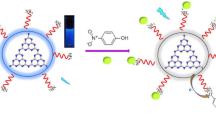
Abstract
An electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL)-DNA sensor was designed and fabricated for the investigation of DNA damage by a potential environmental pollutant, perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). The ECL-DNA sensor consisted of a Au electrode that had a self-assembled monolayer of 15 base-pair double-stranded (ds) DNA oligonucleotides with covalently attached semiconductor CdSe quantum dots (QDs) at the distal end of the DNA. Characterization of the ECL-DNA sensor was conducted with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), ECL, and cyclic voltammetry before and after the exposure of the sensor to PFOA. Consistent data revealed that the dsDNA on Au was severely damaged upon the incubation of the electrode in PFOA, causing significant increase in charge (or electron) transfer (CT) resistance within DNA strands. Consequently, the cathodic coreactant ECL responses of the Au/dsDNA-QDs electrode in the presence of K2S2O8 were markedly decreased. The strong interaction between DNA and PFOA via the hydrophobic interaction, especially the formation of F···H hydrogen bonds by insertion of the difluoro-methylene group of PFOA into the DNA base pairs, was believed to be responsible for the dissociation or loosening of dsDNA structure, which inhibited the CT through DNA. A linear relationship between the ECL signal of the sensor and the logarithmical concentration of PFOA displayed a dynamic range of 1.00 × 10−14–1.00 × 10−4 M, with a limit of detection of 1.00 × 10−15 M at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3.

Illustration of ECL detection of PFOA on a Au/dsDNA-QDs ECL-DNA sensor





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toyooka T, Ibuki Y. DNA damage induced by coexposure to PAHs and light. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007;23(2):256–63.
Guruge KS, Yeung LWY, Yamanaka N, Miyazaki S, Lam PKS, Giesy JP, et al. Gene expression profiles in rat liver treated with perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA). Toxicol Sci. 2006;89(1):93–107.
Richter MM. Electrochemiluminescence (ECL). Chem Rev. 2004;104(6):3003–36.
Miao W. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence and its biorelated applications. Chem Rev. 2008;108(7):2506–53.
Ding Z, Quinn B, Haram S, Pell L, Korgel B, Bard AJ. Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science. 2002;296:1293.
Zou G, Ju H. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from a CdSe nanocrystal film and its sensing application in aqueous solution. Anal Chem. 2004;76(23):6871–6.
Jie G, Zhang J, Wang D, Cheng C, Chen H-Y, Zhu J-J. Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdSe nanocomposites. Anal Chem. 2008;80(11):4033–9.
Myung N, Ding Z, Bard AJ. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett. 2002;2(11):1315–9.
Yin Y, Alivisatos AP. Colloidal nanocrystal synthesis and the organic–inorganic interface. Nature. 2005;437(7059):664–70.
Burda C, Chen X, Narayanan R, El-Sayed MA. Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Rev. 2005;105(4):1025–102.
Lei J, Ju H. Fundamentals and bioanalytical applications of functional quantum dots as electrogenerated emitters of chemiluminescence. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2011;30(8):1351–9.
Huang H, Li J, Zhu J-J. Electrochemiluminescence based on quantum dots and their analytical application. Anal Methods. 2011;3(1):33–42.
Wang J, Shan Y, Zhao W-W, Xu J-J, Chen H-Y. Gold nanoparticle enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdS thin films for ultrasensitive thrombin detection. Anal Chem. 2011;83(11):4004–11.
Drummond TG, Hill MG, Barton JK. Electrochemical DNA sensors. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(10):1192–9.
Kelley SO, Barton JK. Electron transfer between bases in double helical DNA. Science. 1999;283(5400):375–81.
Liu T, Barton JK. DNA Electrochemistry through the base pairs not the sugar-phosphate backbone. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127(29):10160–1.
Slinker JD, Muren NB, Renfrew SE, Barton JK. DNA charge transport over 34 nm. Nat Chem. 2011;3(3):228–33.
Kelley SO, Holmlin RE, Stemp EDA, Barton JK. Photoinduced electron transfer in ethidium-modified DNA duplexes: dependence on distance and base stacking. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119(41):9861–70.
Kelley SO, Barton JK, Jackson NM, Hill MG. Electrochemistry of methylene blue bound to a DNA-modified electrode. Bioconjug Chem. 1997;8(1):31–7.
Pheeney CG, Barton JK. DNA electrochemistry with tethered methylene blue. Langmuir. 2012;28(17):7063–70.
Mui TP, Fuss JO, Ishida JP, Tainer JA, Barton JK. ATP-stimulated, DNA-mediated redox signaling by XPD, a DNA repair and transcription helicase. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(41):16378–81.
Sontz PA, Mui TP, Fuss JO, Tainer JA, Barton JK. DNA charge transport as a first step in coordinating the detection of lesions by repair proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(6):1856–61.
Sontz PA, Muren NB, Barton JK. DNA charge transport for sensing and signaling. Acc Chem Res. 2012;45(10):1792–800.
Muren NB, Olmon ED, Barton JK. Solution, surface, and single molecule platforms for the study of DNA-mediated charge transport. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2012;14(40):13754–71.
Wong ELS, Gooding JJ. Charge transfer through DNA: a selective electrochemical DNA biosensor. Anal Chem. 2006;78(7):2138–44.
Guo X, Gorodetsky AA, Hone J, Barton JK, Nuckolls C. Conductivity of a single DNA duplex bridging a carbon nanotube gap. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3(3):163–7.
Kelley SO, Boon EM, Barton JK, Jackson NM, Hill MG. Single-base mismatch detection based on charge transduction through DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999;27(24):4830–7.
