Abstract
Objective
Recent data suggest that 5-HT7 receptors (5-HT7R) are involved in memory processes and, particularly, those related to novelty-induced arousal, even though this remains so far speculative and controversial. In order to assess the role of 5-HT7R in episodic-like memory, mice were administered 5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT, a 5-HT1A/1B/1D/7R agonist) and/or SB-269970 (a selective 5-HT7R antagonist) immediately after the acquisition session of the novel object recognition test.
Materials and methods
The object recognition test was performed in order to assess the effects of modulation of 5-HT7R during consolidation phase on episodic-like memory performances in mice. A protocol including 3 days of familiarisation to the apparatus has been realised in order to decrease the effect of novelty-induced arousal.
Results
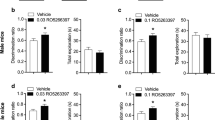
With a 2-h delay, SB-269970 (3 and 10 mg/kg, administered subcutaneously) impaired the discrimination of the novel object. With a 4-h delay, while control mice were not able to discriminate the novel object, mice treated with 5-CT (1 mg/kg) showed a significant discrimination. This promnesic effect with a long delay is effectively mediated by 5-HT7R activation since it was blocked by SB-269970 (10 mg/kg), but not by WAY-100135 (10 mg/kg) or by GR-127935 (10 mg/kg).
Conclusion
These data suggest that 5-HT7R tonically modulates cognitive processes involved in consolidation performances in object recognition. Therefore, 5-HT7R could be a promising target to treat memory dysfunctions (especially episodically related deficits) related to normal or pathological ageing.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriani W, Travaglini D, Lacivita E, Saso L, Leopoldo M, Laviola G (2012) Modulatory effects of two novel agonists for serotonin receptor 7 on emotion, motivation and circadian rhythm profiles in mice. Neuropharmacology 62:833–842
Ballaz SJ, Akil H, Watson SJ (2007a) The 5-HT7 receptor: role in novel object discrimination and relation to novelty-seeking behavior. Neuroscience 149:192–202
Ballaz SJ, Akil H, Watson SJ (2007b) Analysis of 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptor gene expression in rats showing differences in novelty-seeking behavior. Neuroscience 147:428–438
Bevins RA, Besheer J (2006) Object recognition in rats and mice: a one-trail non-matching-tosample learning task to study ‘recognition memory’. Nat Protoc 1:1306–1311
Boast C, Bartolomeo AC, Morris H, Moyer JA (1999) 5HT antagonists attenuate MK801-impaired radial arm maze performance in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 71:259–271
Bonaventure P, Nepomuceno D, Kwok A, Chai W, Langlois X, Hen R, Stark K, Carruthers N, Lovenberg TW (2002) Reconsideration of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)(7) receptor distribution using [(3)H]5-carboxamidotryptamine and [(3)H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetraline: analysis in brain of 5-HT(1A) knockout and 5-HT(1A/1B) double-knockout mice. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 302:240–248
Bosker FJ, Folgering JH, Gladkevich AV, Schmidt A, van der Hart MC, Sprouse J, den Boer JA, Westerink BH, Cremers TI (2009) Antagonism of 5-HT(1A) receptors uncovers an excitatory effect of SSRIs on 5-HT neuronal activity, an action probably mediated by 5-HT(7) receptors. J Neurochem 108:1126–1135
Bouet V, Freret T, Dutar P, Billard JM, Boulouard M (2011) Continuous enriched environment improves learning and memory in adult NMRI mice through theta burst-related-LTP independent mechanisms but is not efficient in advanced aged animals. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 132:240–248
Cifariello A, Pompili A, Gasbarri A (2008) 5-HT(7) receptors in the modulation of cognitive processes. Behavioural Brain Research 195:171–179
Cliffe IA, Brightwell CI, Fletcher A, Forster EA, Mansell HL, Reilly Y, Routledge C, White AC (1993) (S)-N-tert-butyl-3-(4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-phenylpropanamide [(S)-WAY-100135]: a selective antagonist at presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. J Med Chem 36:1509–1510
Da Silva C-AV, Dauphin F, Boulouard M (2011) Serotonin 5-HT6 receptor blockade reverses the age-related deficits of recognition memory and working memory in mice. Behavioural Brain Research 222:134–140
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59
Davidson C, Ho M, Price GW, Jones BJ, Stamford JA (1997) (+)-WAY 100135, a partial agonist, at native and recombinant 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Br J Pharmacol 121:737–742
Fernandez SM, Lewis MC, Pechenino AS, Harburger LL, Orr PT, Gresack JE, Schafe GE, Frick KM (2008) Estradiol-induced enhancement of object memory consolidation involves hippocampal extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation and membrane-bound estrogen receptors. The Journal of Neuroscience 28:8660–8667
Foong JP, Bornstein JC (2009) 5-HT antagonists NAN-190 and SB 269970 block alpha2-adrenoceptors in the guinea pig. Neuroreport 20:325–330
