Abstract
A new online electrochemistry/liquid sample desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (EC/LS DESI MS) system with a simple electrochemical thin-layer flow-through cell was developed and tested using N,N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine (DMPA) as a model probe. Although oxidation of DMPA is observed as a result of ionization of LS in positive ion mode LS DESI, application of voltage to the online electrochemical (EC) cell in EC/LS DESI MS increases yields of oxidation products. An advantage of LS DESI MS is its sensitivity in aqueous electrolyte solutions, which improves efficiency of electrochemical reactions in EC/LS DESI MS. In highly conductive low pH aqueous buffer solutions, oxidation efficiency is close to 100 %. EC/ESI MS typically requires mixed aqueous/organic solvents and low electrolyte concentrations for efficient ionization in MS, limiting efficiency of electrochemistry online with MS. Independently, the results verify higher electrochemical oxidation efficiency during positive mode ESI than during LS DESI.

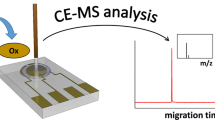
Detection of DMPA oxidation in online electrochemical cell with EC/LS DESI MS.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volk K, Yost R, Brajter-Toth A. Electrochemistry on line with mass-spectrometry—insight into biological redox reactions. Anal Chem. 1992;64(1):21A–33A.
Zhang TY, Brajter-Toth A. On-line investigation of the generation of nonaqueous intermediate radical cations by electrochemistry/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2000;72(11):2533–40.
Baumann A, Karst U. Online electrochemistry/mass spectrometry in drug metabolism studies: principles and applications. Expert Opin Drug Met. 2010;6(6):715–31. doi:10.1517/17425251003713527.
Looi DW, Eyler JR, Brajter-Toth A. Electrochemistry-electrospray ionization FT ICR mass spectrometry (EC ESI MS) of guanine-tyrosine and guanine-glutathione crosslinks formed on-line. Electrochim Acta. 2011;56(6):2633–40. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.009|10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.009.
Permentier HP, Bruins AP, Bischoff R. Electrochemistry-mass spectrometry in drug metabolism and protein research. Mini-Rev Med Chem. 2008;8(1):46–56. doi:10.2174/138955708783331586.
Iftikhar I, Brajter-Toth A. Solution or gas phase? Oxidation and radical formation in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI MS). Electroanalysis. 2015;27.
Volk K, Yost R, Brajter-Toth A, Freeman J. A dynamic approach for studying redox reactions—electrochemistry online with mass-spectrometry. Analusis. 1992;20(7):421–5.
Permentier HP, Jurva U, Barroso B, Bruins AP. Electrochemical oxidation and cleavage of peptides analyzed with on-line mass spectrometric detection. Rapid Commun Mass Sp. 2003;17(14):1585–92. doi:10.1002/rcm.1090.
Permentier HP, Bruins AP. Electrochemical oxidation and cleavage of proteins with on-line mass spectrometric detection: development of an instrumental alternative to enzymatic protein digestion. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2004;15(12):1707–16. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2004.09.003.
Roeser J, Permentier HP, Bruins AP, Bischoff R. Electrochemical oxidation and cleavage of tyrosine- and tryptophan-containing tripeptides. Anal Chem. 2010;82(18):7556–65. doi:10.1021/ac101086w.
Jahn S, Karst U. Electrochemistry coupled to (liquid chromatography/) mass spectrometry-current state and future perspectives. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1259:16–49. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2012.05.066.
Roussel C, Rohner TC, Jensen H, Girault HH. Mechanistic aspects of on-line electrochemical tagging of free L-cysteine residues during electrospray ionisation for mass spectrometry in protein analysis. ChemPhysChem. 2003;4(2):200–6. doi:10.1002/cphc.200390031.
Dayon L, Roussel C, Girault HH. On-line electrochemical tagging of free cysteines in peptides during nanospray ionisation mass spectrometry: an overview. Chimia. 2004;58(4):204–7. doi:10.2533/000942904777678028.
Zheng QL, Zhang H, Chen H. Integration of online digestion and electrolytic reduction with mass spectrometry for rapid disulfide-containing protein structural analysis. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2013;353:84–92. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2013.04.009.
Nicolardi S, Giera M, Kooijman P, Kraj A, Chervet JP, Deelder AM, et al. On-line electrochemical reduction of disulfide bonds: improved FTICR-CID and -ETD coverage of oxytocin and hepcidin. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013;24(12):1980–7. doi:10.1007/s13361-013-0725-7.
