Abstract
We certify that protamine-gold nanoclusters (PRT-AuNCs) synthesized by one-pot method exhibit peroxidase-like activity. The catalytic activity of PRT-AuNCs followed typical Michaelis–Menten kinetics and exhibited higher affinity to 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) as the substrate compared to that of natural horseradish peroxidase. Meanwhile, we found that Hg(II) could dramatically and selectively enhance the peroxidase-like activity of PRT-AuNCs, and the enhanced mechanism by Hg(II) was demonstrated to be generation of the cationic Au species and the partly oxidized Au species (Auδ+) by Hg2+–Au0/Au+ interaction. Based on this finding, quantitative determinations of Hg(II) via visual observation and absorption spectra were achieved. The proposed strategy displays high selectivity that arises from the strong aurophilic interaction of mercury towards gold. Moreover, the developed method is highly sensitive with a wide linear range and low detection limit of 1.16 nM. This strategy is not only helpful to develop effective nanomaterials-based artificial enzyme mimics but also irradiative to discover new applications of artificial mimic enzymes in bio-detection, medical diagnostics, and biotechnology.

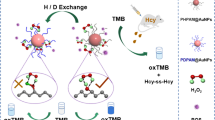
Protamine-gold nanoclusters (PRT-AuNCs) synthesized by one-pot method exhibit peroxidase-like activity. Hg(II) can stimulate the peroxidase-like activity of PRT-AuNCs selectively, enhancing their ability to catalyze the chromogenic reaction of TMB by H2O2






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang X, Sun C, Guo Y, Nie G, Xu L. Peroxidase-like activity of apoferritin paired gold clusters for glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;64:165–70.
Kwon D, Lee S, Ahn MM, Kang IS, Park KH, Jeon S. Colorimetric detection of pathogenic bacteria using platinum-coated magnetic nanoparticle clusters and magnetophoretic chromatography. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;883:61–6.
Wang Q, Zhang L, Shang C, Zhang Z, Dong S. Triple-enzyme mimetic activity of nickel-palladium hollow nanoparticles and their application in colorimetric biosensing of glucose. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016;52:5410–3.
Wei H, Wang E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:6060–93.
Li K, Wang K, Qin W, Deng S, Li D, Shi J, et al. DNA-directed assembly of gold nanohalo for quantitative plasmonic imaging of single-particle catalysis. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:4292–5.
Liu B, Sun Z, Huang JPJ, Liu J. Hydrogen peroxide displacing DNA from nanoceria: mechanism and detection of glucose in serum. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:1290–5.
Fan K, Xi J, Fan L, Wang P, Zhu C, Tang Y, et al. In vivo guiding nitrogen-doped carbon nanozyme for tumor catalytic therapy. Nat Commun. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03903-8.
Lu C, Liu X, Li Y, Yu F, Tang L, Hu Y, et al. Multifunctional Janus hematite–silica nanoparticles: mimicking peroxidase-like activity and sensitive colorimetric detection of glucose. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7:15395–402.
Li Z, Liu R, Xing G, Wang T, Liu S. A novel fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for iodide determination using DNA-templated gold/silver nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;96:44–8.
Tao Y, Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X. A dual fluorometric and colorimetric sensor for dopamine based on BSA-stabilized Au nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;42:41–6.
Liu Y, Ding D, Zhen Y, Guo R. Amino acid-mediated ‘turn-off/turn-on’ nanozyme activity of gold nanoclusters for sensitive and selective detection of copper ions and histidine. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:140–6.
Hong YC, Sun KQ, Zhang GR, Zhong RY, Xu BQ. Fully dispersed Pt entities on nano-Au dramatically enhance the activity of gold for chemoselective hydrogenation catalysis. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47:1300–2.
Han L, Li Y, Fan A. Improvement of mimetic peroxidase activity of gold nanoclusters on the luminol chemiluminescence reaction by surface modification with ethanediamine. Luminescence. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3472.
