Abstract
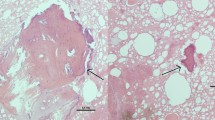
The strontium isotope ratio (87Sr/86Sr) in beef, derived from 206 European cattle, has been measured. These cattle were located in 12 different European regions within France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Spain and the UK. As animal protein is known to be a difficult material on which to conduct Sr isotope analysis, several investigations were undertaken to develop and improve the sample preparation procedure. For example, Sr isotope analysis was performed directly on freeze-dried meat and defatted dry mass from the same samples. It was found that enormous differences—sometimes exceeding the measurement uncertainty—could occur between the fractions and also within one sample even if treated in the same manner. These variations cannot be definitely allocated to one cause but are most likely due to inhomogeneities caused by physiological and biochemical processes in the animals as post mortem contamination during analytical processing could be excluded. For further Sr isotope measurements in meat, careful data handling is recommended, and for the authentic beef samples within this project, it was decided to use only freeze-dried material. It can be demonstrated, however, that Sr isotope measurements in beef proteins are a valuable tool for authentication of geographic origin. Although partly overlapping, some of the European sampling sites could be discriminated even by only using 87Sr/86Sr.

Box plot diagram displaying 87Sr/86Sr in authentic beef samples ordered by Trace sampling sites




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Council Regulation 2081/92, Official Journal L 208, 24/07/1992 P. 0001-0008
Council Regulation No. 510/2006, Official journal of the European Union, L93/12-L93/25
Trace project-FP6. Available at http://www.trace.eu.org/
Goitom Asfaha D, Quetel C, Thomas F, Horacek M, Wimmer B, Heiss G, Dekant C, Deters-Itzelsberger P, Hoelzl S, Rummel S, Brach-Papa C, Van Bocxstaele M, Jamin E, Baxter M, Heinrich K, Kelly S, Bertoldi D, Bontempo L, Camin F, Larcher R, Perini M, Rossmann A, Schellenberg A, Schlicht C, Froeschl H, Hoogewerff J, Ueckermann H (2011) Combining isotopic signatures of n(87Sr)/n(86Sr) and light stable elements (C, N, O, S) with multi-elemental profiling for the authentication of provenance of European cereal samples. J Cereal Sci 53:170–177
Schellenberg A, Chmielus S, Schlicht C, Camin F, Perini M, Bontempo L, Heinrich K, Kelly S, Rossmann A, Thomas F, Jamin E, Horacek M (2010) Multielement stable isotope ratios (H, C, N, S) of honey from different European regions. Food Chem 121:770–777
Franke BM, Koslitz S, Micaux F, Piantini U, Maury V, Pfammatter E, Wunderli S, Gremaud G, Bosset J-O, Hadorn R, Kreuzer M (2008) Tracing the geographic origin of poultry meat and dried beef with oxygen and strontium isotope ratios. Eur Food Res Technol 226:761–769
Regulation (EC) No 1760/2000 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 July 2000 establishing a system for the identification and registration of bovine animals and regarding the labelling of beef and beef products and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 820/97 Official Journal L 204, 11/08/2000 P. 0001-0010. Available at (http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32000R1760:EN:HTML)
Commission Regulation (EC) No 1825/2000 of 25 August 2000 laying down detailed rules for the application of Regulation (EC) No 1760/2000 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the labelling of beef and beef products Official Journal L 216, 26/08/2000 P. 0008-0012. Available at (http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:32000R1825:EN:HTML)
Schmidt H-L (1986) Food quality control and studies on human nutrition by mass spectrometric and nuclear magnetic resonance isotope ratio determination. Fresen J Anal Chem 324(7):760–766
Nollet LM, Toldra F (2009) Handbook of muscle foods analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Dennis MJ (1998) Recent developments in food authentication. Analyst 123:151R–156R
Rossmann A (2001) Determination of stable isotope ratios in food analysis. Food Rev Int 17(3):347–381
Kelly S, Heaton K, Hoogewerff J (2005) Tracing the geographical origin of food: the application of multi-element and multi-isotope analysis. Trends Food Sci 16:555–567
Luykx DMAM, van Ruth SM (2008) An overview of analytical methods for determining the geographical origin of food products. Food Chem 107:897–911
