeo A, Navarro Cano N (2008a) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of old and new Pinus sylvestris wood. Wood Fiber Sci 40(1):111–121
Esteban LG, de Palacios P, García Fernandez F, Guindeo A, Conde M, Baonza V (2008b) Sorption and thermodynamic properties of juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood after 103 years of submersion. Holzforschung 62:745–751
Jahan MS, Mun SP (2005) Effect of tree age on the cellulose structure of Nalita wood (Trema orientalis). Wood Sci Technol 39:367–373
Jowitt R, Wagstaffe PJ (1989) The certification of the water content of microcrystaline cellulose (MCC) at 10 water activities, CRM 302. Commission of the European Communities, Community Bureau of Reference, EUR 12429
Kollmann F (1951) Technologie des holzes und der holzwerkstoffe, vol I. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Macaya D (2002) Diferenciación anatómica de la madera de Pinus sylvestris L. y de Pinus nigra Arnold subsp. salzmannii (Dunal) Franco en poblaciones sorianas. Proyecto Fin de Carrera. E.T.S.I. Montes, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid
Passialis CN (1997) Physico-chemical characteristics of waterlogged archaeological Wood. Holzforschung 51:111–113
Peralta PN, Bangi AP, Lee A (1997) Thermodynamics of moisture sorption by the giant-timber bamboo. Holzforschung 51:177–182
Reimer P, Baillie M, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck J, Bertrand C, Blackwell P, Buck CB, Cutler K, Damon P, Edwards R, Fairbanks R, Friedrich M, Guilderson T, Hughen K, Kromer B, McCormac F, Manning S, Bronk C, Reimer R, Remmele S, Southon J, Stuiver M, Talamo S, Taylor F, van der Plicht J, Weyhenmeyer C (2004) IntCal04 Terrestrial radiocarbon age calibration, 26–0 ka BP. Radiocarbon 46:1029–1058
Rubiales JM, García-Amorena I, Génova M, Gómez F, Morla C (2007) The Holocene history of highland pine forests in a submediterranean mountain: the case of Gredos mountain range (Iberian Central range, Spain). Quat Sci Rev 26:1759–1770
Siau JF (1995) Wood: influence of moisture on physical properties. Department of Wood Science and Forest Products. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Keene, New York
Skaar C (1988) Wood–water relations. Springer, Berlin
Stuiver M, Reimer PJ (1993) Extended 14C database and revised CALIB radiocarbon calibration program. Radiocarbon 35:215–230
Themelin A, Rebollo J, Thibauth A (1997) Method for defining the behaviour of lignocellulosic products at sorption: application to tropical wood species. In: COST Action E8, Mechanical performance of wood and wood products, International conference on wood–water relations. Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–17 June, pp 17–32
Violaz PE, Rovedo CO (1999) Equilibrium sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties of starch and gluten. J Food Eng 40:287–292
Wadsö L (1997) A review of methods to measure sorption isotherms and heats of sorption. In: COST Action E8, Mechanical performance of wood and wood products, International conference on wood–water relations. Copenhagen, Denmark, 16–17 June, pp 45–50
Acknowledgments
This study is part of a project of the Spanish National Plan for Scientific Research, Development and Technological Innovation, funded by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esteban, L.G., de Palacios, P., García Fernández, F. et al. Sorption and thermodynamic properties of buried juvenile Pinus sylvestris L. wood aged 1,170 ± 40 BP. Wood Sci Technol 43, 679–690 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0261-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-009-0261-6