Abstract
Rationale
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1), which encodes the rate-limiting enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase in the biosynthesis of serotonin, is a candidate gene in the development and treatment response of major depressive disorder (MDD); however, its actual role is uncertain.
Objectives
We aimed to compare the allele frequencies of TPH1 in MDD patients and healthy controls in Taiwan, and also to investigate the association between TPH1 A218C and treatment response to either fluoxetine or venlafaxine in a Taiwanese population with MDD.
Methods
One hundred five healthy controls and 115 outpatients diagnosed with MDD were recruited and genotyped for the TPH1 218A/C (rs1800532) polymorphism. Patients were randomized into either the fluoxetine or venlafaxine treatment group. The 21-item Hamilton rating scale for depression (HAM-D) was administered to evaluate depressive symptoms at baseline and bi-weekly over 6 weeks of treatment.
Results
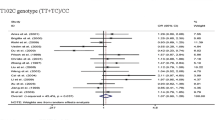
The TPH1 218A/C allele frequencies differed significantly between healthy controls and MDD patients in Taiwan, with a higher prevalence of the A allele in the patient group (p = 0.025). The odds ratio of the A allele to the C allele was 0.507 for the subjects with MDD. There was no significant correlation between the percentage change in HAM-D score and either TPH1 218A/C genotype or TPH1 allele frequencies.
Conclusions
This study indicated that the TPH1 218A/C genotype and allele frequencies differed between the Taiwanese healthy controls and MDD patients but could not be used to predict treatment outcome in Taiwanese MDD patients. Further research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm the role of TPH1 218A/C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anttila S, Huuhka K, Huuhka M, Rontu R, Mattila KM, Leinonen E, Lehtimaki T (2007) Interaction between TPH1 and GNB3 genotypes and electroconvulsive therapy in major depression. J Neural Transm 114:461–468
Bellivier F, Chaste P, Malafosse A (2004) Association between the TPH gene A218C polymorphism and suicidal behavior: a meta-analysis. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 124B:87–91
Chen C, Glatt SJ, Tsuang MT (2008) The tryptophan hydroxylase gene influences risk for bipolar disorder but not major depressive disorder: results of meta-analyses. Bipolar Disord 10:816–821
Du L, Bakish D, Hrdina PD (2001) Tryptophan hydroxylase gene 218A/C polymorphism is associated with somatic anxiety in major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 65:37–44
Evans J, Reeves B, Platt H, Leibenau A, Goldman D, Jefferson K, Nutt D (2000) Impulsiveness, serotonin genes and repetition of deliberate self-harm (DSH). Psychol Med 30:1327–1334
Garriock HA, Hamilton SP (2009a) Genetic studies of drug response and side effects in the STAR*D study, part 1. J Clin Psychiatry 70:1186–1187
Garriock HA, Hamilton SP (2009b) Genetic studies of drug response and side effects in the STAR*D study, part 2. J Clin Psychiatry 70:1323–1325
Gizatullin R, Zaboli G, Jonsson EG, Asberg M, Leopardi R (2006) Haplotype analysis reveals tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) 1 gene variants associated with major depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:295–300
Ham BJ, Lee MS, Lee HJ, Kang RH, Han CS, Choi MJ, Lee SH, Ryu SH (2005) No association between the tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphism and major depressive disorders and antidepressant response in a Korean population. Psychiatr Genet 15:299–301
Ham BJ, Lee BC, Paik JW, Kang RH, Choi MJ, Choi IG, Lee MS (2007) Association between the tryptophan hydroxylase-1 gene A218C polymorphism and citalopram antidepressant response in a Korean population. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:104–107
Harris EC, Barraclough B (1998) Excess mortality of mental disorder. Br J Psychiatry 173:11–53
Illi A, Setala-Soikkeli E, Viikki M, Poutanen O, Huhtala H, Mononen N, Lehtimaki T, Leinonen E, Kampman O (2009) 5-HTR1A, 5-HTR2A, 5-HTR6, TPH1 and TPH2 polymorphisms and major depression. NeuroReport 20:1125–1128
Jonsson EG, Goldman D, Spurlock G, Gustavsson JP, Nielsen DA, Linnoila M, Owen MJ, Sedvall GC (1997) Tryptophan hydroxylase and catechol-O-methyltransferase gene polymorphisms: relationships to monoamine metabolite concentrations in CSF of healthy volunteers. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 247:297–302
Judd LL, Schettler PJ, Solomon DA, Maser JD, Coryell W, Endicott J, Akiskal HS (2008) Psychosocial disability and work role function compared across the long-term course of bipolar I, bipolar II and unipolar major depressive disorders. J Affect Disord 108:49–58
Kato M, Serretti A (2010) Review and meta-analysis of antidepressant pharmacogenetic findings in major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 15:473–500
Kato M, Wakeno M, Okugawa G, Fukuda T, Azuma J, Kinoshita T, Serretti A (2007) No association of TPH1 218A/C polymorphism with treatment response and intolerance to SSRIs in Japanese patients with major depression. Neuropsychobiology 56:167–171