Nicolardi S, Deelder AM, Palmblad M, van der Burgt YEM. Structural analysis of an intact monoclonal antibody by online electrochemical reduction of disulfide bonds and fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2014;86(11):5376–82. doi:10.1021/ac500383c.
van den Brink FTG, Buter L, Odijk M, Olthuis W, Karst U, van den Berg A. Mass spectrometric detection of short-lived drug metabolites generated in an electrochemical microfluidic chip. Anal Chem. 2015;87(3):1527–35. doi:10.1021/ac503384e.
Buter L, Faber H, Wigger T, Vogel M, Karst U. Differential protein labeling based on electrochemically generated reactive intermediates. Anal Chem. 2015;87(19):9931–8. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02497.
Karst U. Electrochemistry/mass spectrometry (EC/MS)—a new tool to study drug metabolism and reaction mechanisms. Angew Chem Int Edit. 2004;43(19):2476–8. doi:10.1002/anie.200301763.
Bruins AP. An overview of electrochemistry combined with mass spectrometry. Trac Trend Anal Chem. 2015;70:14–9. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2015.02.016.
Jurva U, Weidolf L. Electrochemical generation of drug metabolites with applications in drug discovery and development. Trac Trend Anal Chem. 2015;70:92–9. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2015.04.010.
Kertesz V, Van Berkel GJ. Expanded use of a battery-powered two-electrode emitter cell for electrospray mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2006;17(7):953–61. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2006.02.007|10.1016/j.jasms.2006.02.007.
Mautjana NA, Estes J, Eyler JR, Brajter-Toth A. One-electron oxidation and sensitivity of uric acid in on-line electrochemistry and in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Electroanalysis. 2008;20(23):2501–8. doi:10.1002/elan.200804346.
Xu XM, Lu WZ, Cole RB. On-line probe for fast electrochemistry/electrospray mass spectrometry. Investigation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Anal Chem. 1996;68(23):4244–53. doi:10.1021/ac960362i.
Lu WZ, Xu XM, Cole RB. On-line linear sweep voltammetry electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1997;69(13):2478–84.
Deng HT, Van Berkel GJ. A thin-layer electrochemical flow cell coupled on-line with electrospray-mass spectrometry for the study of biological redox reactions. Electroanalysis. 1999;11(12):857–65. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4109(199908)11:12<857::AID-ELAN857>3.0.CO;2-1.
Bokman CF, Zettersten C, Sjoberg PJR, Nyholm L. A setup for the coupling of a thin-layer electrochemical flow cell to electrospray mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2004;76(7):2017–24. doi:10.1021/ac030388r|10.1021/ac030388r.
Modestov AD, Gun J, Savotine I, Lev O. On-line electrochemical-mass spectrometry study of the mechanism of oxidation of N, N-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine in aqueous electrolytes. J Electroanal Chem. 2004;565(1):7–19. doi:10.1016/j.jelechem.2003.09.023.
Zettersten C, Co M, Wende S, Turner C, Nyholm L, Sjoberg PJR. Identification and characterization of polyphenolic antioxidants using on-line liquid chromatography, electrochemistry, and electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81(21):8968–77. doi:10.1021/ac901397c.
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications. Second edn. Brijbasi Art Press Ltd., Noida, U.P. India. 2004.
Looi DW, Iftikhar I, Brajter-Toth A. Electrochemical attributes of electrochemistry in tandem with electrospray mass spectrometry. Electroanalysis. 2014;26(2):319–27. doi:10.1002/elan.201300426.
Zhang TY, Palii SP, Eyler JR, Brajter-Toth A. Enhancement of ionization efficiency by electrochemical reaction products in on-line electrochemistry/electrospray ionization fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2002;74(5):1097–103. doi:10.1021/ac015543l.
Mautjana NA, Estes J, Eyler JR, Brajter-Toth A. Antioxidant pathways and one-electron oxidation of dopamine and cysteine in electrospray and on-line electrochemistry electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Electroanalysis. 2008;20(18):1959–67. doi:10.1002/elan.200804279|10.1002/elan.200804279.
Chowdhury SK, Chait BT. Method for the electrospray ionization of highly conductive aqueous-solutions. Anal Chem. 1991;63(15):1660–4. doi:10.1021/ac00015a030.
Banks JF, Shen S, Whitehouse CM, Fenn JB. Ultrasonically assisted electrospray-ionization for LC/MS determination of nucleosides from a transfer-RNA digest. Anal Chem. 1994;66(3):406–14. doi:10.1021/ac00075a015.
Sainiemi L, Sikanen T, Kostiainen R. Integration of fully microfabricated, three-dimensionally sharp electrospray ionization tips with microfluidic glass chips. Anal Chem. 2012;84(21):8973–9. doi:10.1021/ac301602b.
