Abstract
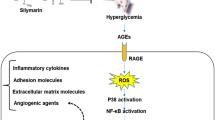
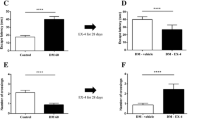
Uncontrolled or poorly controlled blood glucose during diabetes is an important factor in worsened vascular function. While evidence suggests that hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress plays a prominent role in development of microangiopathy of the retina, kidney, and nerves, the role oxidative stress plays on blood–brain barrier (BBB) function and structure has lagged behind. In this study, a natural antioxidant, sesamol, was administered to streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats to examine the role that oxidative stress plays on BBB structure and function. Experiments were conducted at 56 days after STZ injection. Male Sprague–Dawley rats randomly were divided into four treatment groups CON––control; STZ––STZ-induced diabetes; CON + S––control + sesamol; STZ + S––STZ-induced diabetes + sesamol. Functional and structural changes to the BBB were measured by in situ brain perfusion and western blot analysis of changes in tight junction protein expression. Oxidative stress markers were visualized by fluorescent confocal microscopy and assayed by spectrophotometric analysis. Results demonstrated that the increased BBB permeability observed in STZ-induced diabetic rats was attenuated in STZ + S rats to levels observed in CON. Sesamol treatment reduced the negative impact of STZ-induced diabetes on tight junction protein expression in isolated cerebral microvessels. Oxidative stress markers were elevated in STZ as compared to CON. STZ + S displayed an improved antioxidant capacity which led to a reduced expression of superoxide and peroxynitrite and reduced lipid peroxidation. In conclusion, this study showed that sesamol treatment enhanced antioxidant capacity of the diabetic brain and led to decreased perturbation of hyperglycemia-induced changes in BBB structure and function.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Aboul-Enein HY, Kruk I, Kladna A, Lichszteld K, Michalska T (2007) Scavenging effects of phenolic compounds on reactive oxygen species. Biopolymers 86:222–230
Andreeva AY, Krause E, Muller EC, Blasig IE, Utepbergenov DI (2001) Protein kinase C regulates the phosphorylation and cellular localization of occludin. J Biol Chem 276:38480–38486
Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Hollinger LA, Wolpert EB, Gardner TW (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces rapid phosphorylation of tight junction proteins occludin and zonula occluden 1: a potential mechanism for vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy and tumors. J Biol Chem 274:23463–23467
Appelros P, Samuelsson M, Lindell D (2005) Lacunar infarcts: functional and cognitive outcomes at five years in relation to MRI findings. Cerebrovasc Dis 20:34–40
Babu PS, Srinivasan K (1999) Renal lesions in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats maintained on onion and capsaicin containing diets. J Nutr Biochem 10:477–483
Balakumar P, Chakkarwar VA, Krishan P, Singh M (2009) Vascular endothelial dysfunction: a tug of war in diabetic nephropathy? Biomed Pharmacother 63:171–179
Banks WA, Ibrahimi F, Farr SA, Flood JF, Morley JE (1999) Effects of wheatgerm agglutinin and aging on the regional brain uptake of HIV-1GP120. Life Sci 65(1):81–89
Bedoya FJ, Solano F, Lucas M (1996) N-monomethyl-arginine and nicotinamide prevent streptozotocin-induced double strand DNA break formation in pancreatic rat islets. Experientia 52:344–347
Brooks TA, Nametz N, Charles R, Davis TP (2008) Diclofenac attenuates the regional effect of lambda-carrageenan on blood–brain barrier function and cytoarchitecture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 325:665–673
Cam MC, Li WM, McNeill JH (1997) Partial preservation of pancreatic beta-cells by vanadium: evidence for long-term amelioration of diabetes. Metabolism 46:769–778
Cardozo-Pelaez F, Brooks PJ, Stedeford T, Song S, Sanchez-Ramos J (2000) DNA damage, repair, and antioxidant systems in brain regions: a correlative study. Free Radic Biol Med 28(5):779–785
Celik S, Erdogan S (2008) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) protects brain against oxidative stress and inflammation induced by diabetes in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 312:39–46
Chehade JM, Haas MJ, Mooradian AD (2002) Diabetes-related changes in rat cerebral occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) expression. Neurochem Res 27:249–252
Cheng JT, Liu IM, Tzeng TF, Chen WC, Hayakawa S, Yamamoto T (2003) Release of beta-endorphin by caffeic acid to lower plasma glucose in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Horm Metab Res 35:251–258
Colwell J (2000) Pathogenesis of vascular disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 2(Suppl 2):S19–S24
Di Leo MA, Santini SA, Silveri NG, Giardina B, Franconi F, Ghirlanda G (2004) Long-term taurine supplementation reduces mortality rate in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Amino Acids 27:187–191
DiNapoli VA, Huber JD, Houser K, Li X, Rosen CL (2008) Early disruptions of the blood–brain barrier may contribute to exacerbated neuronal damage and prolonged functional recovery following stroke in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging 29:753–764
