Abstract
Stable isotope dilution assays (SIDAs) are becoming ever commoner in mycotoxin analysis, and the number of synthesized or commercially available isotopically labelled compounds has greatly increased in the 7 years since our last review dealing with this topic. Thus, this review is conceived as an update for new applications or improvements of SIDAs for compounds discussed earlier, but the main focus is on newly introduced labelled substances and the development of SIDAs for, for example, fusarin C, moniliformin or the enniatins. Mycotoxin research has concentrated on the emerging group of Alternaria toxins in recent years, and a series of SIDAs have been developed, including ones for tenuazonic acid, alternariol, altertoxins and tentoxin that are discussed in detail in this review. Information about synthetic routes, isotopic purity and mass-spectrometric characterization of labelled compounds is given, as well as about the development and validation of SIDAs and their application to foods, feeds or biological samples. As the number of commercially available labelled standards is increasing continuously, a general tendency for the use of analytical methods based on liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry capable of identifying a series of mycotoxins simultaneously (“multimethods”) and using one or more labelled internal standards can be observed. An overview of these applications is given, thus demonstrating that SIDAs are increasingly being used in routine analysis.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rychlik M, Asam S (2008) Stable isotope dilution assays in mycotoxin analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 390(2):617–628
Hartmann N, Erbs M, Wettstein FE, Schwarzenbach RP, Bucheli TD (2007) Quantification of estrogenic mycotoxins at the ng/L level in aqueous environmental samples using deuterated internal standards. J Chromatogr, A 1138(1–2):132–140
Miles CO, Erasmuson AF, Wilkins AL, Towers NR, Smith BL, Garthwaite I, Scahill BG, Hansen RP (1996) Ovine metabolism of zearalenone to α-zearalanol (zeranol). J Agric Food Chem 44(10):3244–3250
Cramer B, Bretz M, Humpf H (2007) Stable isotope dilution analysis of the Fusarium mycotoxin zearalenone. J Agric Food Chem 55(21):8353–8358
Peters CA (1972) Photochemistry of zearalenone and its derivatives. J Med Chem 15(8):867–868
Köppen R, Riedel J, Emmerling F, Koch M (2012) (3S,11Z )-14,16-Dihydroxy-3-methyl-3,4,5,6,9,10-hexahydro-1 H-2-benzoxacyclotetradecine-1,7(8 H)-dione (cis-zearalenone): a redetermination. Acta Crystallogr E Struct Rep Online 68(3):o832
Köppen R, Riedel J, Proske M, Drzymala S, Rasenko T, Durmaz V, Weber M, Koch M (2012) Photochemical trans-/cis-isomerization and quantitation of zearalenone in edible oils. J Agric Food Chem 60(47):11733–11740
Drzymala S, Riedel J, Köppen R, Garbe L, Koch M (2014) Preparation of 13C-labelled cis-zearalenone and its application as internal standard in stable isotope dilution analysis. World Mycotoxin J 7(1):45–52
Cole RJ, Kirksey JW, Cutler HG, Doupnik BL, Peckham JC (1973) Toxin from Fusarium moniliforme: effects on plants and animals. Science 179(4080):1324–1326
Springer JP, Clardy J, Cole RJ, Kirksey JW, Hill RK, Carlson RM, Isidor JL (1974) Structure and synthesis of moniliformin, a novel cyclobutane microbial toxin. J Am Chem Soc 96(7):2267–2268
Schütt F, Nirenberg HI, Demi G (1998) Moniliformin production in the genus Fusarium. Mycotoxin Res 14(1):35–40
Sharman M, Gilbert J, Chelkowski J (1991) A survey of the occurrence of the mycotoxin moniliformin in cereal samples from sources worldwide. Food Addit Contamin 8(4):459–466
