Abstract
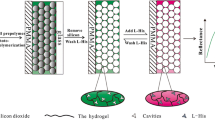
A newly developed molecularly imprinted photonic polymer (MIPP) film, which was prepared by colloidal crystal templating and surface molecular imprinting, was used for selective capture of S-layer protein (SLP) from a complex Lactobacillus acidophilus sample. The colloidal crystal templates were formed by a dipping process followed by chemical binding of the imprinted template SLP molecules. A sandwich structure consisting of two glass slides was formed after the SLP–silica layer had been covered with a poly(methyl methacrylate) glass slide. After polymerization of the SLP–silica layer with the preprepared polymerization solution, hydrofluoric acid and acetic phosphate buffer solutions removed the silica particles and SLP molecules, respectively. The MIPP film obtained exhibited a three-dimensional, highly ordered and interconnected macroporous structure (pore size greater than 200 nm), which is specifically accessible to SLP molecules. The adsorbed SLP molecules were simply and straightforwardly detected by a fiber-optic spectrometer. The redshift of the Bragg diffraction peak of the MIPP film was linearly related to the number of SLP molecules that had been harvested in the film. The detection limit of the SLP–MMIP–fiber-optic spectrometer method for SLP was 1 ng mL-1. The MIPP sensor was successfully applied to detect SLP molecules in a crudely extracted Lactobacillus acidophilus sample. Our results prove the applicability of the SLP–MIPP film for fast and real-time measurement of SLP.

Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiti F, Dobson CM. Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:333–66.
Fields S, O-k S. A novel genetic system to detect protein–protein interactions. Nature. 1989;340(6230):245.
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN. Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature. 2001;411(6833):41.
Sapan CV, Lundblad RL, Price NC. Colorimetric protein assay techniques. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1999;29(2):99–108.
Righetti PG, Campostrini N, Pascali J, Hamdan M, Astner H. Quantitative proteomics: a review of different methodologies. Eur J Mass Spectrom. 2004;10(3):335–48.
Bantscheff M, Lemeer S, Savitski MM, Kuster B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: critical review update from 2007 to the present. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;404(4):939–65.
Bantscheff M, Schirle M, Sweetman G, Rick J, Kuster B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007;389(4):1017–31.
Vandermeeren M, Mercken M, Vanmechelen E, Six J, Van de Voorde A, Martin JJ, et al. Detection of proteins in normal and Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid with a sensitive sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Neurochem. 1993;61(5):1828–34.
Leca-Bouvier B, Blum LJ. Biosensors for protein detection: a review. Anal Lett. 2005;38(10):1491–517.
Bossi A, Bonini F, Turner APF, Piletsky SA. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: the state of the art. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;22(6):1131–7.
Chen L, Xu S, Li J. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40(5):2922–42.
Bossi A, Piletsky SA, Piletska EV, Righetti PG, Turner APF. Surface-grafted molecularly imprinted polymers for protein recognition. Anal Chem. 2001;73(21):5281–6.
Li Y, Yang H-H, You Q-H, Zhuang Z-X, Wang X-R. Protein recognition via surface molecularly imprinted polymer nanowires. Anal Chem. 2006;78(1):317–20.
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, et al. The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40(3):1547–71.
Xie X, Hu Q, Ke R, Zhen X, Bu Y, Wang S. Facile preparation of photonic and magnetic dual responsive protein imprinted nanomaterial for specific recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Eng J. 2019;371:130–7.
Chen L, Wang X, Lu W, Wu X, Li J. Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45(8):2137–211.
Qi Z, Hong Z, Qiang Z, Yan-Shuo X, Yan-Hong W. Preparation and application of methomyl molecularly imprinted photonic crystal sensor. Chin J Anal Chem. 2019;47(6):883–9.
Chen W, Meng Z, Xue M, Shea KJ. Molecular imprinted photonic crystal for sensing of biomolecules. Mol Impr. 2016;4(1):1–12.
Li J, Zhang Z, Xu S, Chen L, Zhou N, Xiong H, et al. Label-free colorimetric detection of trace cholesterol based on molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels. J Mater Chem. 2011;21(48):19267–74.
Zhang Z, Li J, Fu L, Liu D, Chen L. Magnetic molecularly imprinted microsensor for selective recognition and transport of fluorescent phycocyanin in seawater. J Mater Chem A. 2015;3(14):7437–44.
Wang X, Yu S, Liu W, Fu L, Wang Y, Li J, et al. Molecular imprinting based hybrid ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the visual determination of bovine hemoglobin. ACS Sens. 2018;3(2):378–85.
Peng H, Wang S, Zhang Z, Xiong H, Li J, Chen L, et al. Molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels as colorimetric sensors for rapid and label-free detection of vanillin. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60(8):1921–8.