Egleton RD, Campos CC, Huber JD, Brown RC, Davis TP (2003) Differential effects of diabetes on rat choroid plexus ion transporter expression. Diabetes 52:1496–1501
Farshori P, Kachar B (1999) Redistribution and phosphorylation of occludin during opening and resealing of tight junctions in cultured epithelial cells. J Membr Biol 170:147–156
Figueroa-Romero C, Sadidi M, Feldman EL (2008) Mechanisms of disease: the oxidative stress theory of diabetic neuropathy. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 9(4):301–314
Forbes JM, Coughlan MT, Cooper ME (2008) Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 57:1446–1454
Fouillioux C, Contreras F, Lares M, Cano R, Leal E, Arraiz N, Bermudez V, Velasco M (2008) Metabolic and hemodynamic markers of endothelial dysfunction in patients with hypertension and patients with type 2 diabetes during the cold pressor test. Am J Ther 15:389–396
Haorah J, Schall K, Ramirez SH, Persidsky Y (2008) Activation of protein tyrosine kinases and matrix metalloproteinases causes blood–brain barrier injury: novel mechanism for neurodegeneration associated with alcohol abuse. Glia 56:78–88
Harhaj NS, Felinski EA, Wolpert EB, Sundstrom JM, Gardner TW, Antonetti DA (2006) VEGF activation of protein kinase C stimulates occludin phosphorylation and contributes to endothelial permeability. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:5106–5115
Harkness KA, Adamson P, Sussman JD, Davies-Jones GA, Greenwood J, Woodroofe MN (2000) Dexamethasone regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in CNS vascular endothelium. Brain 123(Pt 4):698–709
Hawkins BT, Lundeen TF, Norwood KM, Brooks HL, Egleton RD (2007) Increased blood–brain barrier permeability and altered tight junctions in experimental diabetes in the rat: contribution of hyperglycaemia and matrix metalloproteinases. Diabetologia 50:202–211
Huber JD, Hau VS, Borg L, Campos CR, Egleton RD, Davis TP (2002) Blood–brain barrier tight junctions are altered during a 72-h exposure to lambda-carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 283:H1531–H1537
Huber JD, Campos CR, Mark KS, Davis TP (2006a) Alterations in blood–brain barrier ICAM-1 expression and brain microglial activation after lambda-carrageenan-induced inflammatory pain. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H732–H740
Huber JD, VanGilder RL, Houser KA (2006b) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes progressively increases blood–brain barrier permeability in specific brain regions in rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H2660–H2668
Joshi R, Kumar MS, Satyamoorthy K, Unnikrisnan MK, Mukherjee T (2005) Free radical reactions and antioxidant activities of sesamol: pulse radiolytic and biochemical studies. J Agric Food Chem 53:2696–2703
Karapanayiotides T, Piechowski-Jozwiak B, van Melle G, Bogousslavsky J, Devuyst G (2004) Stroke patterns, etiology, and prognosis in patients with diabetes mellitus. Neurology 62:1558–1562
Kaya M, Gurses C, Kalayci R, Ekizoglu O, Ahishali B, Orhan N, Oku B, Arican N, Ustek D, Bilgic B, Elmas I, Kucuk M, Kemikler G (2008) Morphological and functional changes of blood–brain barrier in kindled rats with cortical dysplasia. Brain Res 1208:181–191
Kim JH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Cho CS, Kim KW (2008) Blockade of angiotensin II attenuates VEGF-mediated blood–retinal barrier breakdown in diabetic retinopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 29:621–628
Kowluru RA, Chan PS (2007) Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy. Exp Diabetes Res 2007:43603
Kuhad ACK (2008) Effect of sesamol on diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Exp Brain Res 185:411–420
Kumagai AK (1999) Glucose transport in brain and retina: implications in the management and complications of diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 15:261–273
Lee MY, Griendling KK (2008) Redox signaling, vascular function, and hypertension. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:1045–1059
Lovell MA, Markesbery WR (2007) Oxidative damage in mild cognitive impairment. Nucleic Acids Res 35(22):7497–7504
Madsen-Bouterse SA, Kowluru RA (2008) Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: Pathophysiological mechanisms and treatment perspectives. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 9(4):315–327
Manea A, Constantinescu E, Popov D, Raicu M (2004) Changes in oxidative balance in rat pericytes exposed to diabetic conditions. J Cell Mol Med 8:117–126
Marathe PA, Parekar RR, Shinde SP, Rege NN (2006) A split dose regimen of streptozotocin to induce diabetes in a neonatal rat model. Indian J Pharmacol 38(6):432–433 Ref Type: Generic
Nelson PT, Smith CD, Abner EA, Schmitt FA, Scheff SW, Davis GJ, Keller JN, Jicha GA, Davis D, Wang-Xia W, Hartman A, Katz DG, Markesbery WR (2008) Human cerebral neuropathology of Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(5):454–469
Nukatsuka M, Yoshimura Y, Nishida M, Kawada J (1990) Importance of the concentration of ATP in rat pancreatic beta cells in the mechanism of streptozotocin-induced cytotoxicity. J Endocrinol 127:161–165