Kriek N, Marasas W, Steyn P, van Rensburg S, Steyn M (1977) Toxicity of a moniliformin-producing strain of Fusarium moniliforme var. subglutinans isolated from maize. Food Cosmet Toxicol 15(6):579–587
Burmeister HR, Ciegler A, Vesonder RF (1979) Moniliformin, a metabolite of Fusarium moniliforme NRRL 6322: purification and toxicity. Appl Environ Microbiol 37(1):11–13
Jonsson M, Jestoi M, Nathanail AV, Kokkonen U, Anttila M, Koivisto P, Karhunen P, Peltonen K (2013) Application of OECD guideline 423 in assessing the acute oral toxicity of moniliformin. Food Chem Toxicol 53:27–32
Jonsson M, Atosuo J, Jestoi M, Nathanail AV, Kokkonen U, Anttila M, Koivisto P, Lilius E, Peltonen K (2015) Repeated dose 28-day oral toxicity study of moniliformin in rats. Toxicol Lett 233(1):38–44
Bellus D, Fischer H, Greuter H, Martin P (1978) Synthesen von Moniliformin, einem Mycotoxin mit Cyclobutendion-Struktur. Helv Chim Acta 61(5):1784–1813
Fétizon M, Hanna I (1990) 2,3-Dihydro-1,4-dioxin in organic chemistry. Part X. 1 A new synthesis of 3-hydroxy-3-cyclobutene-1,2-dione (semisquaric acid). Synthesis 1990:583–584
Lohrey L, Murata T, Uemura D, Humpf H (2011) Synthesis of isotopically labeled Fusarium mycotoxin 13C2-moniliformin [1-hydroxycyclobut-1-ene-3,4-dione]. Synlett 2011(15):2242–2244
Von Bargen KW, Lohrey L, Cramer B, Humpf H (2012) Analysis of the Fusarium mycotoxin moniliformin in cereal samples using 13C2-moniliformin and high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 60(14):3586–3591
Jestoi M, Rokka M, Rizzo A, Peltonen KM (2003) Moniliformin in finnish grains: analysis with LC-MS/MS. Asp Appl Biol 68:211–216
Jin P, Han Z, Cai Z, Wu Y, Ren Y (2010) Simultaneous determination of 10 mycotoxins in grain by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry using 13C15-deoxynivalenol as internal standard. Food Addit Contamin Part A 27(12):1701–1713
Sørensen JL, Nielsen KF, Thrane U (2007) Analysis of moniliformin in maize plants using hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 55(24):9764–9768
Scarpino V, Blandino M, Negre M, Reyneri A, Vanara F (2013) Moniliformin analysis in maize samples from north-west Italy using multifunctional clean-up columns and the LC-MS/MS detection method. Food Addit Contamin Part A 30(5):876–884
Sewram V, Nieuwoudt TW, Marasas WFO, Shephard GS, Ritieni A (1999) Determination of the mycotoxin moniliformin in cultures of Fusarium subglutinans and in naturally contaminated maize by high-performance liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 848(1–2):185–191
Thrane U (1988) Screening for fusarin C production by European isolates of Fusarium species. Mycotoxin Res 4(1):2–10
Farber JM, Sanders GW (1986) Production of fusarin C by Fusarium spp. J Agric Food Chem 34(6):963–966
Wiebe LA, Bjeldanes LF (1981) Fusarin C, a mutagen from Fusarium moniliforme grown on corn. J Food Sci 46(5):1424–1426
Gelderblom WCA, Thiel PG, van der Merwe KJ, Marasas WFO, Spies HSC (1983) A mutagen produced by Fusarium moniliforme. Toxicon 21(4):467–473
Gelderblom WCA, Thiel PG, Marasas WFO, van der Merwe KJ (1984) Natural occurrence of fusarin C, a mutagen produced by Fusarium moniliforme, in corn. J Agric Food Chem 32(5):1064–1067
Thiel PG, Gelderblom WCA, Marasas WFO, Nelson PE, Wilson TM (1986) Natural occurrence of moniliformin and fusarin C in corn screenings known to be hepatocarcinogenic in rats. J Agric Food Chem 34(5):773–775
Kleigrewe K, Söhnel A, Humpf H (2011) A new high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method based on dispersive solid phase extraction for the determination of the mycotoxin fusarin C in corn ears and processed corn samples. J Agric Food Chem 59(19):10470–10476
