Abstract
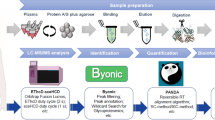
Exosomes are cell-derived functional microparticles which exist in most body fluids. They carry abundant signaling molecules to transfer information between cells and microenvironment. Research on exosomes’ heterogeneity and constitute variations has been a heated topic in recent years. In this work, size-dependent sub-proteome analysis of urinary exosomes was investigated by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) firstly. The particle size of urinary exosomes is distributed in four main ranges naturally. We found out that these fractions contained sub-proteomes with great difference in constitution. In each fraction, 206, 134, 157, and 276 unique proteins were identified by LC-MS/MS. Differential expression of exosomal markers such as TSG101, CD9, CD63, and caveolin-1 was observed in these fractions by western blots. Biological function annotation indicated that the proteins identified in each fraction were involved in different molecular and cellular processes. It is proven that SEC can serve as an efficient analytical tool for exosomes isolation and fractionation. This work provides a new strategy to classify exosomes into sub-populations for comprehensive study of heterogeneous functionalities.

ᅟ





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, Heine U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63–70.
Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, Orr L, Turbide C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412–20.
Colombo M, Raposo G, Théry C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:255–89. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101512-122326.
Chernyshev VS, Rachamadugu R, Tseng YH, Belnap DM, Jia Y, Branch KJ, et al. Size and shape characterization of hydrated and desiccated exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407(12):3285–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8535-3.
Kim DK, Lee J, Simpson RJ, Lötvall J, Gho YS. EVpedia: a community web resource for prokaryotic and eukaryotic extracellular vesicles research. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:4–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.02.005.
Luga V, Zhang L, Viloria-Petit AM, Ogunjimi AA, Inanlou MR, Chiu E, et al. Exosomes mediate stromal mobilization of autocrine Wnt-PCP signaling in breast cancer cell migration. Cell. 2012;151(7):1542–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.11.024.
Li XB, Zhang ZR, Schluesener HJ, Xu SQ. Role of exosomes in immune regulation. J Cell Mol Med. 2006;10(2):364–75.
Hough KP, Chanda D, Duncan SR, Thannickal VJ, Deshane JS. Exosomes in immunoregulation of chronic lung diseases. Allergy. 2017;72(4):534–44.
Choi DS, Lee J, Go G, Kim YK, Gho YS. Circulating extracellular vesicles in cancer diagnosis and monitoring: an appraisal of clinical potential. Mol Diagn Ther. 2013;17(5):265–71.
Rak J. Extracellular vesicles - biomarkers and effectors of the cellular interactome in cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00021.
Shao H, Im H, Castro CM, Breakefield X, Weissleder R, Lee H. New technologies for analysis of extracellular vesicles. Chem Rev. 2018;118(4):1917–50.
Palma J, Yaddanapudi SC, Pigati L, Havens MA, Jeong S, Weiner GA, et al. MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(18):9125–38.
Bobrie A, Colombo M, Krumeich S, Raposo G, Théry C. Diverse subpopulations of vesicles secreted by different intracellular mechanisms are present in exosome preparations obtained by differential ultracentrifugation. J Extracell Vesicles. 2012. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v1i0.18397.
Colombo M, Moita C, van Niel G, Kowal J, Vigneron J, Benaroch P, et al. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J Cell Sci. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.128868.
Sitar S, Kejžar A, Pahovnik D, Kogej K, Tušek-Žnidarič M, Lenassi M, et al. Size characterization and quantification of exosomes by asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation. Anal Chem. 2015;87(18):9225–33.
Yang JS, Lee JC, Byeon SK, Rha KH, Moon MH. Size dependent lipidomic analysis of urinary exosomes from patients with prostate cancer by flow field-flow fractionation and nanoflow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2017;89(4):2488–96.
Collino F, Pomatto M, Bruno S, Lindoso RS, Tapparo M, Sicheng W, et al. Exosome and microvesicle-enriched fractions isolated from mesenchymal stem cells by gradient separation showed different molecular signatures and functions on renal tubular epithelial cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2017;13(2):226–43.
Liu Y, Yan G, Gao M, Zhang X. Magnetic capture of polydopamine-encapsulated Hela cells for the analysis of cell surface proteins. J Proteome. 2018;172:76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2017.10.009.
Chi H, Liu C, Yang H, Zeng WF, Wu L, Zhou WJ, et al. Comprehensive identification of peptides in tandem mass spectra using an efficient open search engine. Nat Biotechnol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.4236.
Huang d W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44–57.
Zhang H, Freitas D, Kim HS, Fabijanic K, Li Z, Chen H, et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(3):332–43.
Maroto R, Zhao Y, Jamaluddin M, Popov VL, Wang H, Kalubowilage M, et al. Effects of storage temperature on airway exosome integrity for diagnostic and functional analyses. J Extracell Vesicles. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1080/20013078.2017.1359478.
Turco AE, Lam W, Rule AD, Denic A, Lieske JC, Miller VM, et al. Specific renal parenchymal-derived urinary extracellular vesicles identify age-associated structural changes in living donor kidneys. J Extracell Vesicles. 2016. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v5.29642.
Logozzi M, De Milito A, Lugini L, Borghi M, Calabrò L, Spada M, et al. High levels of exosomes expressing CD63 and caveolin-1 in plasma of melanoma patients. PLoS One. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005219.
Zhao B, Zhang Y, Han S, Zhang W, Zhou Q, Guan H, et al. Exosomes derived from human amniotic epithelial cells accelerate wound healing and inhibit scar formation. J Mol Histol. 2017;48(2):121–32.
Hanson PI, Cashikar A. Multivesicular body morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2012;28:337–62.
Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, Sze NS, Choo A, Chen TS, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214–22.
Sumiyoshi N, Ishitobi H, Miyaki S, Miyado K, Adachi N, Ochi M. The role of tetraspanin CD9 in osteoarthritis using three different mouse models. Biomed Res. 2016;37(5):283–91.
Tiwari N, Wang CC, Brochetta C, Ke G, Vita F, Qi Z, et al. VAMP-8 segregates mast cell-preformed mediator exocytosis from cytokine trafficking pathways. Blood. 2008;111(7):3665–74.
Grant BD, Donaldson JG. Pathways and mechanisms of endocytic recycling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(9):597–608.
van Niel G, D'Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Cocucci E, Meldolesi J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015;25(6):364–72.
Rao SK, Huynh C, Proux-Gillardeaux V, Galli T, Andrews NW. Identification of SNAREs involved in synaptotagmin VII-regulated lysosomal exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(19):20471–9.
Hiemstra TF, Charles PD, Gracia T, Hester SS, Gatto L, Al-Lamki R, et al. Human urinary exosomes as innate immune effectors. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(9):2017–27.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Projects: 2017YFA0505003), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project: 21775027), and China State Key Research Grant, Project: 2016YFA0501402 2016YFA0501401.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The research was approved by the Ethics Committees of Institutes of Biomedical Sciences in Fudan University and the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University. Written informed consents were obtained from participants who provided the urine samples.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection New Insights into Analytical Science in China with guest editors Lihua Zhang, Hua Cui, and Qiankun Zhuang.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, S., Yu, H., Yan, G. et al. Size-dependent sub-proteome analysis of urinary exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 4141–4149 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01616-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-01616-5