Piasentier E, Valusso R, Camin F, Versini G (2003) Stable isotope ratio analysis for authentication of lamb meat. Meat Sci 64:239–247
Franke BM, Gremaud G, Hadorn R, Kreuzer M (2005) Geographic origin of meat—elements of an analytical approach to its authentication. Eur Food Res Technol 221:493–503
Camin F, Bontempo L, Heinrich K, Horacek M, Kelly SD, Schlicht C, Thomas F, Monahan FJ, Hoogewerff J, Rossmann A (2007) Multi-element (H, C, N, S) stable isotope characteristics of lamb meat from different European regions. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:309–320
Rossmann A, Schlicht C (2007) Stabilisotopenanalytik zur Herkunftsbestimmung tierischer Produkte. Fleischwirtschaft 8:104–109
Heaton K, Kelly SD, Hoogewerff J, Woolfe M (2008) Verifying the geographical origin of beef: the application of multi-element isotope and trace element analysis. Food Chem 107:506–515
Schmidt H-L, Rossmann A, Rummel S, Tanz N (2009) Stable isotope analysis for meat authenticity and origin check. In: Nollet LM, Toldra F (eds.) Handbook of muscle foods analysis, chapter 39. CRC Press, Boca Raton. pp 767–787
Faure G, Mensing T (2005) Isotopes—principles and applications, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Capo RC, Stewart BW, Chadwick OA (1998) Strontium isotopes as tracers of ecosystem processes: theory and methods. Geoderma 82:197–225
Horn P, Schaaf P, Holbach B, Hölzl S, Eschnauer H (1993) 87Sr/86Sr from rock and soil into vine and wine. Zeitschrift für Lebensmitteluntersuchung und—Forschung 196:407–409
Horn P, Hölzl S, Todt W, Matthies D (1998) Isotope abundance ratios of Sr in wine provenance determinations in a tree-root activity study, and of Pb in a pollution study on tree rings. Isot Environ Heal Stud 34:31–42
Rossmann A, Haberhauer G, Hölzl S, Horn P, Pichlmayer F, Voerkelius S (2000) The potential of multielement stable isotope analysis for regional assignment of butter. Eur Food Res Technol 211:32–40
Pillonel L, Badertscher R, Froidevaux P, Haberhauer G, Hölzl S, Horn P, Jakob A, Pfammatter E, Piantini U, Rossmann A, Tabacchi I, Bosset JO (2003) Stable isotope ratios, major, trace and radioactive elements in emmental cheeses of different origins. Lebensm Wiss Technol 36:615–623
Montgomery J, Evans JA, Wildman G (2006) 87Sr/86Sr isotope composition of bottled British mineral waters for environmental and forensic purpose. Appl Geochem 21(10):1626–1634
Voerkelius S, Lorenz GD, Rummel S, Quétel CR, Heiss G, Baxter M, Brach-Papa C, Deters-Itzelsberger P, Hoelzl S, Hoogewerff J, Ponzevera E, Bocxstaele MV, Ueckermann H (2010) Strontium isotopic signatures of natural mineral waters, the reference to a simple geological map and its potential for authentication of food. Food Chem 118:933–940
Swoboda S, Brunner M, Boulyga SF, Galler P, Horacek M, Prohaska T (2008) Identification of Marchfeld asparagus using Sr isotope ratio measurements by MC-ICP-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 390:487–494
Rummel S, Hölzl S, Horn P, Rossmann A, Schlicht C (2010) The combination of stable isotope abundance ratios of H, C, N and S with 87Sr/86Sr for geographical origin assignment of orange juices. Food Chem 118:890–900
Bontempo L, Larcher R, Camin F, Hölzl S, Rossmann A, Horn P, Nicolini G (2010) Elemental and isotopic characterisation of typical Italian alpine cheeses. Int Dairy J 21:441–446
Horwitz EP, Chiarizia R, Dietz ML (1992) A novel strontium-selective extraction chromatographic resin. Solvent Extr Ion Exch 10:313–336
Pin C, Bassin C (1992) Evaluation of a strontium-specific extraction chromatographic method for isotopic analysis in geological materials. Anal Chim Acta 269:249–255
Müller-Sohnius D (2007) 87Sr/86Sr for isotope standards of Eimer and Amend (E&A), modern seawater strontium (MSS), and the Standard Reference Material (SRM) 987: development of interlaboratory mean values, procedures of adjusting, and the comparability of results. Geologica Bavarica 110:5–62
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by the European Commission, under the FP6 Food Quality and Safety Priority, within the framework of the Integrated Project TRACE—006942—entitled ‘Tracing Food Commodities in Europe’. Additionally, we would like to thank the three reviewers for their helpful and constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rummel, S., Dekant, C.H., Hölzl, S. et al. Sr isotope measurements in beef—analytical challenge and first results. Anal Bioanal Chem 402, 2837–2848 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5759-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5759-3