Forbes IT, Douglas S, Gribble AD, Ife RJ, Lightfoot AP, Garner AE, Riley GJ, Jeffrey P, Stevens AJ, Stean TO, Thomas DR (2002) SB-656104-A: a novel 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist with improved in vivo properties. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 12:3341–3344
Gasbarri A, Cifariello A, Pompili A, Meneses A (2008) Effect of 5-HT(7) antagonist SB-269970 in the modulation of working and reference memory in the rat. Behavioural Brain Research 195:164–170
Guscott MR, Egan E, Cook GP, Stanton JA, Beer MS, Rosahl TW, Hartmann S, Kulagowski J, McAllister G, Fone KC, Hutson PH (2003) The hypothermic effect of 5-CT in mice is mediated through the 5-HT7 receptor. Neuropharmacology 44:1031–1037
Gustafson EL, Durkin MM, Bard JA, Zgombick J, Branchek TA (1996) A receptor autoradiographic and in situ hybridization analysis of the distribution of the 5-ht7 receptor in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol 117:657–666
Hagan JJ, Price GW, Jeffrey P, Deeks NJ, Stean T, Piper D, Smith MI, Upton N, Medhurst AD, Middlemiss DN, Riley GJ, Lovell PJ, Bromidge SM, Thomas DR (2000) Characterization of SB-269970-A, a selective 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 130:539–548
Hagiwara H, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Kunitachi S, Shirayama Y, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2008) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of the antipsychotic drug perospirone: role of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18:448–454
Hedlund PB, Sutcliffe JG (2004) Functional, molecular and pharmacological advances in 5-HT7 receptor research. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:481–486
Hedlund PB, Huitron-Resendiz S, Henriksen SJ, Sutcliffe JG (2005) 5-HT7 receptor inhibition and inactivation induce antidepressantlike behavior and sleep pattern. Biol Psychiatry 58:831–837
Hirst WD, Andree TH, Aschmies S, Childers WE, Comery TA, Dawson LA, Day M, Feingold IB, Grauer SM, Harrison BL, Hughes ZA, Kao J, Kelly MG, van der Lee H, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Saab AL, Smith DL, Sullivan K, Rizzo SJ, Tio C, Zhang MY, Schechter LE (2008) Correlating efficacy in rodent cognition models with in vivo 5-hydroxytryptamine1a receptor occupancy by a novel antagonist, (R)-N-(2-methyl-(4-indolyl-1-piperazinyl)ethyl)-N-(2-pyridinyl)-cyclohexane carboxamide (WAY-101405). The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 325:134–145
Horiguchi M, Huang M, Meltzer HY (2011) The role of 5-hydroxytryptamine 7 receptors in the phencyclidine-induced novel object recognition deficit in rats. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 338:605–614
Hoyer D, Hannon JP, Martin GR (2002) Molecular, pharmacological and functional diversity of 5-HT receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:533–554
Jones BJ, Blackburn TP (2002) The medical benefit of 5-HT research. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:555–568
Leopoldo M, Lacivita E, Berardi F, Perrone R, Hedlund PB (2011) Serotonin 5-HT7 receptor agents: structure–activity relationships and potential therapeutic applications in central nervous system disorders. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 129:120–148
Liao Y, Bottcher H, Harting J, Greiner H, van Amsterdam C, Cremers T, Sundell S, Marz J, Rautenberg W, Wikstrom H (2000) New selective and potent 5-HT(1B/1D) antagonists: chemistry and pharmacological evaluation of N-piperazinylphenyl biphenylcarboxamides and biphenylsulfonamides. J Med Chem 43:517–525
Lovell PJ, Bromidge SM, Dabbs S, Duckworth DM, Forbes IT, Jennings AJ, King FD, Middlemiss DN, Rahman SK, Saunders DV, Collin LL, Hagan JJ, Riley GJ, Thomas DR (2000) A novel, potent, and selective 5-HT(7) antagonist: (R)-3-(2-(2-(4-methylpiperidin-1-yl)ethyl)pyrrolidine-1-sulfonyl)phenol (SB-269970). J Med Chem 43:342–345
Manuel-Apolinar L, Meneses A (2004) 8-OH-DPAT facilitated memory consolidation and increased hippocampal and cortical cAMP production. Behavioural Brain Research 148:179–184
Matsushita M, Egashira N, Harada S, Okuno R, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Nishimura R, Fujiwara M (2005) Perospirone, a novel antipsychotic drug, inhibits marble-burying behavior via 5-HT1A receptor in mice: implications for obsessive–compulsive disorder. J Pharmacol Sci 99:154–159
Matthys A, Haegeman G, Van Craenenbroeck K, Vanhoenacker P (2011) Role of the 5-HT7 receptor in the central nervous system: from current status to future perspectives. Mol Neurobiol 43:228–253
McLean SL, Woolley ML, Thomas D, Neill JC (2009) Role of 5-HT receptor mechanisms in sub-chronic PCP-induced reversal learning deficits in the rat. Psychopharmacology 206:403–414
Meneses A (2003) A pharmacological analysis of an associative learning task: 5-HT(1) to 5-HT(7) receptor subtypes function on a Pavlovian/instrumental autoshaped memory. Learning & Memory 10:363–372
Meneses A (2004) Effects of the 5-HT7 receptor antagonists SB-269970 and DR 4004 in autoshaping Pavlovian/instrumental learning task. Behavioural Brain Research 155:275–282