Kadhem A, Xiang S, Nagel S, Lin C-H, Fidalgo de Cortalezzi M. Photonic molecularly imprinted polymer film for the detection of testosterone in aqueous samples. Polymers. 2018;10(4):349.
Huang C, Cheng Y, Gao Z, Zhang H, Wei J. Portable label-free inverse opal photonic hydrogel particles serve as facile pesticides colorimetric monitoring. Sens Actuators B. 2018;273:1705–12.
Li J, Fu J, Yang Q, Wang L, Wang X, Chen L. Thermosensitive molecularly imprinted core–shell CdTe quantum dots as a ratiometric fluorescence nanosensor for phycocyanin recognition and detection in seawater. Analyst. 2018;143(15):3570–8.
Hu X, Li G, Huang J, Zhang D, Qiu Y. Construction of self-reporting specific chemical sensors with high sensitivity. Adv Mater. 2007;19(24):4327–32.
Chen W, Lei W, Xue M, Xue F, Meng Z-H, Zhang W-B, et al. Protein recognition by a surface imprinted colloidal array. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(20):7165–9.
Chen W, Xue M, Shea KJ, Meng Z, Yan Z, Wang Z, et al. Molecularly imprinted hollow sphere array for the sensing of proteins. J Biophoton. 2015;8(10):838–45.
Zhao YJ, Zhao XW, Hu J, Li J, Xu WY, Gu ZZ. Multiplex label-free detection of biomolecules with an imprinted suspension array. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48(40):7350–2.
Zhang Y-X, Zhao P-Y, Yu L-P. Highly-sensitive and selective colorimetric sensor for amino acids chiral recognition based on molecularly imprinted photonic polymers. Sens Actuators B. 2013;181:850–7.
Wu Z, Tao Ca LC, Shen D, Li G. Label-free colorimetric detection of trace atrazine in aqueous solution by using molecularly imprinted photonic polymers. Chem Eur J. 2008;14(36):11358–68.
Frece J, Kos B, Svetec I-K, Zgaga Z, Mrša V, Šušković J. Importance of S-layer proteins in probiotic activity of Lactobacillus acidophilus M92. J Appl Microbiol. 2005;98(2):285–92.
Konstantinov SR, Smidt H, De Vos WM, Bruijns SCM, Singh SK, Valence F, et al. S layer protein A of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM regulates immature dendritic cell and T cell functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(49):19474–9.
Chen X, Xu J, Shuai J, Chen J, Zhang Z, Fang W. The S-layer proteins of Lactobacillus crispatus strain ZJ001 is responsible for competitive exclusion against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium. Int J Food Microbiol. 2007;115(3):307–12.
Johnsonhenry KC, Hagen KE, Gordonpour M, Tompkins TA, Sherman PM. Surface-layer protein extracts from Lactobacillus helveticus inhibit enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 adhesion to epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. 2010;9(2):356–67.
Martínez MG, Prado AM, Candurra NA, Ruzal SM. S-layer proteins of Lactobacillus acidophilus inhibits JUNV infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;422(4):590–5.
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci. 1968;26(1):62–9.
Yang Q, Peng H, Li J, Li Y, Xiong H, Chen L. Label-free colorimetric detection of tetracycline using analyte-responsive inverse-opal hydrogels based on molecular imprinting technology. New J Chem. 2017;41(18):10174–80.
Yang Z, Shi D, Chen M, Liu S. Free-standing molecularly imprinted photonic hydrogels based on β-cyclodextrin for the visual detection of l-tryptophan. Anal Methods. 2015;7(19):8352–9.
Tennico YH, Hutanu D, Koesdjojo MT, Bartel CM, Remcho VT. On-chip aptamer-based sandwich assay for thrombin detection employing magnetic beads and quantum dots. Anal Chem. 2010;82(13):5591–7.
Bo BK, Im WJ, Ju YB, Kim HM, Kim MG, Shin YB. Label-free CRP detection using optical biosensor with one-step immobilization of antibody on nitrocellulose membrane. Sens Actuators B. 2014;190(1):243–8.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Natural Science Funding of China (31671869, 31471598, 31571852, and 31601487), Natural Science Funding of Jiangsu (BK20151544), and Natural Science Funding of Zhejiang (LQ16C200002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Research involving humans and/or animals
No human participants and/or animals were involved in this research.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 206 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, D., Xun, M., Lan, H. et al. Selective, sensitive, and fast determination of S-layer proteins by a molecularly imprinted photonic polymer coated film and a fiber-optic spectrometer. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 7737–7745 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02109-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02109-1