Abstract
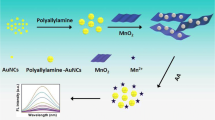
Ascorbic acid (AA) detection in biological sample and food sample is critical for human health. Herein, a MnO2 nanosheet (MnO2-NS)-based ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor has been developed for high sensitive and specific detection of AA. The MnO2-NS presents peroxidase-like activity and can oxidize non-fluorescent substrate of o-phenylenediamine (OPDA) into fluorescent substrate, presenting maximum fluorescence at 568 nm (F568). If MnO2-NS is premixed with AA, the MnO2-NS is then decomposed as Mn2+ by AA, decreasing the fluorescent intensity of F568. Meantime, AA is oxidized as dehydroascorbic acid (DHAA), which can react with OPDA to generate fluorescent substrate. A new fluorescence response is found at 425 nm (F425). The dual fluorescent responses can be excited with a universal excitation wavelength, simplifying the detection procedure. With F425/F568 as readout, limit of detection for AA reaches as low as 10.0 nM. Satisfactory recoveries are found for AA detection in serum and diverse beverages. The ratiometric strategy significantly eliminates false-negative and false-positive results, providing a cost-effective, rapid, and reliable way for AA detection in real sample.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nam H, Kwon J, Choi M, Seo J, Shin S, Kim S, et al. Highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for ascorbic acid with a broad detection range through dual-quenching and bimodal action of nitronyl-nitroxide. ACS Sensors. 2016;1:392–8.
Eggersdorfer M, Laudert D, Létinois U, McClymont T, Medlock J, Netscher T, et al. One hundred years of vitamins-a success story of the natural sciences. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51:12960–90.
Zhao P, He K, Han Y, Zhang Z, Yu M, Wang H, et al. Near-infrared dual-emission quantum dots-gold nanoclusters nanohybrid via co-template synthesis for ratiometric fluorescent detection and bioimaging of ascorbic acid in vitro and in vivo. Anal Chem. 2015;87:9998–10005.
Liu H, Na W, Liu Z, Chen X, Su X. A novel turn-on fluorescent strategy for sensing ascorbic acid using graphene quantum dots as fluorescent probe. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:229–33.
Frajese GV, Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Ambrosin E, Sacchetti P, Masuelli L, et al. Potassium increases the antitumor effects of ascorbic acid in breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:4224–34.
Bi H, Duarte CM, Brito M, Vilas-Boas V, Cardoso S, Freitas P. Performance enhanced UV/vis spectroscopic microfluidic sensor for ascorbic acid quantification in human blood. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;85:568–72.
Figueroa-Méndez R, Rivas-Arancibia S. Vitamin C in health and disease: its role in the metabolism of cells and redox state in the brain. Front Physiol. 2015;6:397.
Meng H, Yang D, Tu Y, Yan J. Turn-on fluorescence detection of ascorbic acid with gold nanolcusters. Talanta. 2017;165:346–50.
Zhu X, Zhao T, Nie Z, Liu Y, Yao S. Non-redox modulated fluorescence strategy for sensitive and selective ascorbic acid detection with highly photoluminescent nitrogen-doped carbon nanoparticles via solid-state synthesis. Anal Chem. 2015;87:8524–30.
Li L, Wang C, Liu K, Wang Y, Liu K, Lin Y. Hexagonal cobalt oxyhydroxide-carbon dots hybridized surface: high sensitive fluorescence turn-on probe for monitoring of ascorbic acid in rat brain following brain ischemia. Anal Chem. 2015;87:3404–11.
Ji D, Du Y, Meng H, Zhang L, Huang Z, Hu Y, et al. A novel colorimetric strategy for sensitive and rapid sensing of ascorbic acid using cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflakes and 3, 3′, 5, 5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;256:512–9.
Feng L, Wu Y, Zhang D, Hu X, Zhang J, Wang P, et al. Near infrared graphene quantum dots-based two-photon nanoprobe for direct bioimaging of endogenous ascorbic acid in living cells. Anal Chem. 2017;89:4077–84.
Wang H, Pu G, Devaramani S, Wang Y, Yang Z, Li L, et al. Bimodal electrochemiluminescence of G-CNQDs in the presence of double coreactants for ascorbic acid detection. Anal Chem. 2018;90:4871–7.
Lima DRS, Cossenza M, Garcia CG, Portugal CC, de C Marques FF, Paes-de-Carvalho R, et al. Determination of ascorbic acid in the retina during chicken embryo development using high performance liquid chromatography and UV detection. Anal Methods. 2016;8:5441–7.
Lin X, Liu Y, Tao Z, Gao J, Deng J, Yin J, et al. Nanozyme-based bio-barcode assay for high sensitive and logic-controlled specific detection of multiple DNAs. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:471–7.
Lin X, Liu Y, Deng J, Lyu Y, Qian P, Li Y, et al. Multiple advanced logic gates made of DNA-Ag nanocluster and the application for intelligent detection of pathogenic bacterial genes. Chem Sci. 2018;9:1774–81.
Han Q, Dong Z, Tang X, Wang L, Ju Z, Liu W. A ratiometric nanoprobe consisting of up-conversion nanoparticles functionalized with cobalt oxyhydroxide for detecting and imaging ascorbic acid. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:167–72.
Rong M, Lin L, Song X, Wang Y, Zhong Y, Yan J, et al. Fluorescence sensing of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid using graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a fluorescent “switch”. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:210–7.
Zhai W, Wang C, Yu P, Wang Y, Mao L. Single-layer MnO2 nanosheets suppressed fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarin: mechanistic study and application for sensitive sensing of ascorbic acid in vivo. Anal Chem. 2014;86:12206–13.