Sokol E, Noll RJ, Cooks RG, Beegle LW, Kim HI, Kanik I. Miniature mass spectrometer equipped with electrospray and desorption electrospray ionization for direct analysis of organics from solids and solutions. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2011;306(2–3):187–95. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2010.10.019.
Cech NB, Enke CG. Practical implications of some recent studies in electrospray ionization fundamentals. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2001;20(6):362–87. doi:10.1002/mas.10008.
Liigand J, Kruve A, Leito I, Girod M, Antoine R. Effect of mobile phase on electrospray ionization efficiency. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014;25(11):1853–61. doi:10.1007/s13361-014-0969-x.
Tang L, Kebarle P. Effect of the conductivity of the electrosprayed solution on the electrospray current—factors determining analyte sensitivity in electrospray mass-spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1991;63(23):2709–15.
Miao ZX, Chen H. Direct analysis of liquid samples by desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (DESI-MS). J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20(1):10–9. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2008.09.023|10.1016/j.jasms.2008.09.023.
Li JW, Dewald HD, Chen H. Online coupling of electrochemical reactions with liquid sample desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009;81(23):9716–22. doi:10.1021/ac901975j.
Roach PJ, Laskin J, Laskin A. Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization: an ambient method for liquid-extraction surface sampling in mass spectrometry. Analyst. 2010;135(9):2233–6. doi:10.1039/c0an00312c.
Liu PY, Lanekoff IT, Laskin J, Dewald HD, Chen H. Study of electrochemical reactions using nanospray desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2012;84(13):5737–43. doi:10.1021/ac300916k.
Lu M, Wolff C, Cui WD, Chen H. Investigation of some biologically relevant redox reactions using electrochemical mass spectrometry interfaced by desorption electrospray ionization. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;403(2):355–65. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5679-7.
Liu PY, Zheng QL, Dewald HD, Zhou R, Chen H. The study of electrochemistry with ambient mass spectrometry. Trac Trend Anal Chem. 2015;70:20–30. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2015.02.018.
Zhang Y, Dewald HD, Chen H. Online mass spectrometric analysis of proteins/peptides following electrolytic cleavage of disulfide bonds. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(3):1293–304. doi:10.1021/pr101053q|10.1021/pr101053q.
Tong LKJ. Kinetics of deamination of oxidized N, N-disubstituted para-phenylenediamines. J Phys Chem US. 1954;58(12):1090–7. doi:10.1021/j150522a012.
Mark HB, Anson FC. Electro-oxidation of phenylenediamines and related compounds at platinum electrodes - effects of acid strength. Anal Chem. 1963;35(6):722–4. doi:10.1021/ac60199a012.
Nickel U, Kemnitz K, Jaenicke W. Kinetics and mechanism of acid deamination of n-substituted quinone di-imines measured with a multi-mixing, stopped-flow technique. J Chen Soc Perk T. 1978;2(11):1188–93. doi:10.1039/p29780001188.
Nickel U, Jaenicke W. Activation parameters and mechanism of the deamination of n-substituted quinone monoimines and di-imines. J Chen Soc Perk T. 1980;2(11):1601–5. doi:10.1039/p29800001601.
Salem IA, Gaber M, Badr-Eldeen DF. Kinetics and mechanism of the copper(II) catalyzed oxidation of N-substituted p-phenylenediamines by 2,3,9,10-tetramethyl-1,4,5,7,8,11,12,14-octaazacyclotetradeca-1,3,8,10-t etraenecopper(II). Transit Metal Chem. 1999;24(5):511–6. doi:10.1023/a:1006935718594.
Regino MCS, Brajter-Toth A. An electrochemical cell for on-line electrochemistry mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1997;69(24):5067–72. doi:10.1021/ac961261n.
Barnes EO, O’Mahony AM, Belding SR, Compton RG. Kinetics and thermodynamics of redox processes in room temperature ionic liquids: the use of voltammetry and the disproportionation of radical cations of N, N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine in 1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium Tetrafluoroborate. J Chem Eng Data. 2010;55(6):2219–24. doi:10.1021/je900770b.
Takats Z, Wiseman JM, Cooks RG. Ambient mass spectrometry using desorption electrospray ionization (DESI): instrumentation, mechanisms and applications in forensics, chemistry, and biology. J Mass Spectrom. 2005;40(10):1261–75. doi:10.1002/jms.922|10.1002/jms.922.