Lien CW, Chen YC, Chang HT, Huang CC. Logical regulation of the enzyme-like activity of gold nanoparticles by using heavy metal ions. Nanoscale. 2013;5:8227–34.
Long YJ, Li YF, Liu Y, Zheng JJ, Tang J, Huang CZ. Visual observation of the mercury-stimulated peroxidase mimetic activity of gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47:11939–41.
Sivamani E, DeLong RK, Qu R. Protamine-mediated DNA coating remarkably improves bombardment transformation efficiency in plant cells. Plant Cell Rep. 2009;28:213–21.
DeLong RK, Akhtar U, Sallee M, Parker B, Barber S, Zhang J, et al. Characterization and performance of nucleic acid nanoparticles combined with protamine and gold. Biomaterials. 2009;30:6451–9.
Fan Y, Long YF, Li YF. A sensitive resonance light scattering spectrometry of trace Hg2+ with sulfur ion modified gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;653:207–11.
Ramalhosaa E, Rıo Segadeb S, Pereira E, Valed C, Duartec A. Simple methodology for methylmercury and inorganic mercury determinations by high-performance liquid chromatography–cold vapour atomic fluorescence spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2001;448:135–43.
de Jesus RM, Silva LOB, Castro JT, de Azevedo Neto AD, de Jesus RM, Ferreira SLC. Determination of mercury in phosphate fertilizers by cold vapor atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta. 2013;106:293–7.
Wang M, Feng W, Shi J, Zhang F, Wang B, Zhu M, et al. Development of a mild mercaptoethanol extraction method for determination of mercury species in biological samples by HPLC-ICP-MS. Talanta. 2007;71:2034–9.
Chen SH, Wang YS, Chen YS, Tang X, Cao JX, Li MH, et al. Dual-channel detection of metallothioneins and mercury based on a mercury-mediated aptamer beacon using thymidine-mercury-thymidine complex as a quencher. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015;151:315–21.
Tang X, Wang YS, Xue JH, Zhou B, Cao JX, Chen SH, et al. A novel strategy for dual-channel detection of metallothioneins and mercury based on the conformational switching of functional chimera aptamer. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2015;107:258–64.
Wang Q, Yang X, Yang X, Liu P, Wang K, Huang J, et al. Colorimetric detection of mercury ion based on unmodified gold nanoparticles and target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015;136:283–7.
Zhu R, Zhou Y, Wang XL, Liang LP, Long YJ, Wang QL, et al. Detection of Hg2+ based on the selective inhibition of peroxidase mimetic activity of BSA-Au clusters. Talanta. 2013;117:127–32.
Tseng CW, Chang HY, Chang JY, Huang CC. Detection of mercury ions based on mercury-induced switching of enzyme-like activity of platinum/gold nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2012;4:6823–30.
Liu H, Ding Y, Yang B, Liu Z, Liu Q, Zhang X. Colorimetric and ultrasensitive detection of H2O2 based on Au/Co3O4-CeOx nanocomposites with enhanced peroxidase-like performance. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;271:336–45.
Ding Y, Yang B, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zheng X, et al. FePt-Au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018;259:775–83.
Wu K, Zhao X, Chen M, Zhang H, Liu Z, Zhang X, et al. Synthesis of well-dispersed Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded on montmorillonite and sensitive colorimetric detection of H2O2 based on its peroxidase-like activity. New J Chem. 2018;42:9578–87.
Zhu X, Chen W, Wu K, Li H, Fu M, Liu Q, et al. A colorimetric sensor of H2O2 based on Co3O4–montmorillonite nanocomposites with peroxidase activity. New J Chem. 2018;42:1501–9.
Houston JB, Kenworthy KE. In vitro-in vivo scaling of CYP kinetic data not consistent with the classical Michaelis-Menten model. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28:246–54.
Tan H, Ma C, Gao L, Li Q, Song Y, Xu F, et al. Metal-organic framework-derived copper nanoparticle@carbon nanocomposites as peroxidase mimics for colorimetric sensing of ascorbic acid. Chemistry. 2014;20:16377–83.