Fan S, Zhao M, Ding L, Li H, Chen S. Preparation of Co3O4/crumpled graphene microsphere as peroxidase mimetic for colorimetric assay of ascorbic acid. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;89:846–52.
Zheng M, Xie Z, Qu D, Li D, Du P, Jing X, et al. On-off-on fluorescent carbon dot nanosensor for recognition of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5:13242–7.
Luo X, Zhang W, Han Y, Chen X, Zhu L, Tang W, et al. S co-doped carbon dots based fluorescent “on-off-on” sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in common fruits. Food Chem. 2018;258:214–21.
Liu R, Yang R, Qu C, Mao H, Hu Y, Li J, et al. Synthesis of glycine-functionalized graphene quantum dots as highly sensitive and selective fluorescent sensor of ascorbic acid in human serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017;241:644–51.
Hu L, Deng L, Alsaiari S, Zhang D, Khashab NM. “Light-on” sensing of antioxidants using gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem. 2014;86:4989–94.
Li N, Li Y, Han Y, Pan W, Zhang T, Tang B. A highly selective and instantaneous nanoprobe for detection and imaging of ascorbic acid in living cells and in vivo. Anal Chem. 2014;86:3924–30.
Cen Y, Tang J, Kong X, Wu S, Yuan J, Yu R, et al. A cobalt oxyhydroxide-modified upconversion nanosystem for sensitive fluorescence sensing of ascorbic acid in human plasma. Nanoscale. 2015;7:13951–7.
Meng H, Zhang X, Yang C, Kuai H, Mao G, Gong L, et al. Efficient two-photon fluorescence nanoprobe for turn-on detection and imaging of ascorbic acid in living cells and tissues. Anal Chem. 2016;88:6057–63.
Deng R, Xie X, Vendrell M, Chang Y, Liu X. Intracellular glutathione detection using MnO2-nanosheet-modified upconversion nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:20168–71.
Dong Z, Lu L, Ko C, Yang C, Li S, Lee M, et al. A MnO2 nanosheet-assisted GSH detection platform using an iridium (iii) complex as a switch-on luminescent probe. Nanoscale. 2017;9:4677–82.
Fan H, Zhao Z, Yan G, Zhang X, Yang C, Meng H, et al. A smart DNAzyme-MnO2 nanosystem for efficient gene silencing. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;12:4883–7.
Xiao T, Sun J, Zhao J, Wang S, Liu G, Yang X. FRET effect between fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles and MnO2 nanosheets and its application for sensitive sensing of alkaline phosphatase. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10:6560–9.
Omomo Y, Sasaki T, Wang L, Watanabe M. Redoxable nanosheet crystallites of MnO2 derived via delamination of a layered manganese oxide. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:3568–75.
Fan D, Shang C, Gu W, Wang E, Dong S. Introducing ratiometric fluorescence to MnO2 nanosheet-based biosensing: a simple, label-free ratiometric fluorescent sensor programmed by cascade logic circuit for ultrasensitive GSH detection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:25870–7.
Liu J, Meng L, Fei Z, Dyson P, Jing X, Liu X. MnO2 nanosheets as an artificial enzyme to mimic oxidase for rapid and sensitive detection of glutathione. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;90:69–74.
Han L, Liu S, Zhang X, Tao B, Li N, Luo H. A sensitive polymer dots-manganese dioxide fluorescent nanosensor for “turn-on” detection of glutathione in human serum. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;258:25–31.
Kong X, Wu S, Chen T, Yu R, Chu X. MnO2-induced synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles for reduced glutathione sensing in human whole blood. Nanoscale. 2016;8:15604–10.
Lin Z, Li M, Lv S, Zhang K, Lu M, Tang D. In situ synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine nanoparticles coupled with enzyme-controlled dissolution of MnO2 nanoflakes for a sensitive immunoassay of cancer biomarkers. J Mater Chem B. 2017;5:8506–13.
Guo B, Pan X, Liu Y, Nie L, Zhao H, Liu Y, et al. A reversible water-soluble naphthalimide-based chemosensor for imaging of cellular copper (II) ion and cysteine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;256:632–8.
Lu H, Xu S. Visualizing BPA by molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor based on dual emission nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:147–53.
Zhang X, Zheng C, Guo S, Li J, Yang H, Chen G. Turn-on fluorescence sensor for intracellular imaging of glutathione using g-C3N4 nanosheet–MnO2 sandwich nanocomposite. Anal Chem. 2014;86:3426–34.
Hu Y, Zhang L, Geng X, Ge J, Liu H, Li Z. A rapid and sensitive turn-on fluorescent probe for ascorbic acid detection based on carbon dots–MnO2 nanocomposites. Anal Methods. 2017;9:5653–8.
Chung HK, Ingle JD Jr. Fluorimetric kinetic method for the determination of total ascorbic acid with o-phenylenediamine. Anal Chim Acta. 1991;243:89–95.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21575138 and No. 21775108), the China International Science and Technology Cooperation Based of Food Nutrition/Safety and Medicinal Chemistry, the Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (Project No. 16PTSYJC00130), and the International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of China (Project No. 2014DFR30350).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection New Insights into Analytical Science in China with guest editors Lihua Zhang, Hua Cui, and Qiankun Zhuang.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 327 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, Y., Tao, Z., Lin, X. et al. A MnO2 nanosheet-based ratiometric fluorescent nanosensor with single excitation for rapid and specific detection of ascorbic acid. Anal Bioanal Chem 411, 4093–4101 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1439-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1439-2