Kleigrewe K, Niehaus E, Wiemann P, Tudzynski B, Humpf H (2012) New approach via gene knockout and single-step chemical reaction for the synthesis of isotopically labeled fusarin C as an internal standard for the analysis of this Fusarium mycotoxin in food and feed samples. J Agric Food Chem 60(34):8350–8355
Logrieco A, Rizzo A, Ferracane R, Ritieni A (2002) Occurrence of beauvericin and enniatins in wheat affected by Fusarium avenaceum head blight. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(1):82–85
Morrison E, Kosiak B, Ritieni A, Aastveit AH, Uhlig S, Bernhoft A (2002) Mycotoxin production by Fusarium avenaceum strains isolated from Norwegian grain and the cytotoxicity of rice culture extracts to porcine kidney epithelial cells. J Agric Food Chem 50(10):3070–3075
Thrane U, Adler A, Clasen P, Galvano F, Langseth W, Lew H, Logrieco A, Nielsen KF, Ritieni A (2004) Diversity in metabolite production by Fusarium langsethiae, Fusarium poae, and Fusarium sporotrichioides. Int J Food Microbiol 95(3):257–266
Benford D, Ceccatelli S, Cottrill B, Dinovi M, Dogliotti E, Edler L, Farmer P, Furst P, Hoogenboom L, Knutsen HK, Lundebye A, Metzler M, Nebbia CS, O'Keeffe M, Rietjens I, Schrenk D, Silano V, van Loveren H, Vleminckx C, Wester P (2014) Scientific opinion on the risks to human and animal health related to the presence of beauvericin and enniatins in food and feed. EFSA J 12(8):3802
Sørensen JL, Nielsen KF, Rasmussen PH, Thrane U (2008) Development of a LC-MS/MS method for the analysis of enniatins and beauvericin in whole fresh and ensiled maize. J Agric Food Chem 56(21):10439–10443
Uhlig S, Ivanova L (2004) Determination of beauvericin and four other enniatins in grain by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, A 1050(2):173–178
Sewram V, Nieuwoudt TW, Marasas WFO, Shephard GS, Ritieni A (1999) Determination of the Fusarium mycotoxins, fusaproliferin and beauvericin by high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, A 858(2):175–185
Jestoi M, Rokka M, Järvenpää E, Peltonen K (2009) Determination of Fusarium mycotoxins beauvericin and enniatins (A, A1, B, B1) in eggs of laying hens using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). Food Chem 115(3):1120–1127
Bräse S, Encinas A, Keck J, Nising CF (2009) Chemistry and biology of mycotoxins and related fungal metabolites. Chem Rev 109(9):3903–3990
Hu L, Rychlik M (2012) Biosynthesis of 15N3-labeled enniatins and beauvericin and their application to stable isotope dilution assays. J Agric Food Chem 60(29):7129–7136
Bottalico A, Logrieco A (1998) Toxigenic Alternaria species of economic importance. In: Kaushal K, Bhatnagar D (eds) Mycotoxins in agriculture and food safety. Dekker, New York, pp 65–108
Fehr M, Pahlke G, Fritz J, Christensen MO, Boege F, Altemöller M, Podlech J, Marko D (2009) Alternariol acts as a topoisomerase poison, preferentially affecting the IIα isoform. Mol Nutr Food Res 53(4):441–451
Brugger E, Wagner J, Schumacher DM, Koch K, Podlech J, Metzler M, Lehmann L (2006) Mutagenicity of the mycotoxin alternariol in cultured mammalian cells. Toxicol Lett 164(3):221–230
Asam S, Konitzer K, Schieberle P, Rychlik M (2009) Stable isotope dilution assays of alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in beverages. J Agric Food Chem 57(12):5152–5160
Asam S, Konitzer K, Rychlik M (2011) Precise determination of the Alternaria mycotoxins alternariol and alternariol monomethyl ether in cereal, fruit and vegetable products using stable isotope dilution assays. Mycotoxin Res 27(1):23–28
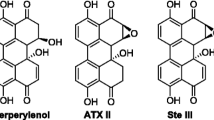