Khataee A, Haddad Irani-Nezhad M, Hassanzadeh J. Improved peroxidase mimetic activity of a mixture of WS2 nanosheets and silver nanoclusters for chemiluminescent quantification of H2O2 and glucose. Microchim Acta. 2018;185:190.
Su L, Xiong Y, Yang H, Zhang P, Ye F. Prussian blue nanoparticles encapsulated inside a metal–organic framework via in situ growth as promising peroxidase mimetics for enzyme inhibitor screening. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4:128–34.
Zhang XQ, Gong SW, Zhang Y, Yang T, Wang CY, Gu N. Prussian blue modified iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles and their high peroxidase-like activity. J Mater Chem. 2010;20:5110–6.
Dong YL, Zhang HG, Rahman ZU, Su L, Chen XJ, Hu J, et al. Graphene oxide-Fe3O4 magnetic nanocomposites with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of glucose. Nanoscale. 2012;4:3969–76.
Stratakis M, Garcia H. Catalysis by supported gold nanoparticles: beyond aerobic oxidative processes. Chem Rev. 2012;112:4469–506.
Matthey D, Wang JG, Wendt S, Matthiesen J, Schaub R, Laegsgaard E, et al. Enhanced bonding of gold nanoparticles on oxidized TiO2(110). Science. 2007;315:1692–6.
Klyushin AY, Rocha TC, Havecker M, Knop-Gericke A, Schlogl R. A near ambient pressure XPS study of Au oxidation. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014;16:7881–6.
Huai Q, Zhang B, Sheng F, Tao Z. Raman and ATR infrared studies of the conformation of metallothionein in solution. Spectrosc Lett. 1995;28:829–38.
Awotwe-Otoo D, Agarabi C, Keire D, Lee S, Raw A, Yu L, et al. Physicochemical characterization of complex drug substances: evaluation of structural similarities and differences of protamine sulfate from various sources. AAPS J. 2012;14:619–26.
Vener MV, Odinokov AV, Wehmeyer C, Sebastiani D. The structure and IR signatures of the arginine-glutamate salt bridge. Insights from the classical MD simulations. J Chem Phys. 2015;142:215106.
Zhang JQ, Wang YS, Xue JH, He Y, Yang HX, Liang J, et al. A gold nanoparticles-modified aptamer beacon for urinary adenosine detection based on structure-switching/fluorescence-“turning on” mechanism. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2012;70:362–8.
Xu J, Kong DM. Specific Hg2+ quantitation using intramolecular split G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Chin J Anal Chem. 2012;40:347–53.
Kong DM, Wang N, Guo XX, Shen HX. ‘Turn-on’ detection of Hg2+ ion using a peroxidase-like split G-quadruplex-hemin DNAzyme. Analyst. 2010;135:545–9.
Liu X, Cheng X, Bing T, Fang C, Shangguan D. Visual detection of Hg2+ with high selectivity using thymine modified gold nanoparticles. Anal Sci. 2010;26:1169–72.
Xu H, Zhu X, Ye H, Yu L, Liu X, Chen G. A simple “molecular beacon”-based fluorescent sensing strategy for sensitive and selective detection of mercury (II). Chem Commun (Camb). 2011;47:12158–60.
Ge J, Li XP, Jiang JH, Yu RQ. A highly sensitive label-free sensor for mercury ion (Hg2+) by inhibiting thioflavin T as DNA G-quadruplexes fluorescent inducer. Talanta. 2014;122:85–90.
Li Q, Zhou X, Xing D. Rapid and highly sensitive detection of mercury ion (Hg2+) by magnetic beads-based electrochemiluminescence assay. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;26:859–62.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21177052, 81502850), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province in China (No. 2015JJ2122), and the Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province in China (No. 2010SK3039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 3.24 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YQ., Fu, S., Wang, YS. et al. Protamine-gold nanoclusters as peroxidase mimics and the selective enhancement of their activity by mercury ions for highly sensitive colorimetric assay of Hg(II). Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 7385–7394 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1344-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1344-8