Hall DB, Holmlin RE, Barton JK. Oxidative DNA damage through long-range electron transfer. Nature. 1996;382(6593):731–5.
Husale S, Persson HHJ, Sahin O. DNA nanomechanics allows direct digital detection of complementary DNA and microRNA targets. Nature. 2009;462(7276):1075–8.
Krafft MP. Fluorocarbons and fluorinated amphiphiles in drug delivery and biomedical research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(2–3):209–28.
Nakata H, Kannan K, Nasu T, Cho H-S, Sinclair E, Takemura A. Perfluorinated contaminants in sediments and aquatic organisms collected from shallow water and tidal flat areas of the Ariake Sea, Japan: environmental fate of perfluorooctane sulfonate in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(16):4916–21.
Kerger BD, Copeland TL, DeCaprio AP. Tenuous dose–response correlations for common disease states: case study of cholesterol and perfluorooctanoate/sulfonate (PFOA/PFOS) in the C8 health project. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2011;34(4):396–404.
Kennedy Jr GL, Butenhoff JL, Olsen GW, O’Connor JC, Seacat AM, Perkins RG, et al. The toxicology of perfluorooctanoate. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2004;34(4):351–84.
Lu L, Xu L, Kang T, Cheng S. Investigation of DNA damage treated with perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) on ZrO2/DDAB active nano-order film. Biosens Bioelectron. 2012;35(1):180–5.
Rogach AL, Kornowski A, Gao M, Eychmüller A, Weller H. Synthesis and characterization of a size series of extremely small thiol-stabilized CdSe nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B. 1999;103(16):3065–9.
Li Y, Han M, Bai H, Wu Y, Dai Z, Bao J. A sensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on water soluble CdSe quantum dots (QDs) for thrombin determination. Electrochim Acta. 2011;56(20):7058–63.
Liu X, Guo L, Cheng L, Ju H. Determination of nitrite based on its quenching effect on anodic electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots. Talanta. 2009;78(3):691–4.
Yu WW, Qu L, Guo W, Peng X. Experimental determination of the extinction coefficient of CdTe, CdSe, and CdS nanocrystals. Chem Mater. 2003;15(14):2854–60.
Hermanson GT. Bioconjugate techniques. New York: Academic; 1996.
Petrovykh DY, Kimura-Suda H, Whitman LJ, Tarlov MJ. Quantitative analysis and characterization of DNA immobilized on gold. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(17):5219–26.
Rieley H, Kendall GK, Zemicael FW, Smith TL, Yang S. X-ray studies of self-assembled monolayers on coinage metals. 1. Alignment and photooxidation in 1,8-octanedithiol and 1-octanethiol on Au. Langmuir. 1998;14(18):5147–53.
Bain CD, Biebuyck HA, Whitesides GM. Comparison of self-assembled monolayers on gold: coadsorption of thiols and disulfides. Langmuir. 1989;5(3):723–7.
Hao E, Sun H, Zhou Z, Liu J, Yang B, Shen J. Synthesis and optical properties of CdSe and CdSe/CdS nanoparticles. Chem Mater. 1999;11(11):3096–102.
Katari JEB, Colvin VL, Alivisatos AP. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of CdSe nanocrystals with applications to studies of the nanocrystal surface. J Phys Chem. 1994;98(15):4109–17.
Herne TM, Tarlov MJ. Characterization of DNA probes immobilized on gold surfaces. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119(38):8916–20.
Lee C-Y, Gong P, Harbers GM, Grainger DW, Castner DG, Gamble LJ. Surface coverage and structure of mixed DNA/alkylthiol monolayers on gold: characterization by XPS, NEXAFS, and fluorescence intensity measurements. Anal Chem. 2006;78(10):3316–25.
Nordfors D, Ågren H. Calculation of core electron binding energies from structural formulas. J Electron Spectrosc Relat Phenom. 1991;56(1):1–11.
Macdonald DD. Reflections on the history of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim Acta. 2006;51(8–9):1376–88.
Chang B-Y, Park S-M. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Annu Rev Anal Chem. 2010;3:207–29.
Lisdat F, Schaefer D. The use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;391(5):1555–67.
Orazem ME, Tribollet B, editors. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Wiley; 2008.
Park J-Y, Park S-M. DNA hybridization sensors based on electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as a detection tool. Sensors. 2009;9(12):9513–32.
Yu D, Wang C, Guyot-Sionnest P. n-Type conducting CdSe nanocrystal solids. Science. 2003;300(5623):1277–80.
Pittman TL, Miao W. Examination of electron transfer through DNA using electrogenerated chemiluminescence. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112(43):16999–7004.
Miao W, Choi J-P. Coreactants. In: Bard AJ, editor. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. New York: Marcel Dekker; 2004. p. 213–72.
So M, Hvastkovs EG, Schenkman JB, Rusling JF. Electrochemiluminescent/voltammetric toxicity screening sensor using enzyme-generated DNA damage. Biosens Bioelectron. 2007;23(4):492–8.
Zhou L, Yang J, Estavillo C, Stuart JD, Schenkman JB, Rusling JF. Toxicity screening by electrochemical detection of DNA damage by metabolites generated in situ in ultrathin DNA–enzyme films. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125(5):1431–6.
Acknowledgments
We thank the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21005005, 21345005, and 21475006), Beijing Nova Program (2010B009), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0603), and the National Science Foundation CAREER award (CHE-0955878, WJM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Analytical Electrochemiluminescence with guest editors Hua Cui, Francesco Paolucci, Neso Sojic, and Guobao Xu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Guo, L., Li, M. et al. Investigation of perfluorooctanoic acid induced DNA damage using electrogenerated chemiluminescence associated with charge transfer in DNA. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 7137–7145 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9559-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9559-z