Liu Y, Rychlik M (2015) Biosynthesis of seven carbon-13 labeled Alternaria toxins including altertoxins, alternariol, and alternariol methyl ether, and their application to a multiple stable isotope dilution assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(5):1357–1369
Pero RW, Posner H, Blois M, Harvan D, Spalding JW (1973) Toxicity of metabolites produced by the Alternaria. Environ Health Perspect 4:87–94
Asam S, Liu Y, Konitzer K, Rychlik M (2011) Development of a stable isotope dilution assay for tenuazonic acid. J Agric Food Chem 59(7):2980–2987
Siegel D, Merkel S, Bremser W, Koch M, Nehls I (2010) Degradation kinetics of the Alternaria mycotoxin tenuazonic acid in aqueous solutions. Anal Bioanal Chem 397(2):453–462
Siegel D, Rasenko T, Koch M, Nehls I (2009) Determination of the Alternaria mycotoxin tenuazonic acid in cereals by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization ion-trap multistage mass spectrometry after derivatization with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. J Chromatogr, A 1216(21):4582–4588
Siegel D, Merkel S, Koch M, Nehls I (2010) Quantification of the Alternaria mycotoxin tenuazonic acid in beer. Food Chem 120(3):902–906
Asam S, Lichtenegger M, Liu Y, Rychlik M (2012) Content of the Alternaria mycotoxin tenuazonic acid in food commodities determined by a stable isotope dilution assay. Mycotoxin Res 28(1):9–15
Asam S, Rychlik M (2013) Potential health hazards due to the occurrence of the mycotoxin tenuazonic acid in infant food. Eur Food Res Technol 236(3):491–497
Kroes R, Renwick AG, Cheeseman M, Kleiner J, Mangelsdorf I, Piersma A, Schilter B, Schlatter J, van Schothorst F, Vos JG, Wurtzen G (2004) Structure-based thresholds of toxicological concern (TTC): guidance for application to substances present at low levels in the diet. Food Chem Toxicol 42(1):65–83
Alexander J, Benford D, Boobis A, Ceccatelli S, Cottrill B, Cravedi J, Di Domenico A, Doerge D, Dogliotti E, Edler L, Farmer P, Filipic M, Fink-Gremmels J, Furst P, Guerin T, Knutsen HK, Machala M, Mutti A, Schlatter J, Rose M, van Leeuwen R, Metzler M, Rauscher-Gabernig E, van Peteghem C, Civera AV, Cioacata G, Curtui V, Eskola M, Heppner C (2011) Scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of Alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J 9(10):2407
Asam S, Lichtenegger M, Muzik K, Liu Y, Frank O, Hofmann T, Rychlik M (2013) Development of analytical methods for the determination of tenuazonic acid analogues in food commodities. J Chromatogr, A 1289:27–36
Asam S, Habler K, Rychlik M (2013) Determination of tenuazonic acid in human urine by means of a stable isotope dilution assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(12):4149–4158
Van de Perre E, Deschuyffeleer N, Jacxsens L, Vekeman F, Van der Hauwaert W, Asam S, Rychlik M, Devlieghere F, De Meulenaer B (2014) Screening of moulds and mycotoxins in tomatoes, bell peppers, onions, soft red fruits and derived tomato products. Food Control 37:165–170
Walravens J, Mikula H, Rychlik M, Asam S, Ediage EN, Di Mavungu JD, Van Landschoot A, Vanhaecke L, De Saeger S (2014) Development and validation of an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric method for the simultaneous determination of free and conjugated Alternaria toxins in cereal-based foodstuffs. J Chromatogr, A 1372:91–101
Lohrey L, Marschik S, Cramer B, Humpf H (2013) Large-scale synthesis of isotopically labeled 13C2-tenuazonic acid and development of a rapid HPLC-MS/MS method for the analysis of tenuazonic acid in tomato and pepper products. J Agric Food Chem 61(1):114–120
Stack ME, Prival MJ (1986) Mutagenicity of the Alternaria metabolites altertoxins I, II, and III. Appl Environ Microbiol 52(4):718–722