Meneses A, Terron JA (2001) Role of 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(7) receptors in the facilitatory response induced by 8-OH-DPAT on learning consolidation. Behavioural Brain Research 121:21–28
Meneses A, Terron JA, Hong E (1997) Effects of the 5-HT receptor antagonists GR127935 (5-HT1B/1D) and MDL100907 (5-HT2A) in the consolidation of learning. Behavioural Brain Research 89:217–223
Meneses A, Perez-Garcia G, Liy-Salmeron G, Flores-Galvez D, Castillo C, Castillo E (2008) The effects of the 5-HT(6) receptor agonist EMD and the 5-HT(7) receptor agonist AS19 on memory formation. Behavioural Brain Research 195:112–119
Mengod G, Vilaro MT, Raurich A, Lopez-Gimenez JF, Cortes R, Palacios JM (1996) 5-HT receptors in mammalian brain: receptor autoradiography and in situ hybridization studies of new ligands and newly identified receptors. Histochem J 28:747–758
Nagai T, Murai R, Matsui K, Kamei H, Noda Y, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (2009) Aripiprazole ameliorates phencyclidine-induced impairment of recognition memory through dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology 202:315–328
Neumaier JF, Sexton TJ, Yracheta J, Diaz AM, Brownfield M (2001) Localization of 5-HT(7) receptors in rat brain by immunocytochemistry, in situ hybridization, and agonist stimulated cFos expression. J Chem Neuroanat 21:63–73
Okuda S, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL (2004) Glucocorticoid effects on object recognition memory require training-associated emotional arousal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:853–858
Perez-Garcia GS, Meneses A (2005) Effects of the potential 5-HT7 receptor agonist AS 19 in an autoshaping learning task. Behavioural Brain Research 163:136–140
Perez-Garcia G, Meneses A (2009) Memory time-course: mRNA 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors. Behavioural Brain Research 202:102–113
Pitsikas N, Rigamonti AE, Cella SG, Muller EE (2003) The 5-HT 1A receptor antagonist WAY 100635 improves rats performance in different models of amnesia evaluated by the object recognition task. Brain Research 983:215–222
Plassat JL, Amlaiky N, Hen R (1993) Molecular cloning of a mammalian serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol 44:229–236
Przegalinski E, Golda A, Filip M (2008) Effects of serotonin (5-HT)(1B) receptor ligands on cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Pharmacological Reports 60:798–810
Roberts AJ, Krucker T, Levy CL, Slanina KA, Sutcliffe JG, Hedlund PB (2004) Mice lacking 5-HT receptors show specific impairments in contextual learning. The European Journal of Neuroscience 19:1913–1922
Roth BL, Craigo SC, Choudhary MS, Uluer A, Monsma FJ Jr, Shen Y, Meltzer HY, Sibley DR (1994) Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotic agents to 5-hydroxytryptamine-6 and 5-hydroxytryptamine-7 receptors. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 268:1403–1410
Ruat M, Traiffort E, Leurs R, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Arrang JM, Schwartz JC (1993) Molecular cloning, characterization, and localization of a high-affinity serotonin receptor (5-HT7) activating cAMP formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:8547–8551
Sarkisyan G, Hedlund PB (2009) The 5-HT7 receptor is involved in allocentric spatial memory information processing. Behavioural Brain Research 202:26–31
Schmitt JA, Wingen M, Ramaekers JG, Evers EA, Riedel WJ (2006) Serotonin and human cognitive performance. Current pharmaceutical design 12:2473–2486
Sik A, van Nieuwehuyzen P, Prickaerts J, Blokland A (2003) Performance of different mouse strains in an object recognition task. Behavioural Brain Research 147:49–54
Waters KA, Stean TO, Hammond B, Virley DJ, Upton N, Kew JN, Hussain I (2012) Effects of the selective 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist SB-269970 in animal models of psychosis and cognition. Behavioural Brain Research 228:211–218
Wedzony K, Mackowiak M, Zajaczkowski W, Fijal K, Chocyk A, Czyrak A (2000) WAY 100135, an antagonist of 5-HT1A serotonin receptors, attenuates psychotomimetic effects of MK-801. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:547–559
Wesolowska A, Nikiforuk A, Stachowicz K, Tatarczynska E (2006) Effect of the selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB 269970 in animal models of anxiety and depression. Neuropharmacology 51:578–586
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Emma McCallion and Dr. Eric T. MacKenzie for their English-editing advice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related directly or indirectly to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All experiments comply with the current directives of the European Community and the French Agriculture and Forestry Ministry.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freret, T., Paizanis, E., Beaudet, G. et al. Modulation of 5-HT7 receptor: effect on object recognition performances in mice. Psychopharmacology 231, 393–400 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3247-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3247-x