Abstract
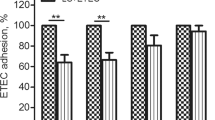
Surface layer proteins had been proposed that it could protect human intestine from pathogens and aid in maintaining cellular integrity. However, the functions of S-layer proteins have not yet been fully revealed, and it has been proposed that these structures protected the intestinal microbes from hostile environmental agents. In this study, the ability of the Lactobacilli to inhibit adhesion of Salmonella to intestinal mucosa was studied on cultured HT-29 cells. Lactobacillus paracasei M7 was shown to inhibit the adhesion of Salmonella to epithelial cells, a process which may be related to the specific component of the bacterial surface. Human epithelial HT-29 cells were treated with S-layer proteins after Salmonella injection and pretreated with S-layer proteins to determine their importance in the inhibition of pathogen adherence. According to the analysis of cell cycle by flow cytometry, the HT-29 cells treated by Salmonella in S phase were 26.88 % compared with 36.70 % in the normal HT-29 cells. However, the addition of S-layer proteins made the HT-29 cells in S phase increase to 30.13 %. The activity of caspase-3 in the HT-29 cell was determined using a caspase-3 activity kit, which indicated the degree of apoptosis. Moreover, we also found that Lactobacillus S-layer proteins could protect Salmonella-induced apoptosis through reducing the caspase-3 activity. This mechanism might represent a novel approach for antagonizing Salmonella infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaaskelainen SA, Palva A (2005) Lactobacillus surface layers and their applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:511–529
Sanchez B, Arias S, Chaignepain S, Denayrolles M, Schmitter JM, Bressollier P, Urdaci MC (2009) Identification of surface proteins involved in the adhesion of a probiotic Bacillus cereus strain to mucin and fibronectin. Microbiology 155:1708–1716
Hynönen U, Palva A (2013) Lactobacillus surface layer proteins: structure, function and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:5225–5243
IIk N, Egelseer EM, Sleytr UB (2011) S-layer fusion proteins—construction principles and applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 22:824–831
Pum D, Toca-Herrera JL, Sleytr UB (2013) S-layer protein self-assembly. Int J Mol Sci 14:2484–2501
Johnson-Henry KC, Hagen JH, Gordonpour M, Tompkins TA, Sherman PM (2007) Surface-layer protein extracts from Lactobacillus helveticus inhibit enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 adhesion to epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol 9:356–367
Zhang Y, Higashide WM, McCormick BA, Chen J, Zhou D (2006) The inflammation associated Salmonella SopA is a HECT-like E3 ubiquitin ligase. Mol Microbiol 62:786–793
Haraga A, Miller SIA (2006) Salmonella type III secretion effector interacts with the mammalian serine/threonine protein kinase PKN1. Cell Microbiol 8:837–846
Gueimonde M, Jalonen L, He F, Hiramatsu M, Salminen S (2006) Adhesion and competitive inhibition and displacement of human enteropathogens by selected Lactobacilli. Food Res Int 39:467–471
Riedel UC, Foata F, Goldstein DR, Blum S, Eikmanns BJ (2006) Interaction of bifidobacteria with Caco-2 cells-adhesion and impact on expression profiles. Int J Food Microbiol 110:62–68
Collado MC, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2007) Role of commercial probiotic strains against human pathogen adhesion to intestinal mucus. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:454–460
Shimotahira N, Oogai Y, Kawada-Matsuo M, Yamada S (2013) The S-layer of Tannerella forsythia contributes to serum resistance and oral bacterial co-aggregation. Infect Immun 81:1198–1206
Zhang YC, Zhang LW, Tuo YF, Guo CF, Yi HX, Li YH, Han X, Du M (2010) Inhibition of Shigella sonnei adherence to HT-29 cells by lactobacilli from Chinese fermented food and preliminary characterization of S-layer protein involvement. Res Microbiol 161:667–672
Frece J, Kos B, Svetec IK, Zgaga Z, Mrsa V, Suskovic J (2005) Importance of S-layer proteins in probiotic activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol 982:285–292
Golowczyc MA, Mobili P, Garrote GL, Abraham AG, De Antoni GL (2007) Protective action of Lactobacillus kefir carrying S-layer protein against Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Int J Food Microbiol 118:264–273