Fleck SC, Burkhardt B, Pfeiffer E, Metzler M (2012) Alternaria toxins: altertoxin II is a much stronger mutagen and DNA strand breaking mycotoxin than alternariol and its methyl ether in cultured mammalian cells. Toxicol Lett 214(1):27–32
Templeton GE, Grable CI, Fulton ND, Bollenbacher K (1967) Factors affecting the amount and pattern of chlorosis caused by a metabolite of Alternaria tenuis. Phytopathology 57(5):516–518
Kono Y, Gardner JM, Takeuchi S (1986) Nonselective phytotoxins simultaneously produced with host-selective ACTG-toxins by a pathotype of Alternaria citri causing brown spot disease of mandarins. Agric Biol Chem 50(9):2401–2403
Arntzen CJ (1972) Inhibition of photophosphorylation by tentoxin, a cyclic tetrapeptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 283(3):539–542
Liu Y, Rychlik M (2013) Development of a stable isotope dilution LC–MS/MS method for the Alternaria toxins tentoxin, dihydrotentoxin, and isotentoxin. J Agric Food Chem 61(12):2970–2978
Lindenmeier M, Schieberle P, Rychlik M (2004) Quantitation of ochratoxin A in foods by a stable isotope dilution assay using high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, A 1023:57–66
Noba S, Uyama A, Mochizuki N (2009) Determination of ochratoxin A in ready-to-drink coffee by immunoaffinity cleanup and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 57(14):6036–6040
Han Z, Zhao Z, Shi J, Liao Y, Zhao Z, Zhang D, Wu Y, De Saeger S, Wu A (2013) Combinatorial approach of LC–MS/MS and LC–TOF-MS for uncovering in vivo kinetics and biotransformation of ochratoxin A in rat. J Chromatogr, B 925:46–53
Cramer B, Königs M, Humpf HU (2013) Identification and in vitro cytotoxicity of Ochratoxin A degradation products formed during coffee roasting. J Agric Food Chem 56(14):5673–5681
Korn M, Frank O, Hofmann T, Rychlik M (2011) Development of stable isotope dilution assays for ochratoxin A in blood samples. Anal Biochem 419:88–94
Bouisseau A, Roland A, Reillon F, Schneider R, Cavelier F (2013) First synthesis of a stable isotope of Ochratoxin A metabolite for a reliable detoxification monitoring. Org Lett 15(15):3888–3890
Roland A, Bros P, Bouisseau A, Cavelier F, Schneider R (2014) Analysis of ochratoxin A in grapes, musts and wines by LC–MS/MS: First comparison of stable isotope dilution assay and diastereomeric dilution assay methods. Anal Chim Acta 818(1):39–45
Gabriele B, Attya M, Fazio A, Di Donna L, Plastina P, Sindona G (2009) A new and expedient total synthesis of ochratoxin A and d5-ochratoxin A. Synthesis 2009(11):1815–1820
Lenz CA, Rychlik M (2013) Efficient synthesis of (R)-ochratoxin alpha, the key precursor to the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Tetrahedron Lett 54(8):883–886
Pereira VL, Fernandes JO, Cunha SC (2014) Mycotoxins in cereals and related foodstuffs: a review on occurrence and recent methods of analysis. Trends Food Sci Technol 36(2):96–136
Herebian D, Zühlke S, Lamshöft M, Spiteller M (2009) Multi-mycotoxin analysis in complex biological matrices using LC-ESI/MS: experimental study using triple stage quadrupole and LTQ-Orbitrap. J Sep Sci 32(7):939–948
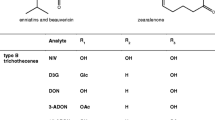
Gottschalk C, Barthel J, Engelhardt G, Bauer J, Meyer K (2009) Simultaneous determination of type A, B and D trichothecenes and their occurrence in cereals and cereal products. Food Addit Contamin Part A 26(9):1273–1289
Vaclavik L, Zachariasova M, Hrbek V, Hajslova J (2010) Analysis of multiple mycotoxins in cereals under ambient conditions using direct analysis in real time (DART) ionization coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 82(5):1950–1957