Ifa DR, Wu CP, Ouyang Z, Cooks RG. Desorption electrospray ionization and other ambient ionization methods: current progress and preview. Analyst. 2010;135(4):669–81. doi:10.1039/b925257f.
Moore BN, Hamdy O, Julian RR. Protein structure evolution in liquid DESI as revealed by selective noncovalent adduct protein probing. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2012;330:220–5. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2012.08.013.
Chen YH, Nickel U, Spiro M. Electrochemical study of the heterogeneously catalyzed reaction between N, N-Dimethyl-P-Phenylenediamine and Co(III)(NH3)5Cl2+ at monometallic and bimetallic surfaces of silver and gold. J Chem Soc Faraday T. 1994;90(4):617–23. doi:10.1039/ft9949000617.
Clare LA, Rojas-Sligh LE, Maciejewski SM, Kangas K, Woods JE, Deiner LJ, et al. The effect of H-bonding and proton transfer on the voltammetry of 2,3,5,6-tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine in acetonitrile. An unexpectedly complex mechanism for a simple redox couple. J Phys Chem C. 2010;114(19):8938–49. doi:10.1021/jp100079q.
Li Y, Pozniak BP, Cole RB. Mapping of potential gradients within the electrospray emitter. Anal Chem. 2003;75(24):6987–94. doi:10.1021/ac030212p.
Kapturkiewicz A, Jaenicke W. Comparison between heterogeneous and homogeneous electron-transfer in P-phenylenediamine systems. J Chem Soc Faraday T. 1987;1(83):2727–34. doi:10.1039/f19878302727.
Chung YC, Su YO. Effects of phenyl- and methyl-Substituents on p-phenylenediamine, an electrochemical and spectral study. J Chin Chem Soc-TAIP. 2009;56(3):493–503.
Michaelis L, Schubert MP, Granick S. The free radicals of the type of wurster’s salts. J Am Chem Soc. 1939;61(8):1981–92.
Blackbur GM, Jencks WP. Mechanism of aminolysis of methyl formate. J Am Chem Soc. 1968;90(10):2638–45. doi:10.1021/ja01012a031.
Reddy PG, Kumar GDK, Baskaran S. A convenient method for the N-formylation of secondary amines and anilines using ammonium formate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41(47):9149–51.
Iranpoor N, Firouzabadi H, Jamalian A. Silphos PCl3-n(SiO2)(n): a heterogeneous phosphine reagent for the regioselective synthesis of vic-haloalcohols. Phosphorus Sulfur. 2006;181(11):2615–21. doi:10.1080/10426500600775989.
Yang XJ, Chen B, Zheng LQ, Wu LZ, Tung CH. Highly efficient and selective photocatalytic hydrogenation of functionalized nitrobenzenes. Green Chem. 2014;16(3):1082–6. doi:10.1039/c3gc42042f.
Benassi M, Wu CP, Nefliu M, Ifa DR, Volny M, Cooks RG. Redox transformations in desorption electrospray ionization. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2009;280(1–3):235–40. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2008.10.012.
Pasilis SP, Kertesz V, Van Berkel GJ. Unexpected analyte oxidation during desorption electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2008;80(4):1208–14. doi:10.1021/ac701791w.
Bedner M, Maccrehan WA. Transformation of acetaminophen by chlorination produces the toxicants 1,4-benzoquinone and N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40(2):516–22. doi:10.1021/es0509073.
Faber H, Lutze H, Lareo PL, Frensemeier L, Vogel M, Schmidt TC, et al. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry to study oxidative degradation of environmentally relevant pharmaceuticals by electrochemistry and ozonation. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1343:152–9. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2014.03.081.
Kanev IL, Mikheev AY, Shlyapnikov YM, Shlyapnikova EA, Morozova TY, Morozov VN. Are reactive oxygen species generated in electrospray at low currents? Anal Chem. 2014;86(3):1511–7. doi:10.1021/ac403129f.
Cataldo F. On the polymerization of p-phenylenediamine. Eur Polym J. 1996;32(1):43–50. doi:10.1016/0014-3057(95)00118-2.
Ciric-Marjanovic G, Marjanovic B, Bober P, Rozlivkova Z, Stejskal J, Trchova M, et al. The oxidative polymerization of p-Phenylenediamine with silver nitrate: toward highly conducting micro/nanostructured silver/conjugated polymer composites. J Polym Sci Part A1. 2011;49(15):3387–403. doi:10.1002/pola.24775.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Looi, W.D., Brown, B., Chamand, L. et al. Merits of online electrochemistry liquid sample desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (EC/LS DESI MS). Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 2227–2238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9246-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9246-5