Li PC, Ye XL, Yang Q (2011) Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356 S-layer protein on Salmonella enterica enterica serovar Typhimurium in Caco-2 cells. Ann Microbiol 10:011–0327
Ramiah K, Reenen CA, Dicks LMT (2008) Surface-bound proteins of Lactobacillus plantarum 423 that contribute to adhesion of Caco-2 cells and their role in competitive exclusion and displacement of Clostridium sporogenes and Enterococcus faecalis. Res Microbiol 159:470–475
Viljanen MJ, Palva A (2007) Isolation of surface layer protein carrying Lactobacillus species from porcine intestine and faeces and characterization of their adhesion properties to different host tissues. Vet Microbiol 124:264–273
Prince T, McBain AJ, O’Neill CA (2012) Lactobacillus reuteri protects epidermal keratinocytes from Staphylococcus aureus-induced cell death by competitive exclusion. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5119–5126
Walsh S, Ponte´n A, Fleischmann BK, Jovinge S (2010) Cardiomyocyte cell cycle control and growth estimation in vivo—an analysis based on cardiomyocyte nuclei. Cardiovasc Res 86:365–373
Pozarowski P, Darzynkiewicz Z (2004) Analysis of cell cycle by flow cytometry. Methods Mol Biol 281:301–311
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bedner E, Smonlewski P (2011) Flow cytometry in analysis of cell cycle and apoptosis. Semin Hematol 38:179–193
Singh R, Pervin S, Wu G, Chaudhuri G (2001) Activation of caspase-3 activity and apoptosis in MDA-MB-468 cells by Nω-hydroxy-l-arginine, an inhibitor of arginase, is not solely dependent on reduction in intracellular polyamines. Mol Carcinog 22:1863–1869
Mobili P, Serradell MA, Trejo SA, Puigvert FXA, Abraham AG, De Antoni GL (2009) Heterogeneity of S-layer proteins from aggregating and non-aggregating Lactobacillus kefir strains. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 95:363–372
Johnson B, Selle K, O’Flaherty S, Goh YJ (2013) Identification of extracellular surface-layer associated proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. Microbiology 159:2269–2282
Xue CH, Zhang LW, Li HB, Wang SM, Li Q, Luo X, Liu WL, Du M, Yi HX, Xu H (2013) Functionality of the S-layer proteins from Lactobacillus in the competitive against enteropathogens infection. Eur Food Res Technol 236:249–255
Beganovic J, Frece J, Kos B, Pavunc AL, Habjanic K, Suskovic J (2011) Functionality of the S-layer protein from the probiotic strain Lactobacillus helveticus M92. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100:43–53
Cheng XY, Jingjing X, Jiangbing S, Jianshun C, Zhang ZF, Fang WH (2007) The S-layer proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus strain ZJ001is responsible for competitive exclusion against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium. Int J Food Microbiol 115:307–312
Li PC, Yu QH, Ye XL, Wang ZS, Yang Q (2011) Lactobacillus S-layer protein inhibition of Salmonella-induced reorganization of the cytoskeleton and activation of MAPK signalling pathways in Caco-2 cells. Microbiology 157:2639–2646
Li PC, Yin YY, Yu QH, Yang Q (2011) Lactobacillus acidophilus S-layer protein-mediated inhibition of Salmonella-induced apoptosis in Caco-2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:142–147
Taverniti V, Stuknyte M, Minuzzo M, Arioli S, DeNoni I, Scabiosi C (2012) S-layer protein mediates the stimulatory effect of Lactobacillus helveticus MIMLh5 on innate immunity. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1221–1231
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National High-Tech R&D Program Foundation of China (2011AA100805-1, 2011AA100902), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31271906/C200204) and the Foundation of Heilongjiang province Education (1055GZD03).
Conflict of interest
None.
Compliance with Ethics Requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, C., Zhang, L., Fan, R. et al. Protective action of S-layer proteins from Lactobacillus paracasei M7 against Salmonella infection and mediated inhibition of Salmonella-induced apoptosis. Eur Food Res Technol 240, 923–929 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2396-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-014-2396-4