Zachariasova M, Lacina O, Malachova A, Kostelanska M, Poustka J, Godula M, Hajslova J (2010) Novel approaches in analysis of Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals employing ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 662(1):51–61
Tam J, Pantazopoulos P, Scott P, Moisey J, Dabeka R, Richard I (2011) Application of isotope dilution mass spectrometry: determination of ochratoxin A in the Canadian Total Diet Study. Food Addit Contamin Part A 28(6):754–761
Pettersson H, Brown C, Hauk J, Hoth S, Meyer J, Wessels D (2011) Survey of T-2 and HT-2 toxins by LC–MS/MS in oats and oat products from European oat mills in 2005–2009. Food Addit Contamin Part B 4(2):110–115
Juan C, Ritieni A, Mañes J (2012) Determination of trichothecenes and zearalenones in grain cereal, flour and bread by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 134(4):2389–2397
Varga E, Glauner T, Koeppen R, Mayer K, Sulyok M, Schuhmacher R, Krska R, Berthiller F (2012) Stable isotope dilution assay for the accurate determination of mycotoxins in maize by UHPLC-MS/MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(9):2675–2686
Barthel J, Gottschalk C, Rapp M, Berger M, Bauer J, Meyer K (2012) Occurrence of type A, B and D trichothecenes in barley and barley products from the Bavarian market. Mycotoxin Res 28(2):97–106
Köppen R, Bremser W, Rasenko T, Koch M (2013) Development and certification of a reference material for Fusarium mycotoxins in wheat flour. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(14):4755–4763
Rychlik M, Humpf H, Marko D, Dänicke S, Mally A, Berthiller F, Klaffke H, Lorenz N (2014) Proposal of a comprehensive definition of modified and other forms of mycotoxins including “masked” mycotoxins. Mycotoxin Res 30(4):197–205
Kluger B, Bueschl C, Lemmens M, Berthiller F, Häubl G, Jaunecker G, Adam G, Krska R, Schuhmacher R (2013) Stable isotopic labelling-assisted untargeted metabolic profiling reveals novel conjugates of the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol in wheat. Anal Bioanal Chem 405(15):5031–5036
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (2011) Safety evaluation of certain contaminants in food / prepared by the seventy-second meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). WHO food additives series: 63
European Food Safety Authority (2014) Evaluation of the increase of risk for public health related to a possible temporary derogation from the maximum level of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone and fumonisins for maize and maize products. EFSA J 12(5):3699–3730
Liao C, Wong JW, Zhang K, Yang P, Wittenberg JB, Trucksess MW, Hayward DG, Lee NS, Chang JS (2014) Multi-mycotoxin analysis of finished grain and nut products using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography and positive electrospray ionization–quadrupole orbital ion trap high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf505049a
Mata AT, Ferreira JP, Oliveira BR, Batoreu MC, Barreto Crespo MT, Pereira VJ, Bronze MR (2015) Bottled water: analysis of mycotoxins by LC-MS/MS. Food Chem 176:455–464
Kirincic S, Skrjanc B, Kos N, Kozolc B, Pirnat N, Tavcar-Kalcher G (2015) Mycotoxins in cereals and cereal products in Slovenia - official control of foods in the years 2008-2012. Food Control 50:157–165
Brezina U, Rempe I, Kersten S, Valenta H, Humpf H, Daenicke S (2014) Diagnosis of intoxications of piglets fed with Fusarium toxin-contaminated maize by the analysis of mycotoxin residues in serum, liquor and urine with LC-MS/MS. Arch Anim Nutr 68(6):425–447