Kraft JB, Slager SL, McGrath PJ, Hamilton SP (2005) Sequence analysis of the serotonin transporter and associations with antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry 58:374–381
Li D, He L (2006) Further clarification of the contribution of the tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH) gene to suicidal behavior using systematic allelic and genotypic meta-analyses. Hum Genet 119:233–240
Lin CH, Lin KS, Lin CY, Chen MC, Lane HY (2008) Time to rehospitalization in patients with major depressive disorder taking venlafaxine or fluoxetine. J Clin Psychiatry 69:54–59
Lin E, Chen PS (2008) Pharmacogenomics with antidepressants in the STAR*D study. Pharmacogenomics 9:935–946
Lin E, Chen PS, Chang HH, Gean PW, Tsai HC, Yang YK, Lu RB (2009) Interaction of serotonin-related genes affects short-term antidepressant response in major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:1167–1172
Moncrieff J, Kirsch I (2005) Efficacy of antidepressants in adults. BMJ 331:155–157
Nakamura K, Sugawara Y, Sawabe K, Ohashi A, Tsurui H, Xiu Y, Ohtsuji M, Lin QS, Nishimura H, Hasegawa H, Hirose S (2006) Late developmental stage-specific role of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 in brain serotonin levels. J Neurosci 26:530–534
Nielsen DA, Jenkins GL, Stefanisko KM, Jefferson KK, Goldman D (1997) Sequence, splice site and population frequency distribution analyses of the polymorphic human tryptophan hydroxylase intron 7. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 45:145–148
Nielsen DA, Virkkunen M, Lappalainen J, Eggert M, Brown GL, Long JC, Goldman D, Linnoila M (1998) A tryptophan hydroxylase gene marker for suicidality and alcoholism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:593–602
Peters EJ, Slager SL, McGrath PJ, Knowles JA, Hamilton SP (2004) Investigation of serotonin-related genes in antidepressant response. Mol Psychiatry 9:879–889
Rujescu D, Giegling I, Bondy B, Gietl A, Zill P, Moller HJ (2002) Association of anger-related traits with SNPs in the TPH gene. Mol Psychiatry 7:1023–1029
Rush AJ, Warden D, Wisniewski SR, Fava M, Trivedi MH, Gaynes BN, Nierenberg AA (2009) STAR*D: revising conventional wisdom. CNS Drugs 23:627–647
Serretti A, Lorenzi C, Cusin C, Zanardi R, Lattuada E, Rossini D, Lilli R, Pirovano A, Catalano M, Smeraldi E (2003) SSRIs antidepressant activity is influenced by G beta three variants. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 13:117–122
Souery D, Van Gestel S, Massat I, Blairy S, Adolfsson R, Blackwood D, Del-Favero J, Dikeos D, Jakovljevic M, Kaneva R, Lattuada E, Lerer B, Lilli R, Milanova V, Muir W, Nothen M, Oruc L, Papadimitriou G, Propping P, Schulze T, Serretti A, Shapira B, Smeraldi E, Stefanis C, Thomson M, Van Broeckhoven C, Mendlewicz J (2001) Tryptophan hydroxylase polymorphism and suicidality in unipolar and bipolar affective disorders: a multicenter association study. Biol Psychiatry 49:405–409
Sullivan PF, Neale MC, Kendler KS (2000) Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 157:1552–1562
Sun HS, Fann CS, Lane HY, Chang YT, Chang CJ, Liu YL, Cheng AT (2005) A functional polymorphism in the promoter region of the tryptophan hydroxylase gene is associated with alcohol dependence in one aboriginal group in Taiwan. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1–7
Viikki M, Kampman O, Illi A, Setala-Soikkeli E, Anttila S, Huuhka M, Nuolivirta T, Poutanen O, Mononen N, Lehtimaki T, Leinonen E (2010) TPH1 218A/C polymorphism is associated with major depressive disorder and its treatment response. Neurosci Lett 468:80–84
Walther DJ, Bader M (2003) A unique central tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Biochem Pharmacol 66:1673–1680
Walther DJ, Peter JU, Bashammakh S, Hortnagl H, Voits M, Fink H, Bader M (2003) Synthesis of serotonin by a second tryptophan hydroxylase isoform. Science 299:76
Yu YW, Tsai SJ, Liou YJ, Hong CJ, Chen TJ (2006) Association study of two serotonin 1A receptor gene polymorphisms and fluoxetine treatment response in Chinese major depressive disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:498–503
Zill P, Buttner A, Eisenmenger W, Moller HJ, Ackenheil M, Bondy B (2007) Analysis of tryptophan hydroxylase I and II mRNA expression in the human brain: a post-mortem study. J Psychiatr Res 41:168–173
Zill P, Buttner A, Eisenmenger W, Muller J, Moller HJ, Bondy B (2009) Predominant expression of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 mRNA in the pituitary: a postmortem study in human brain. Neuroscience 159:1274–1282
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Department of Health, Taiwan (DOH98-TD-D-113-96002) to fund this research.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HC., Yeh, T.L., Chang, H.H. et al. TPH1 is associated with major depressive disorder but not with SSRI/SNRI response in Taiwanese patients. Psychopharmacology 213, 773–779 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2034-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2034-1