Oltman CL, Kleinschmidt TL, Davidson EP, Coppey LJ, Lund DD, Yorek MA (2008) Treatment of cardiovascular dysfunction associated with the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Vascul Pharmacol 48:47–53
Osawa A, Maeshima S, Shimamoto Y, Maeshima E, Sekiguchi E, Kakishita K, Ozaki F, Moriwaki H (2004) Relationship between cognitive function and regional cerebral blood flow in different types of dementia. Disabil Rehabil 23(12):739–745
Popov D, Simionescu M (2001) Structural and transport property alterations of the lung capillary endothelium in diabetes. Ital J Anat Embryol 106:405–412
Preston JE, Al-Sarraf H, Segal MB (1995) Permeability of the developing blood–brain barrier to 14C-mannitol using the rat in situ brain perfusion technique. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 87:69–76
Ramachandra R, Shetty AK, Salimath PV (2005) Quercetin alleviates activities of intestinal and renal disaccharidases in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Nutr Food Res 49:355–360
Ramsay TG, White ME (2000) Insulin regulation of leptin expression in streptozotocin diabetic pigs. J Anim Sci 78:1497–1503
Reiter RJ, Garcia JJ, Pie J (1998) Oxidative toxicity in models of neurodegeneration: responses to melatonin. Restor Neurol Neurosci 12:135–142
Ristow M (2004) Neurodegenerative disorders associated with diabetes mellitus. J Mol Med 82:510–529
Riva CE, Logean E, Falsini B (2005) Visually evoked hemodynamical response and assessment of neurovascular coupling in the optic nerve and retina. Prog Retin Eye Res 24:183–215
Ryan CM (2005) Diabetes, aging, and cognitive decline. Neurobiol Aging 26(Suppl 1):21–25
Ryan CM, Geckle MO, Orchard TJ (2003) Cognitive efficiency declines over time in adults with Type 1 diabetes: effects of micro- and macrovascular complications. Diabetologia 46:940–948
Santos MS, Santos DL, Palmeira CM, Seica R, Moreno AJ, Oliveira CR (2001) Brain and liver mitochondria isolated from diabetic Goto–Kakizaki rats show different susceptibility to induced oxidative stress. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17:223–230
Schreibelt G, Kooij G, Reijerkerk A, van Doorn R, Gringhuis SI, van der Pol S, Weksler BB, Romero IA, Couraud PO, Piontek J, Blasig IE, Dijkstra CD, Ronken E, de Vries HE (2007) Reactive oxygen species alter brain endothelial tight junction dynamics via RhoA, PI3 kinase, and PKB signaling. FASEB J 21:3666–3676
Simionescu M, Antohe F (2006) Functional ultrastructure of the vascular endothelium: changes in various pathologies. Handb Exp Pharmacol 4:1–69
Sindrup SH, Gram LF, Brosen K, Eshoj O, Mogensen EF (1990) The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine is effective in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms. Pain 42:135–144
Sindrup SH, Grodum E, Gram LF, Beck-Nielsen H (1991) Concentration-response relationship in paroxetine treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms: a patient-blinded dose-escalation study. Ther Drug Monit 13:408–414
Singh N, Kamath V, Rajini PS (2005) Protective effect of potato peel powder in ameliorating oxidative stress in streptozotocin diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 60:49–54
The ADVANCE Collaborative Group (2008) Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 358:2560–2572
Tomkins O, Shelef I, Kaizerman I, Eliushin A, Afawi Z, Misk A, Gidon M, Cohen A, Zumsteg D, Friedman A (2008) Blood–brain barrier disruption in post-traumatic epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:774–777
Triguero D, Buciak J, Pardridge WM (1990) Capillary depletion method for quantification of blood–brain barrier transport of circulating peptides and plasma proteins. J Neurochem 54:1882–1888
Turk J, Corbett JA, Ramanadham S, Bohrer A, McDaniel ML (1993) Biochemical evidence for nitric oxide formation from streptozotocin in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197:1458–1464
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MTD, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:44–84
VanDyke K, Ghareeb E, VanDyke M, Sosa A, Hoeldtke RD, Van Thiel DH (2008) Luminescence experiments involved in the mechanism of streptozotocin diabetes and cataract formation. Luminescence 23(6):386–391
Wachtel M, Frei K, Ehler E, Fontana A, Winterhalter K, Gloor SM (1999) Occludin proteolysis and increased permeability in endothelial cells through tyrosine phosphotase inhibition. J Cell Sci 112(Pt 23):4347–4356
Wellmann KF, Volk BW (1977) Modification of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats by pretreatment with cortisone. Diabetologia 13:331–337
West E, Simon OR, Morrison EY (1996) Streptozotocin alters pancreatic beta-cell responsiveness to glucose within six hours of injection into rats. West Indian Med J 45:60–62
Zlokovic BV (2008) The blood–brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57:178–201
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Faculty Development Award (7-05JF-22) through the American Diabetes Association (J.D.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VanGilder, R.L., Kelly, K.A., Chua, M.D. et al. Administration of sesamol improved blood–brain barrier function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Brain Res 197, 23–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1866-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1866-6