Zhang K, Wong JW, Jia Z, Vaclavikova M, Trucksess MW, Begley TH (2014) Screening multimycotoxins in food-grade gums by stable isotope dilution and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. J AOAC Int 97(3):889–895
Zhang K, Wong JW, Krynitsky AJ, Trucksess MW (2014) Determining mycotoxins in baby foods and animal feeds using stable isotope dilution and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 62(36):8935–8943
Zhao Z, Rao Q, Song S, Liu N, Han Z, Hou J, Wu A (2014) Simultaneous determination of major type B trichothecenes and deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in animal feed and raw materials using improved DSPE combined with LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 963:75–82
Pietruszka K, Sell B, Burek O, Wisniewska-Dmytrow H (2013) Simultaneous determination of multi - component mycotoxin in feeds by liquid chromatography - tandem mass spectrometry. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 57(4):567–572
Han Z, Feng Z, Shi W, Zhao Z, Wu Y, Wu A (2014) A quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe sample pretreatment and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of 33 mycotoxins in Lentinula edodes. J Sep Sci 37(15):1957–1966
Desmarchelier A, Tessiot S, Bessaire T, Racault L, Fiorese E, Urbani A, Chan W, Cheng P, Mottier P (2014) Combining the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe approach and clean-up by immunoaffinity column for the analysis of 15 mycotoxins by isotope dilution liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr, A 1337:75–84
Blajet-Kosicka A, Twaruzek M, Kosicki R, Sibiorowska E, Grajewski J (2014) Co-occurrence and evaluation of mycotoxins in organic and conventional rye grain and products. Food Control 38:61–66
Abia WA, Warth B, Sulyok M, Krska R, Tchana A, Njobeh PB, Turner PC, Kouanfack C, Eyongetah M, Dutton M, Moundipa PF (2013) Bio-monitoring of mycotoxin exposure in Cameroon using a urinary multi-biomarker approach. Food Chem Toxicol 62:927–934
Gratz SW, Duncan G, Richardson AJ (2013) The human fecal microbiota metabolizes deoxynivalenol and deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside and may be responsible for urinary deepoxy-deoxynivalenol. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(6):1821–1825
Osselaere A, Devreese M, Goossens J, Vandenbroucke V, De Baere S, De Backer P, Croubels S (2013) Toxicokinetic study and absolute oral bioavailability of deoxynivalenol, T-2 toxin and zearalenone in broiler chickens. Food Chem Toxicol 51:350–355
Al-Taher F, Banaszewski K, Jackson L, Zweigenbaum J, Ryu D, Cappozzo J (2013) Rapid method for the determination of multiple mycotoxins in wines and beers by LC-MS/MS using a stable isotope dilution assay. J Agric Food Chem 61(10):2378–2384
Zhang K, Wong JW, Hayward DG, Vaclavikova M, Liao C, Trucksess MW (2013) Determination of mycotoxins in milk-based products and infant formula using stable isotope dilution assay and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 61(26):6265–6273
De Baere S, Goossens J, Osselaere A, Devreese M, Vandenbroucke V, De Backer P, Croubels S (2011) Quantitative determination of T-2 toxin, HT-2 toxin, deoxynivalenol and deepoxy-deoxynivalenol in animal body fluids using LC-MS/MS detection. J Chromatogr, B: Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(24):2403–2415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asam, S., Rychlik, M. Recent developments in stable isotope dilution assays in mycotoxin analysis with special regard to Alternaria toxins. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 7563–7577 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8904-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8904-y